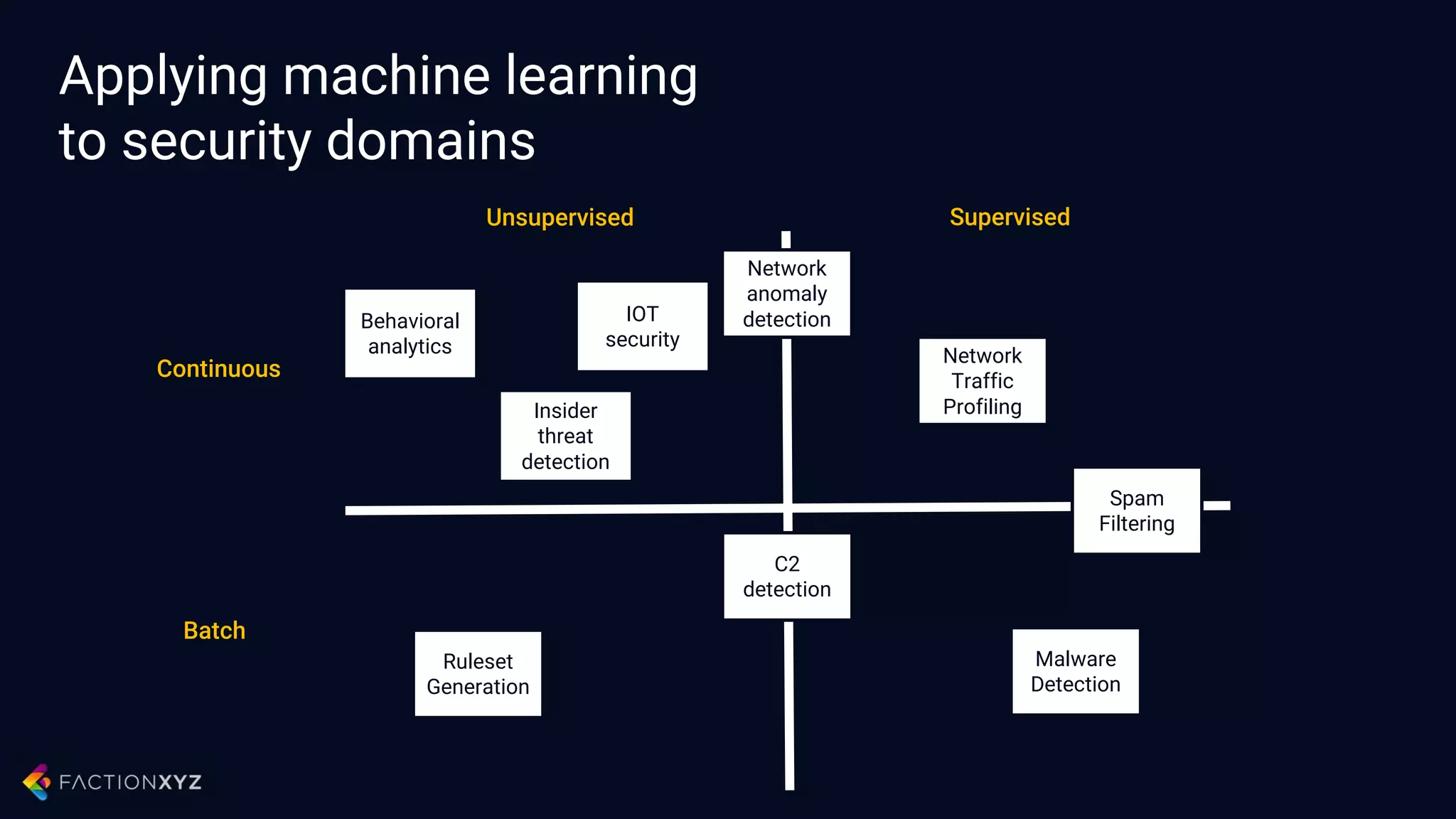
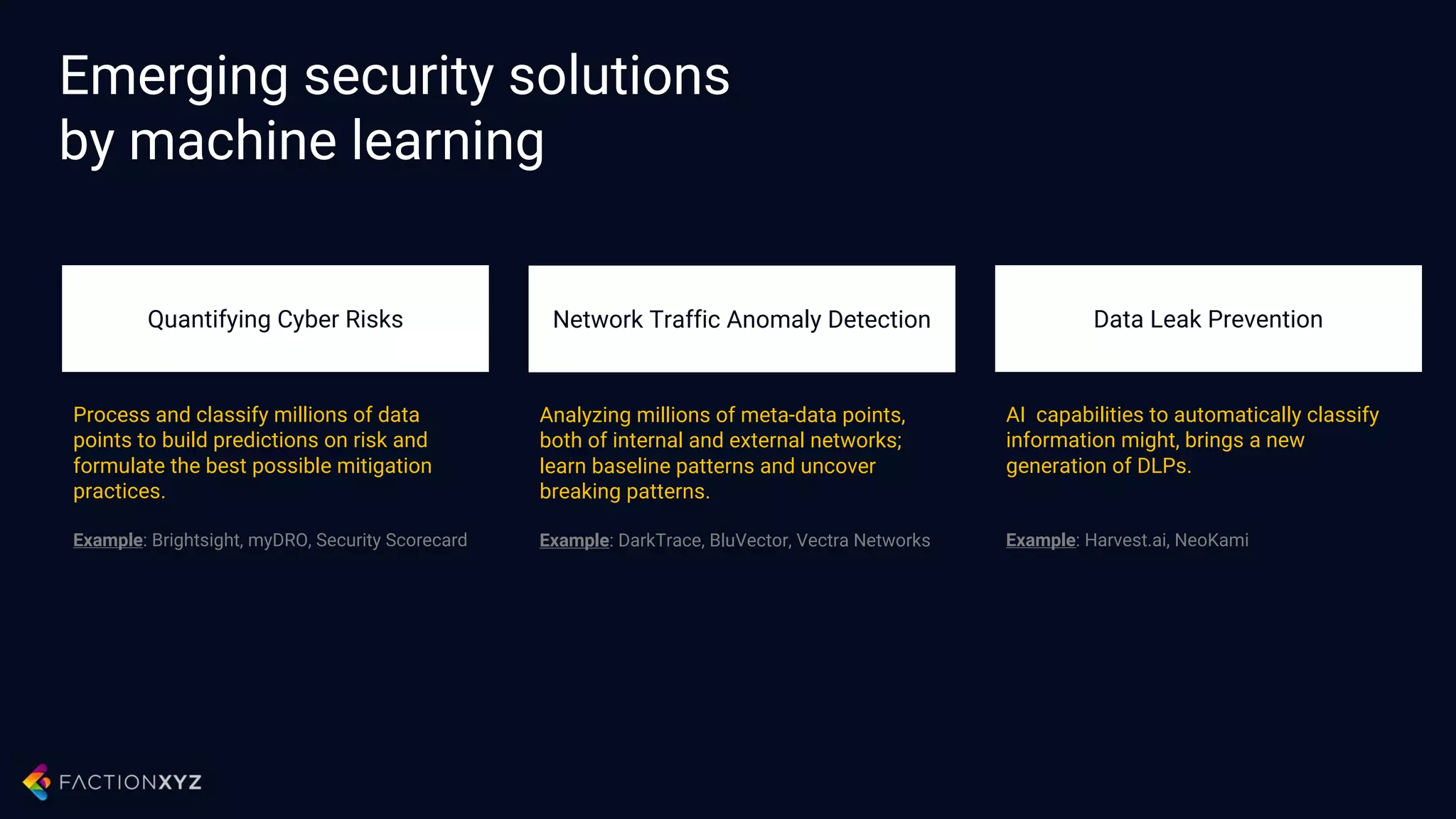
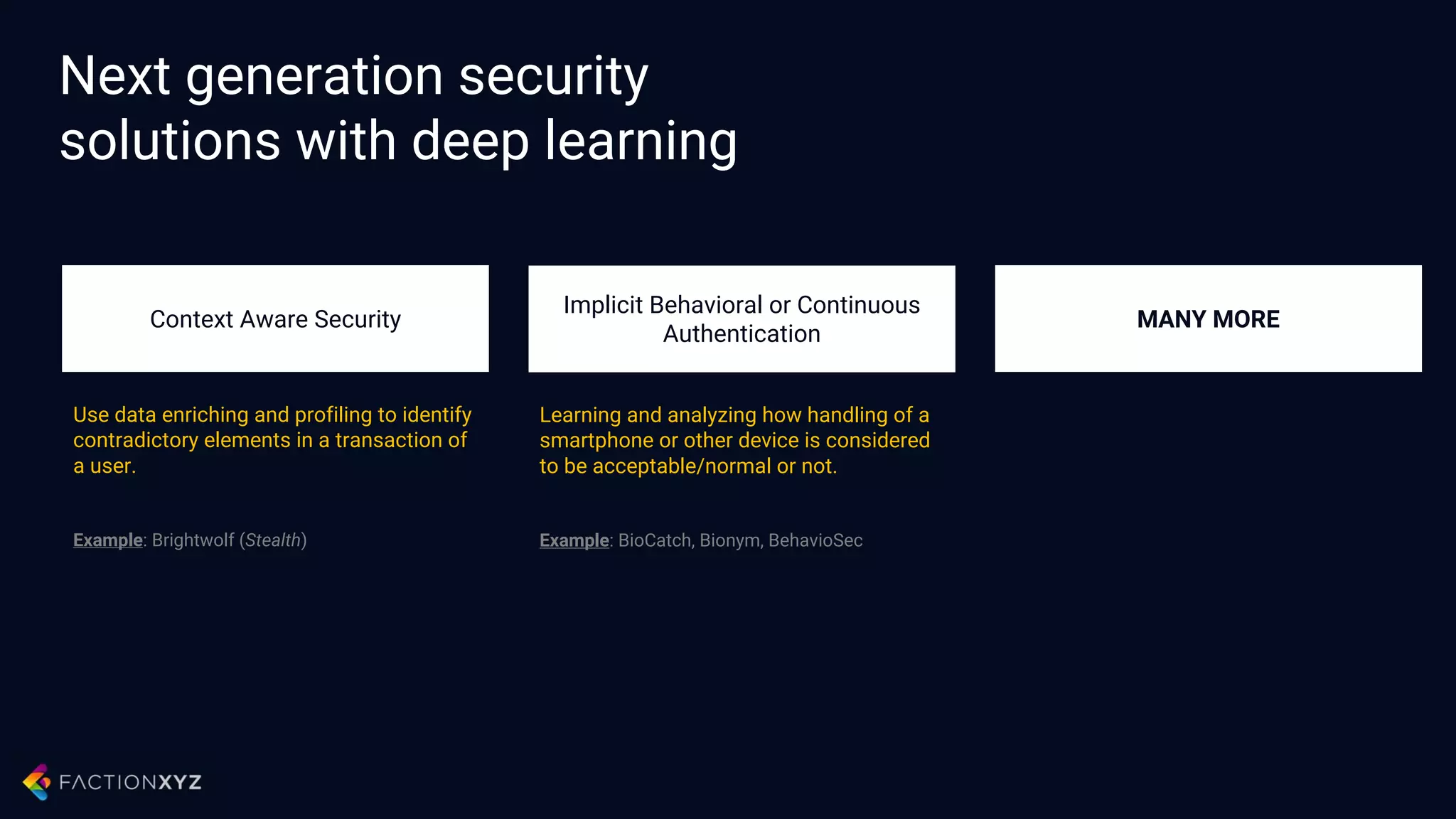
