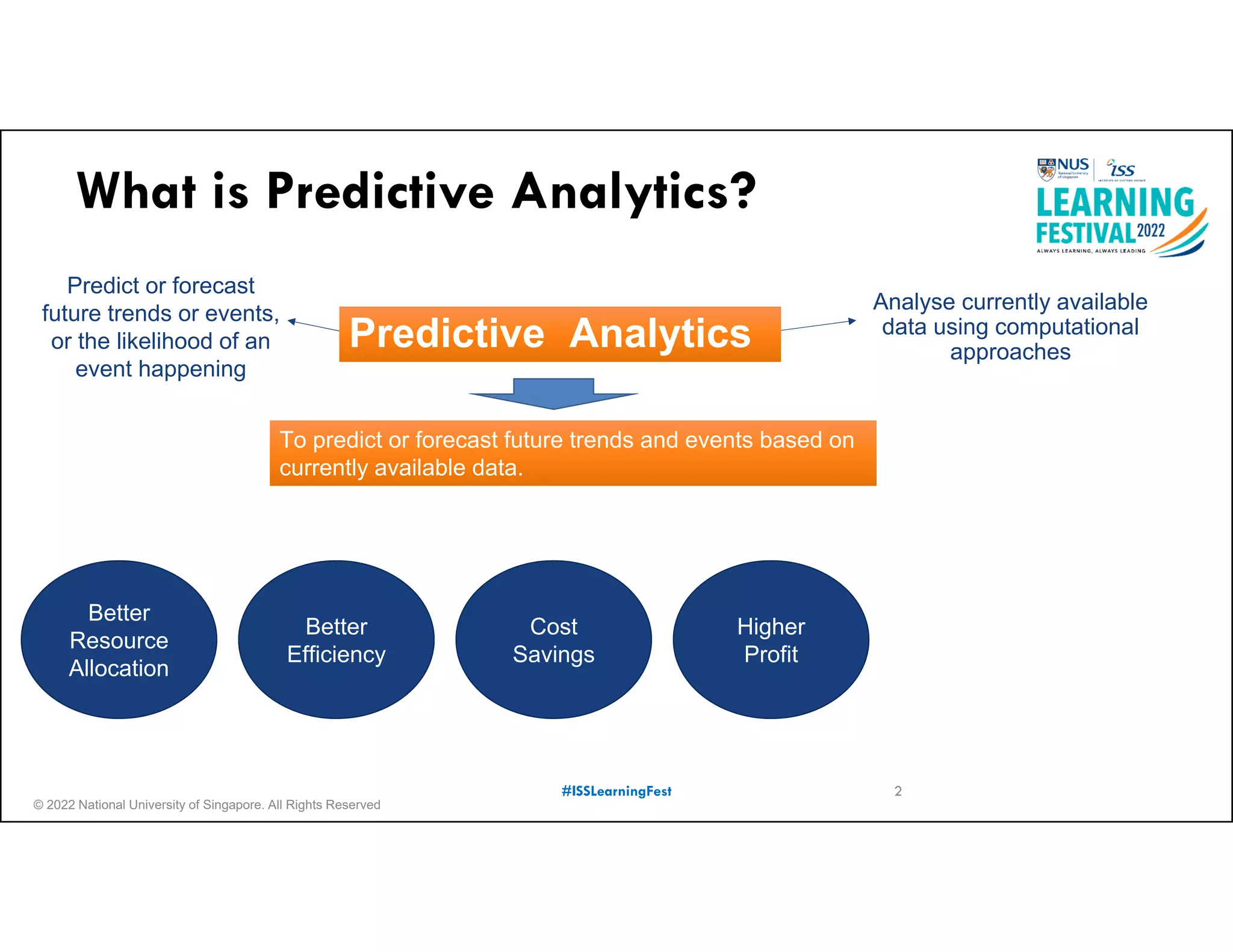
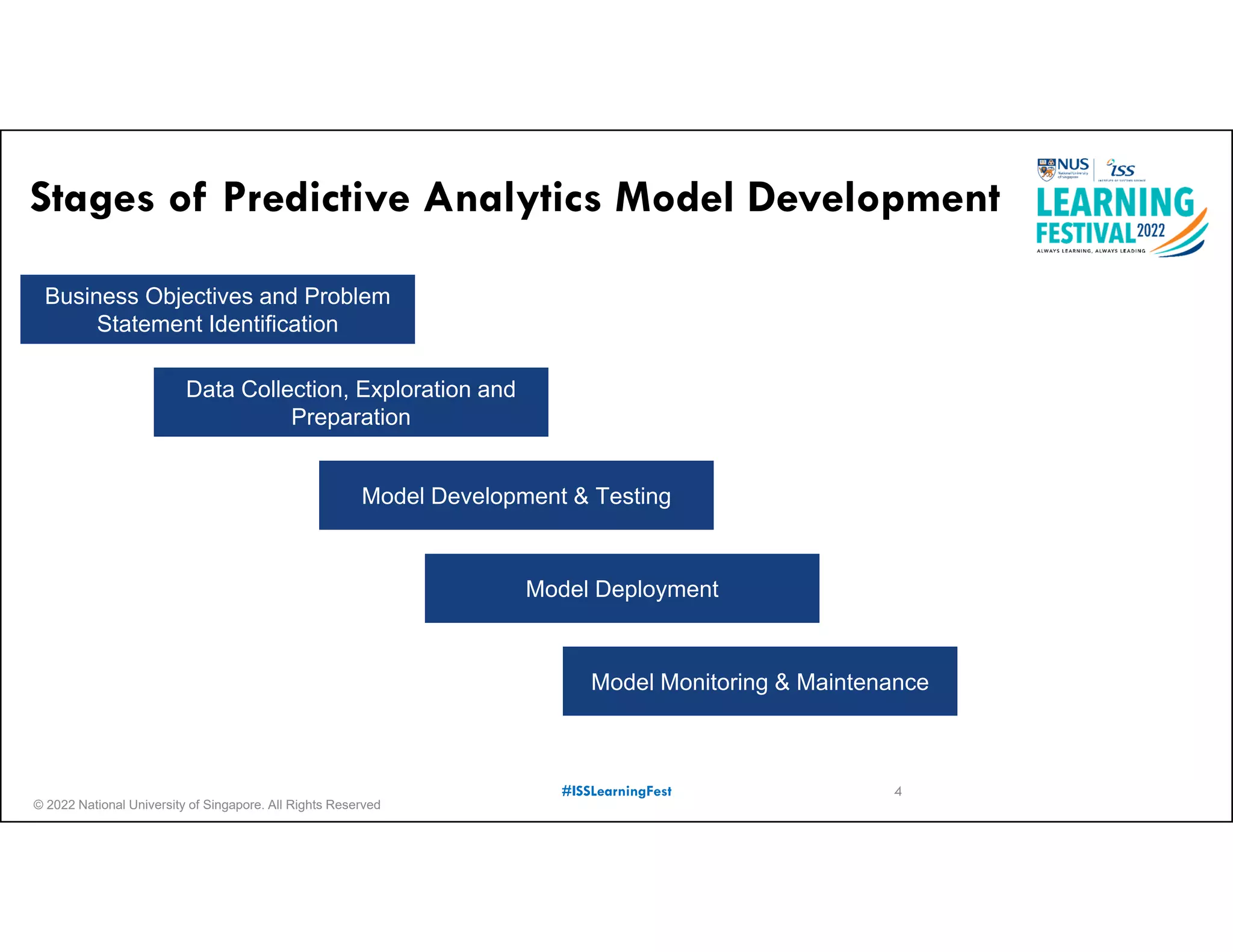
