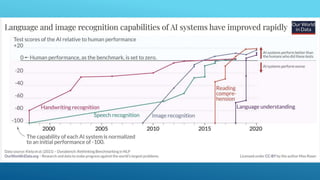
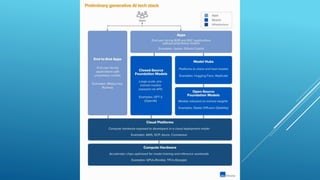
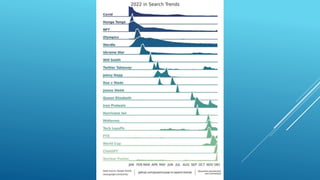
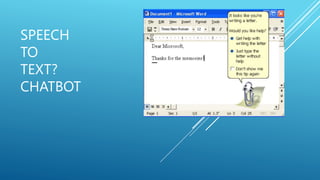
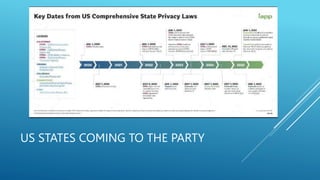
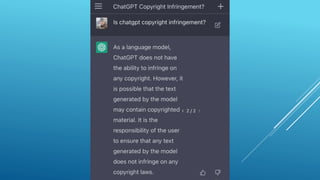
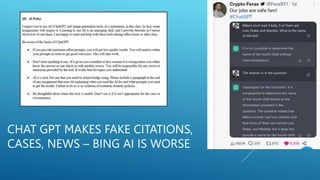
The presentation discusses the intersection of generative AI, responsible innovation, and the law, emphasizing the need for inclusivity, sustainability, and safety in the development of AI technology. Key legal concerns include data protection, intellectual property issues related to AI-generated content, and the regulatory frameworks specific to sensitive sectors like healthcare and education. Ultimately, the potential of generative AI must be harnessed responsibly, ensuring compliance with relevant laws and addressing ethical considerations.