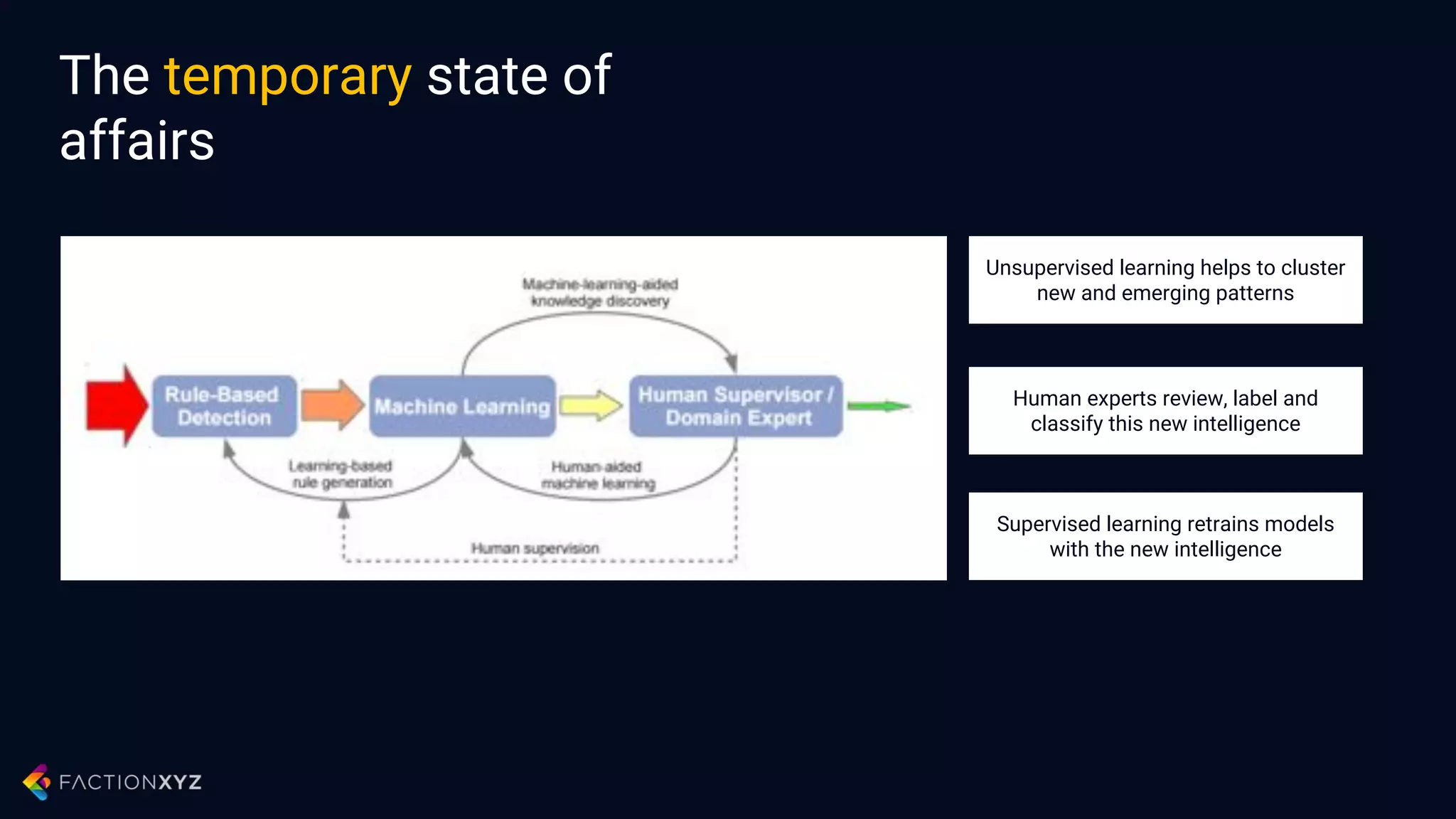
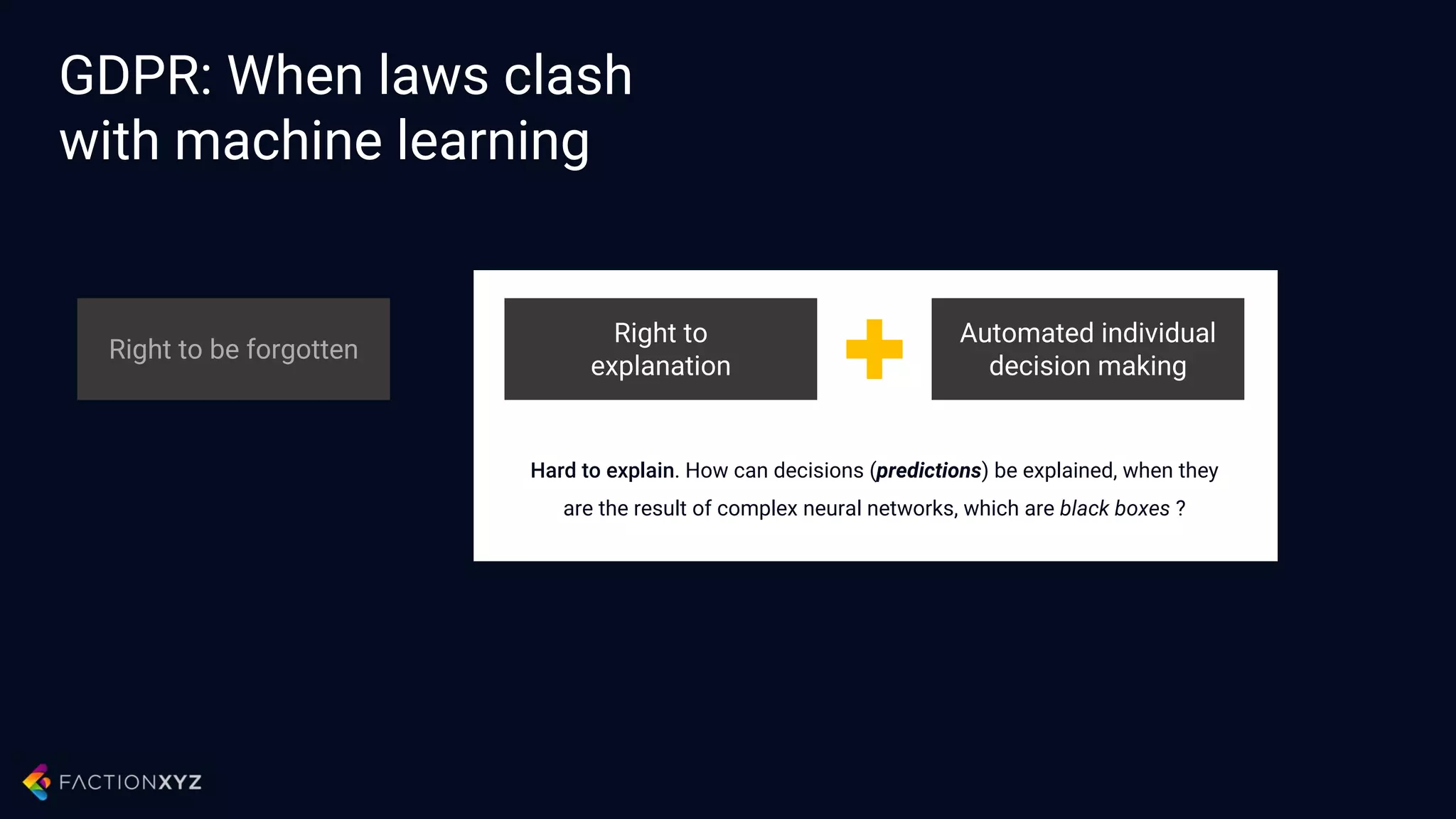
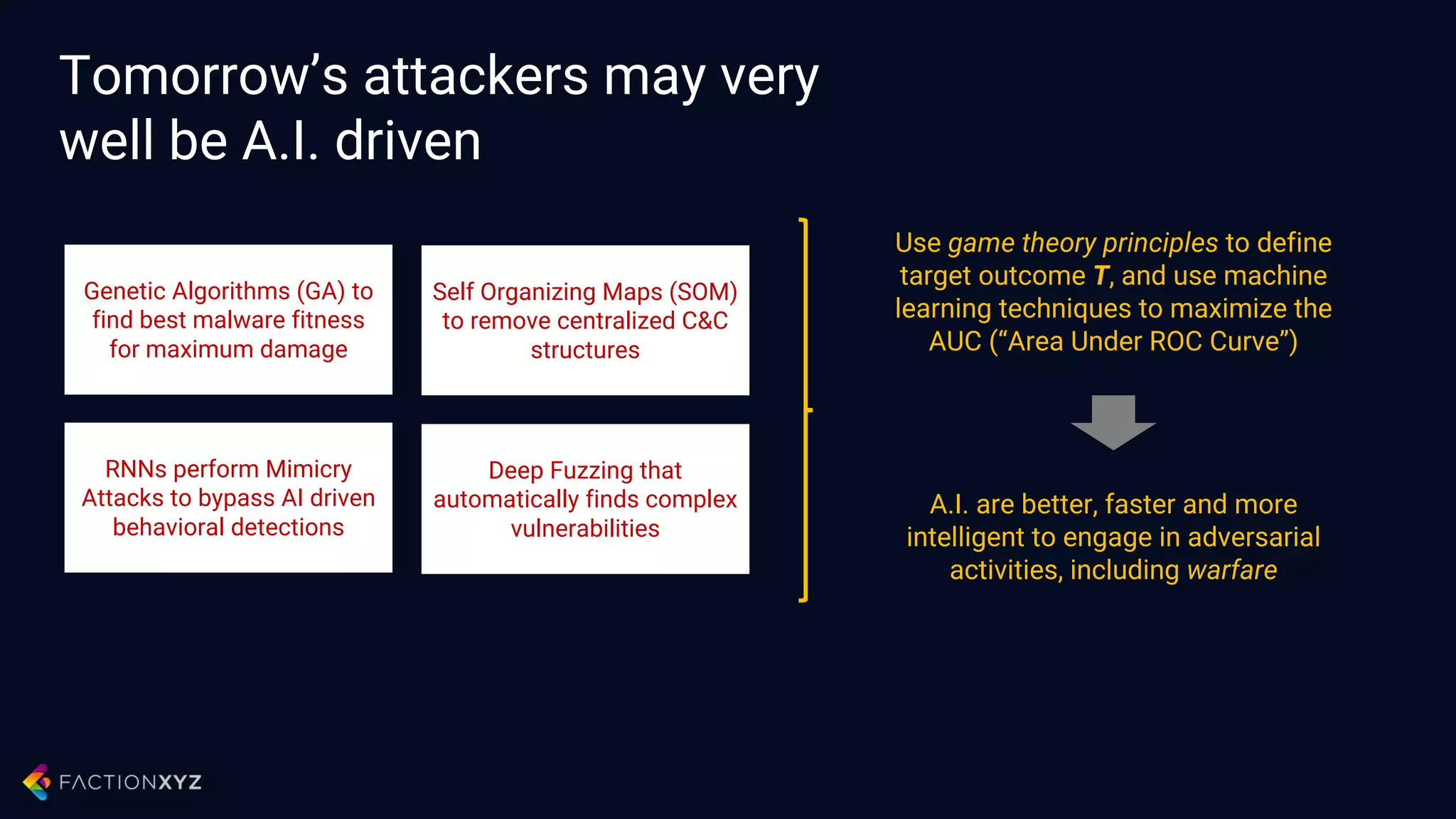