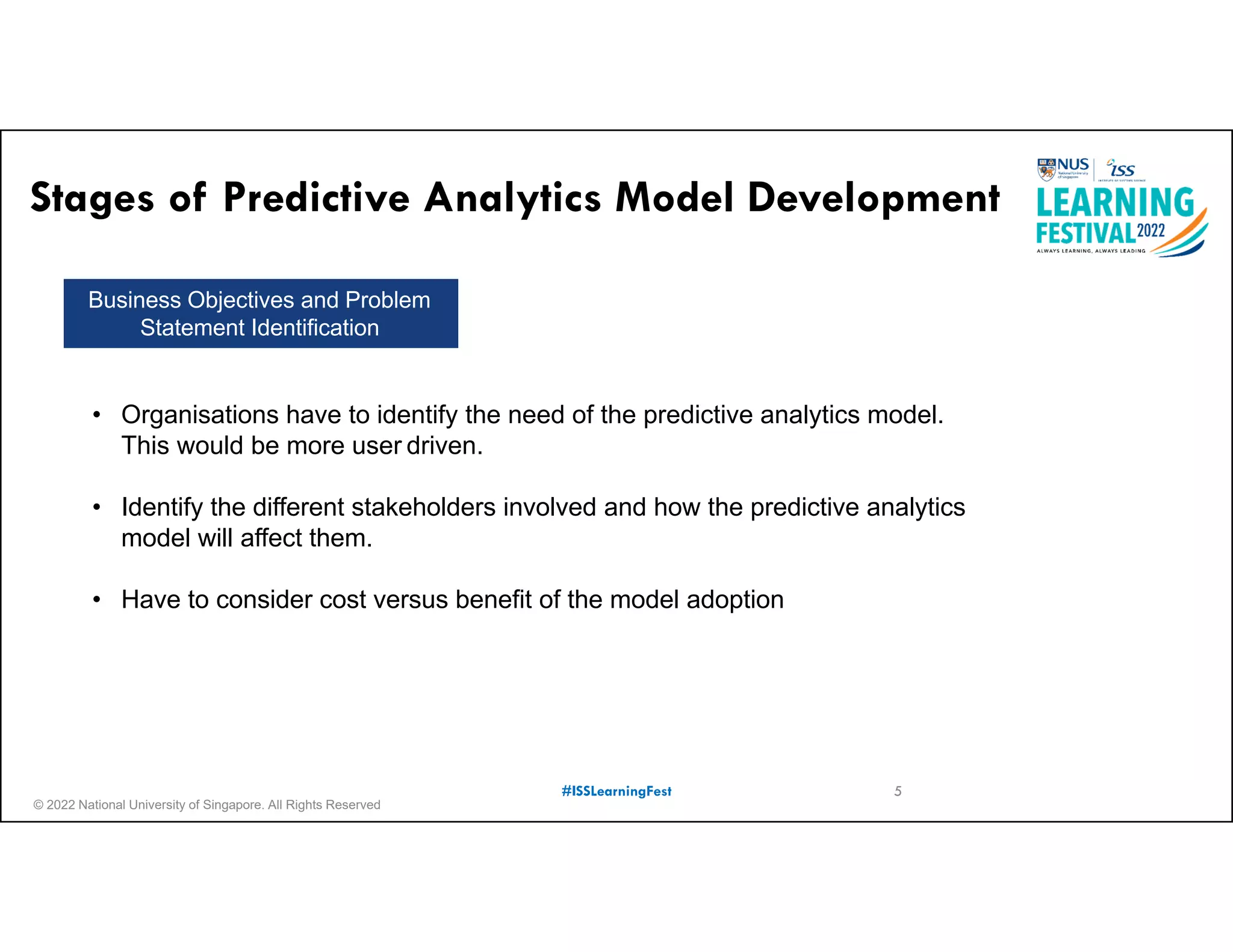