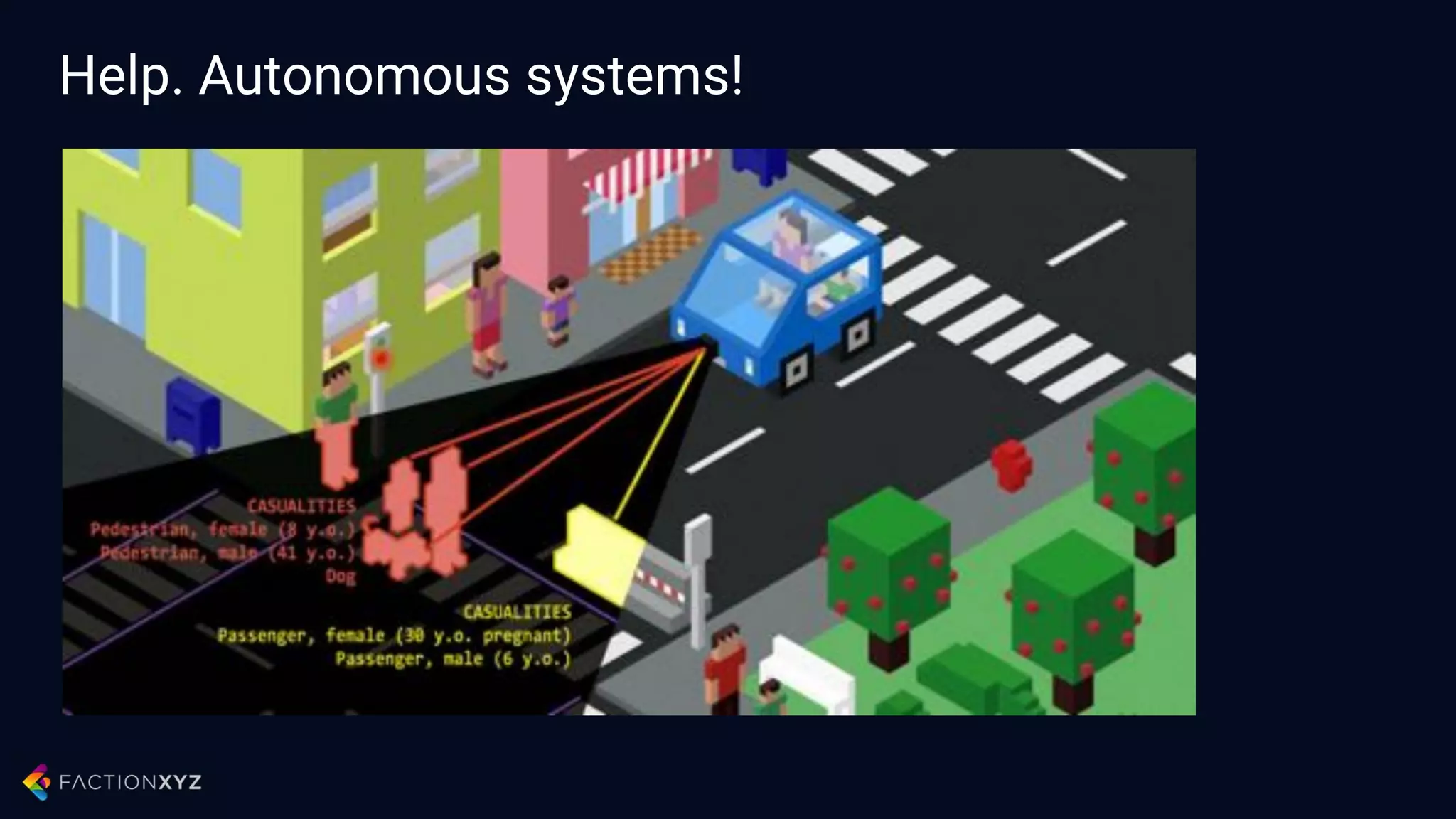
The document discusses how artificial intelligence will impact security and introduces both opportunities and challenges. It describes current AI techniques like deep learning and how they are being applied to security domains such as malware detection, network anomaly detection, and insider threat detection. While AI has the potential to make systems more scalable and adaptive, it also introduces new vulnerabilities if misused to generate sophisticated attacks. The document argues for developing morality systems to ensure autonomous systems continue making moral decisions even if compromised.