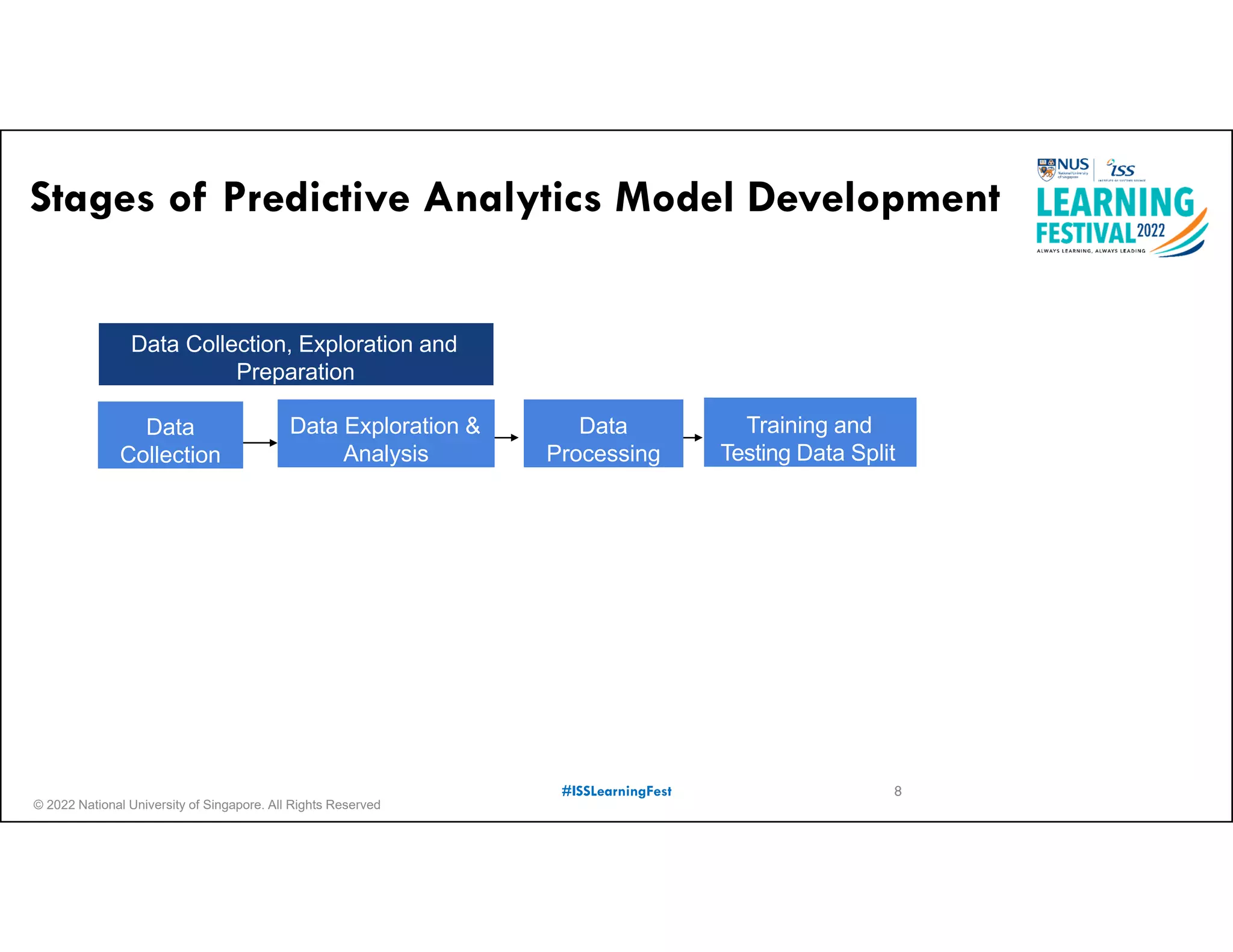
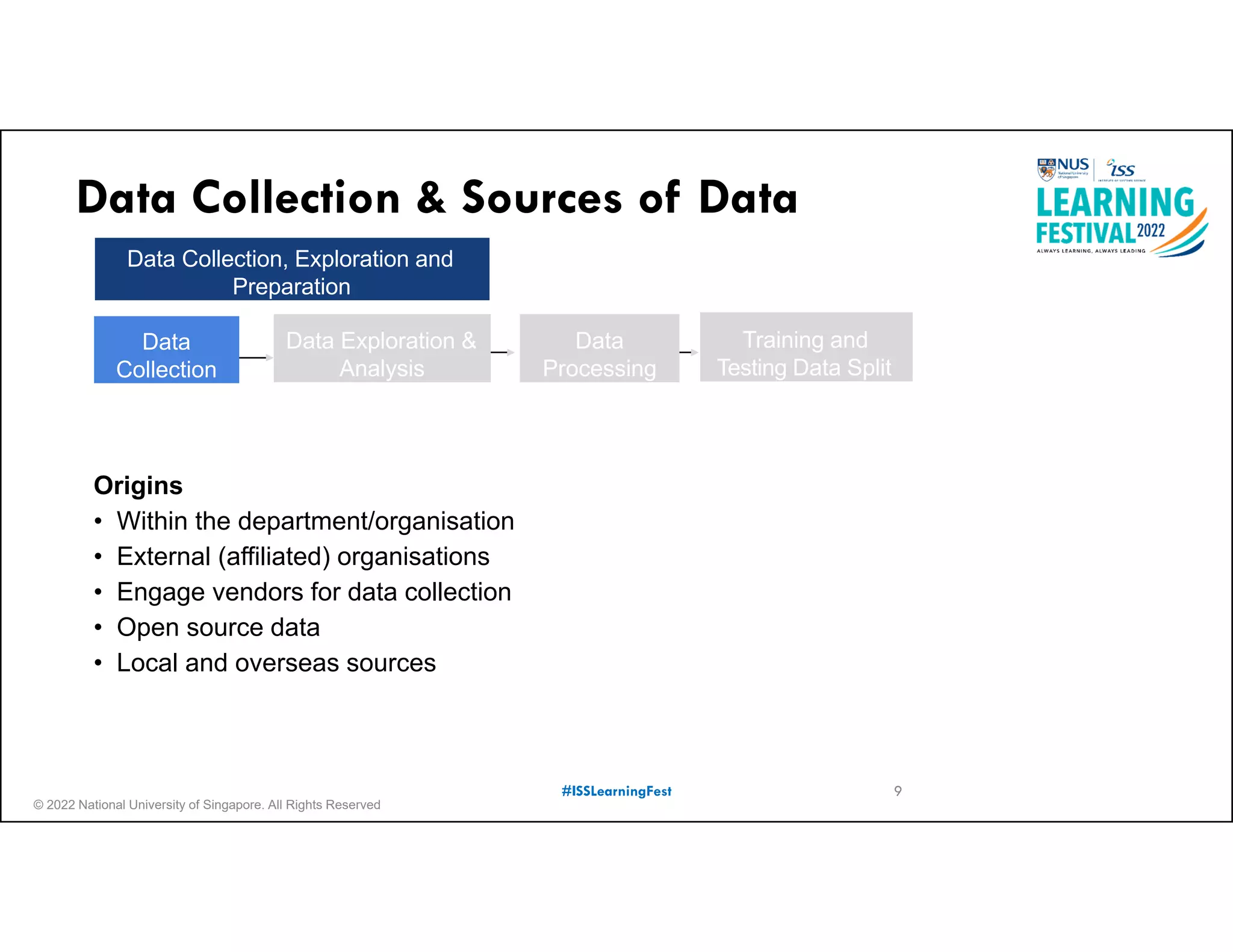
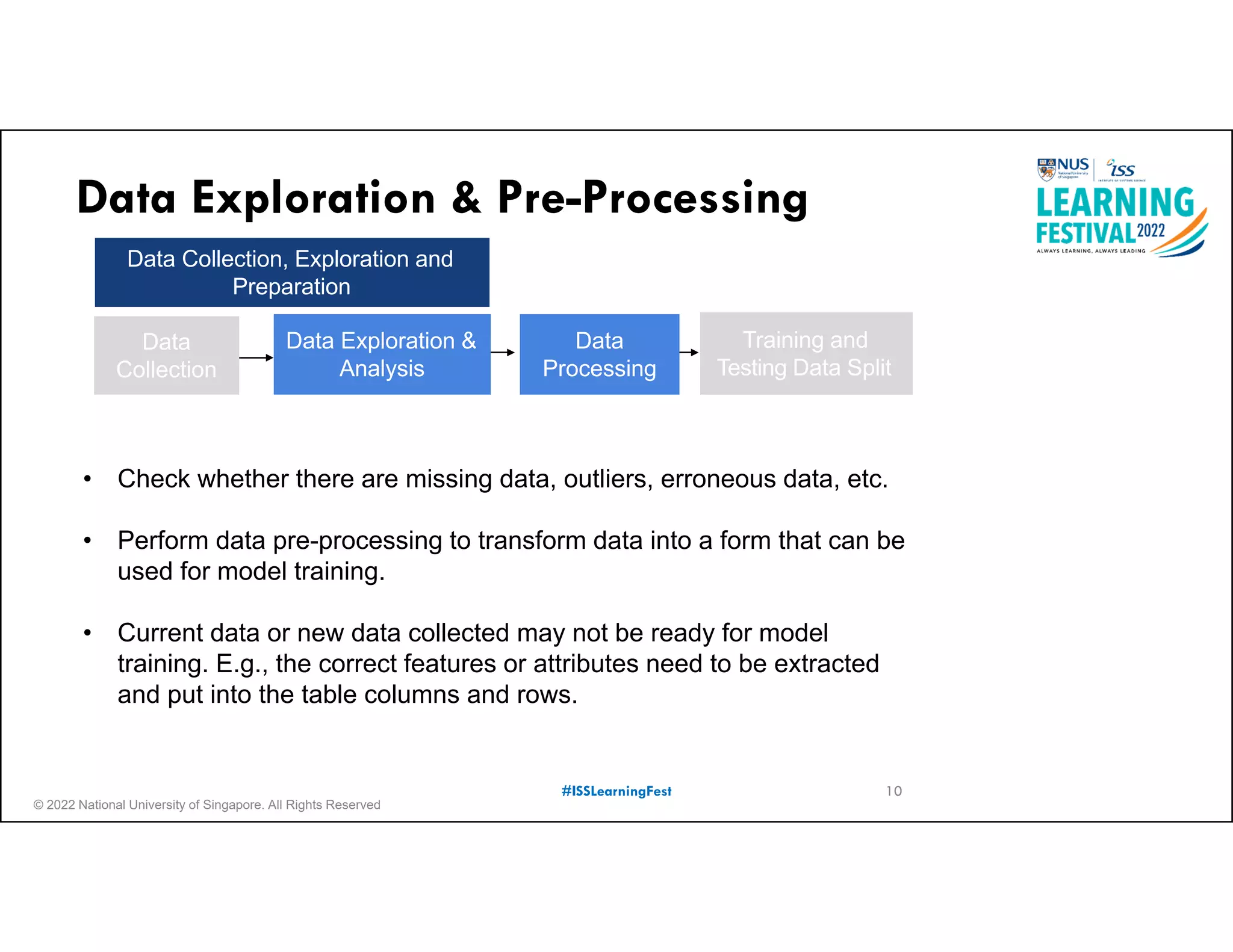