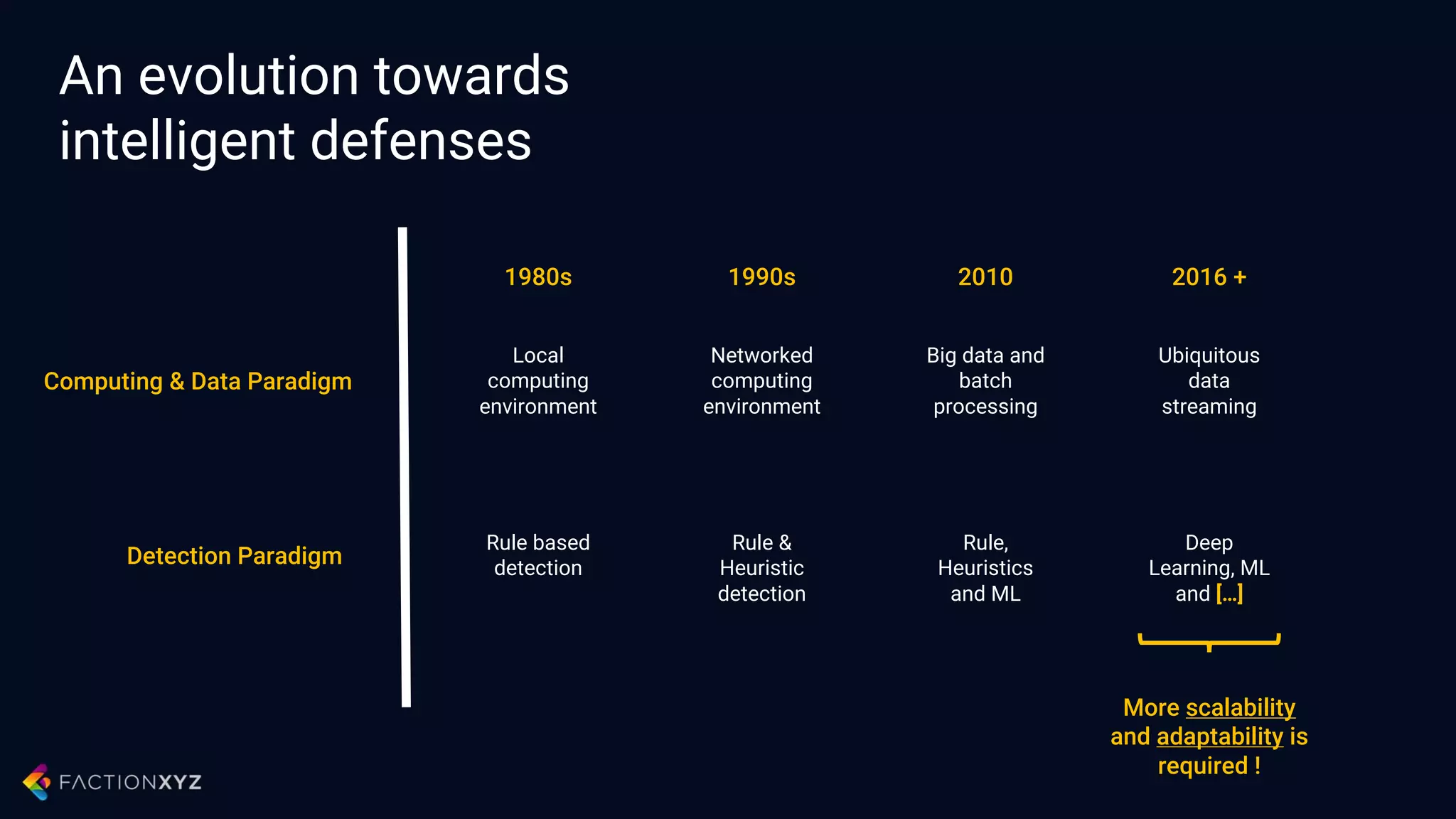
![An evolution towards
intelligent defenses
Computing & Data Paradigm
Detection Paradigm
1980s 1990s 2010 2016 +
Local
computing
environment
Networked
computing
environment
Big data and
batch
processing
Ubiquitous
data
streaming
Rule based
detection
Rule &
Heuristic
detection
Rule,
Heuristics
and ML
Deep
Learning, ML
and […]
More scalability
and adaptability is
required !](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xyzpresentation-cybersecurityintheageofa-170206144449/75/Security-in-the-age-of-Artificial-Intelligence-16-2048.jpg)