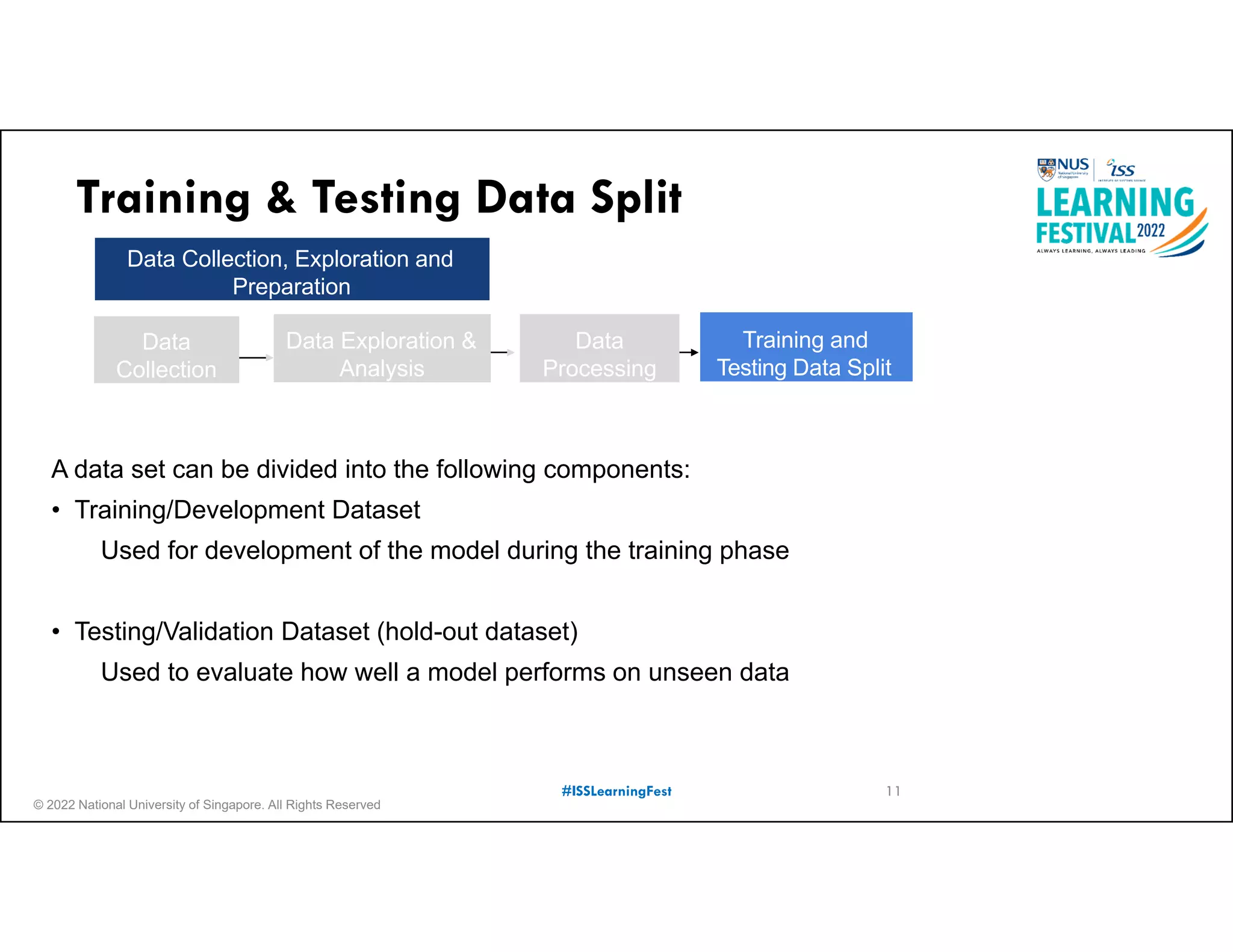
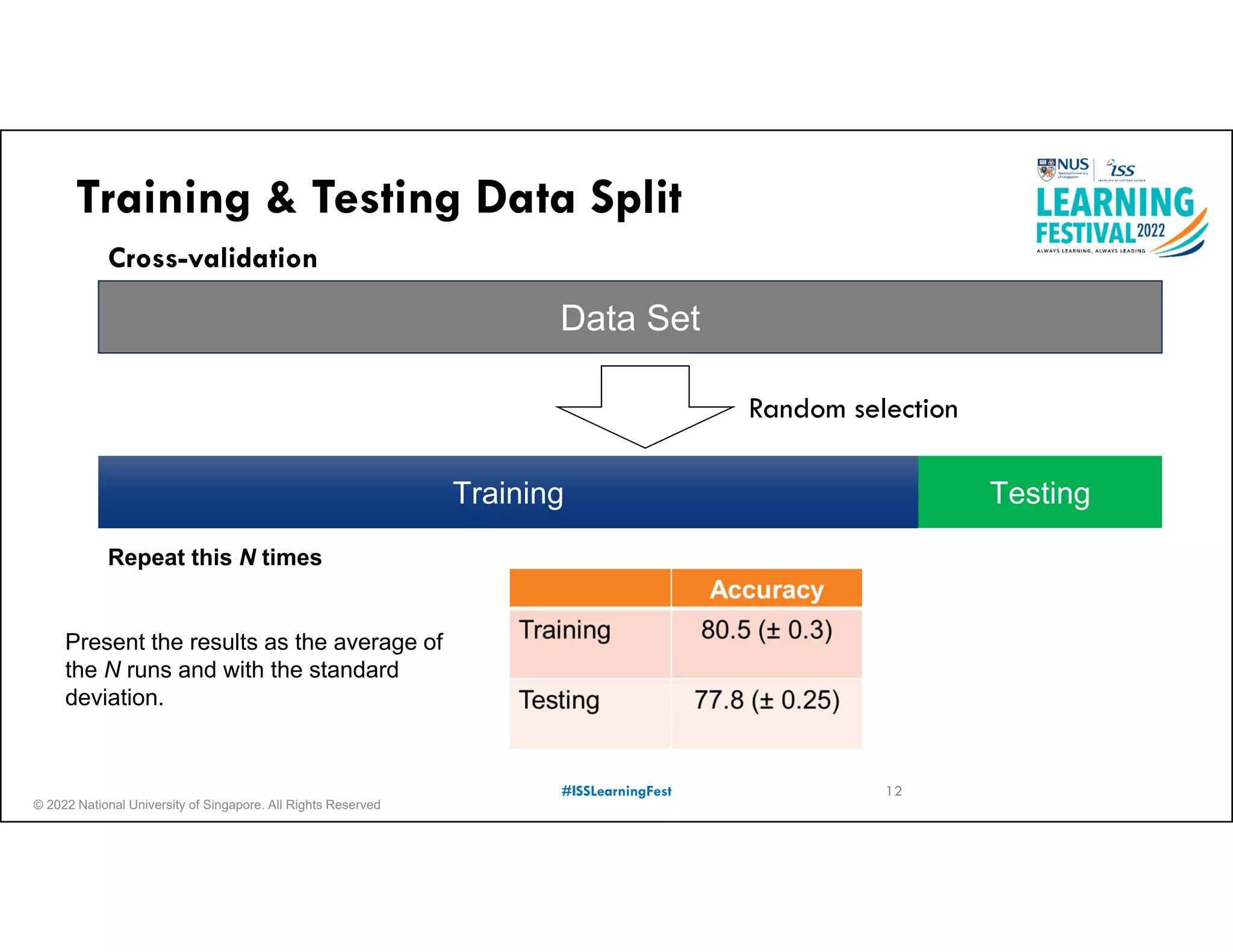
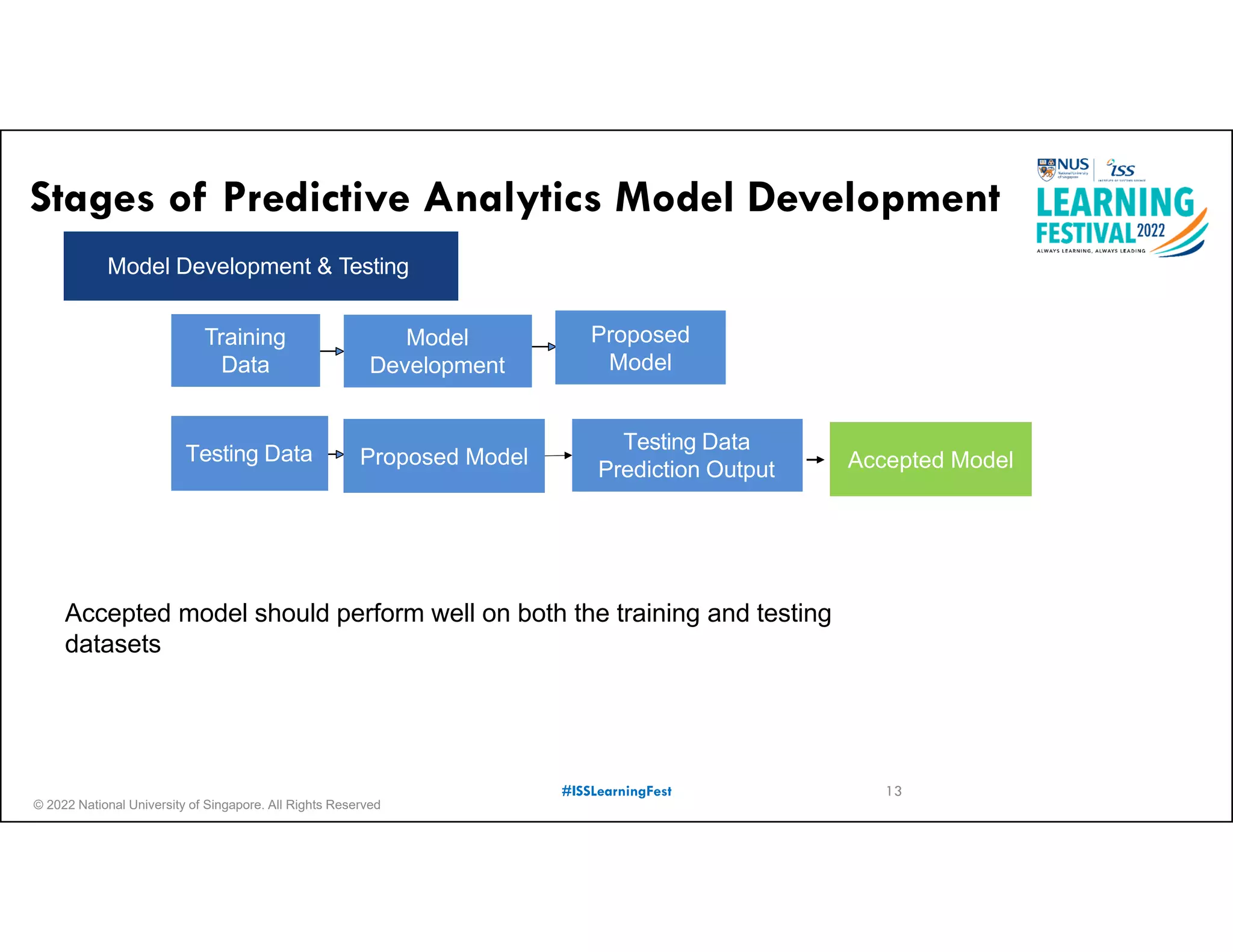
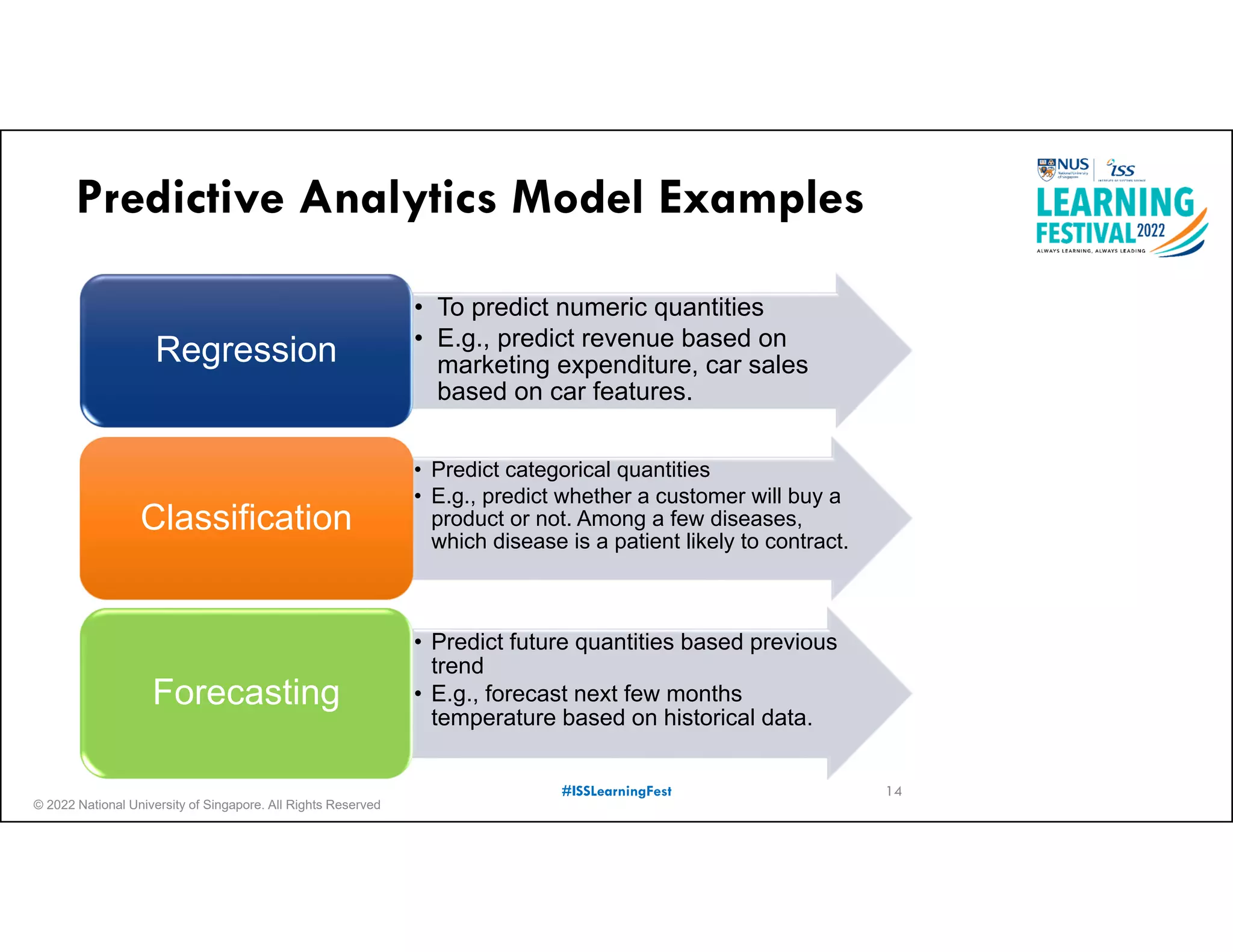
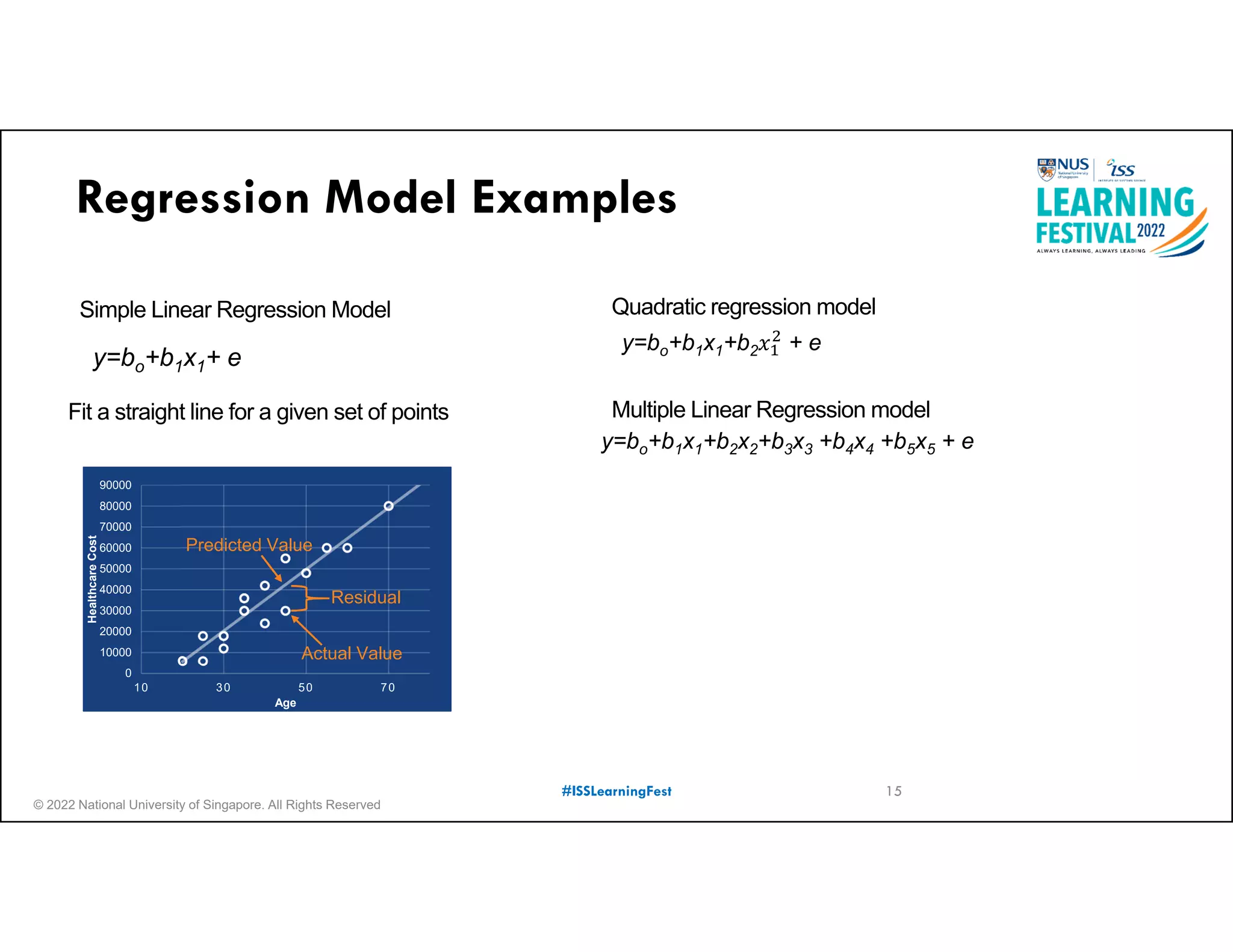
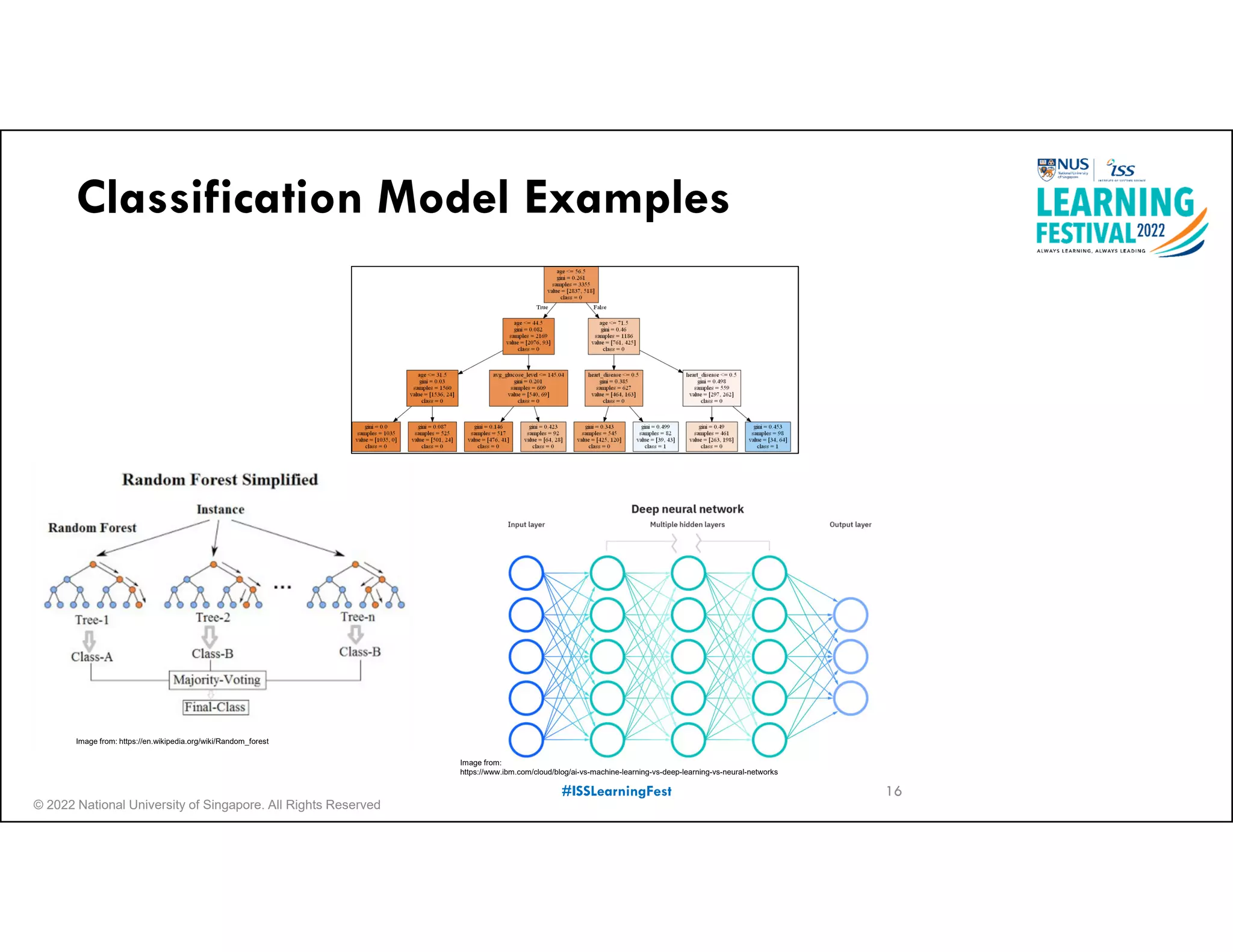
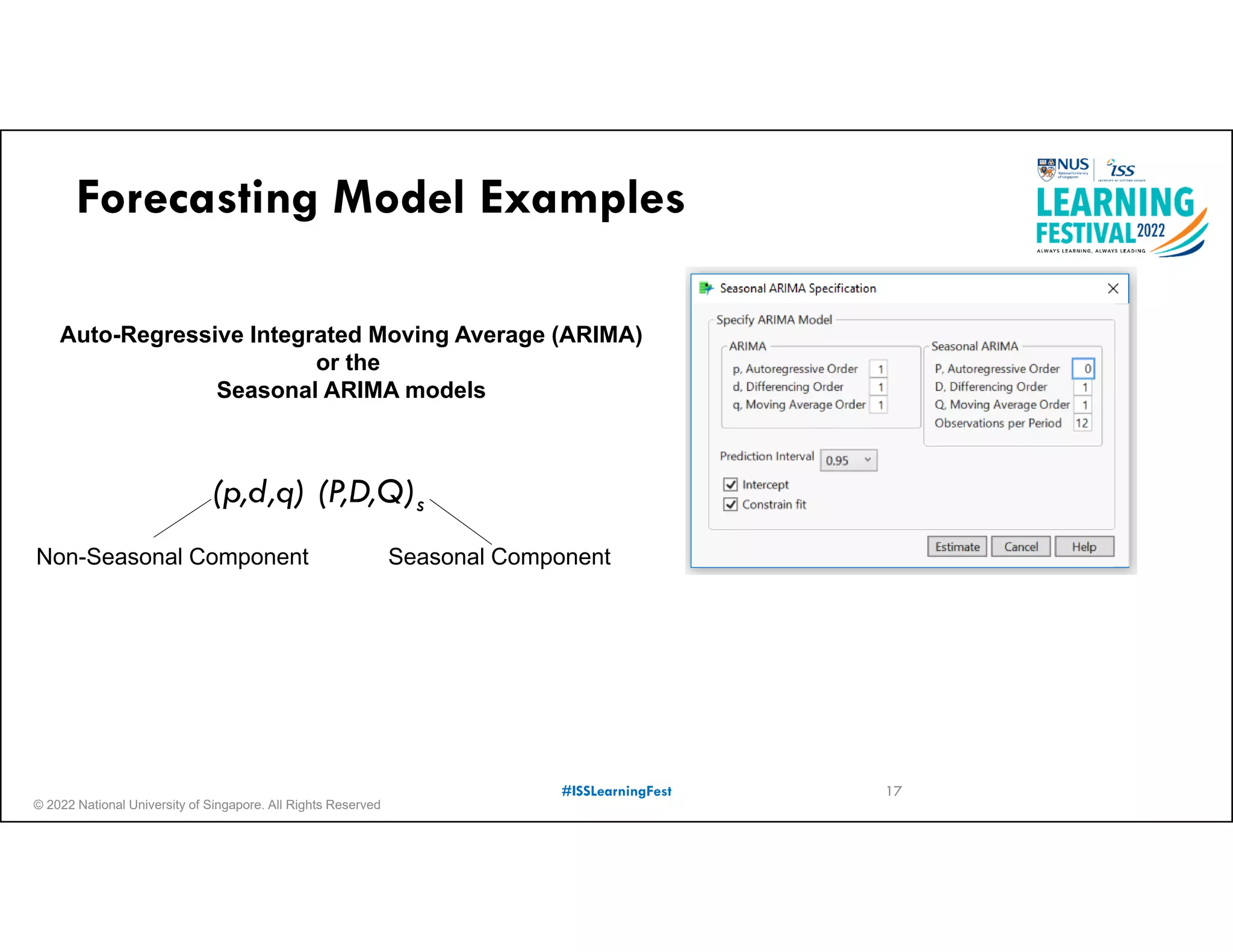
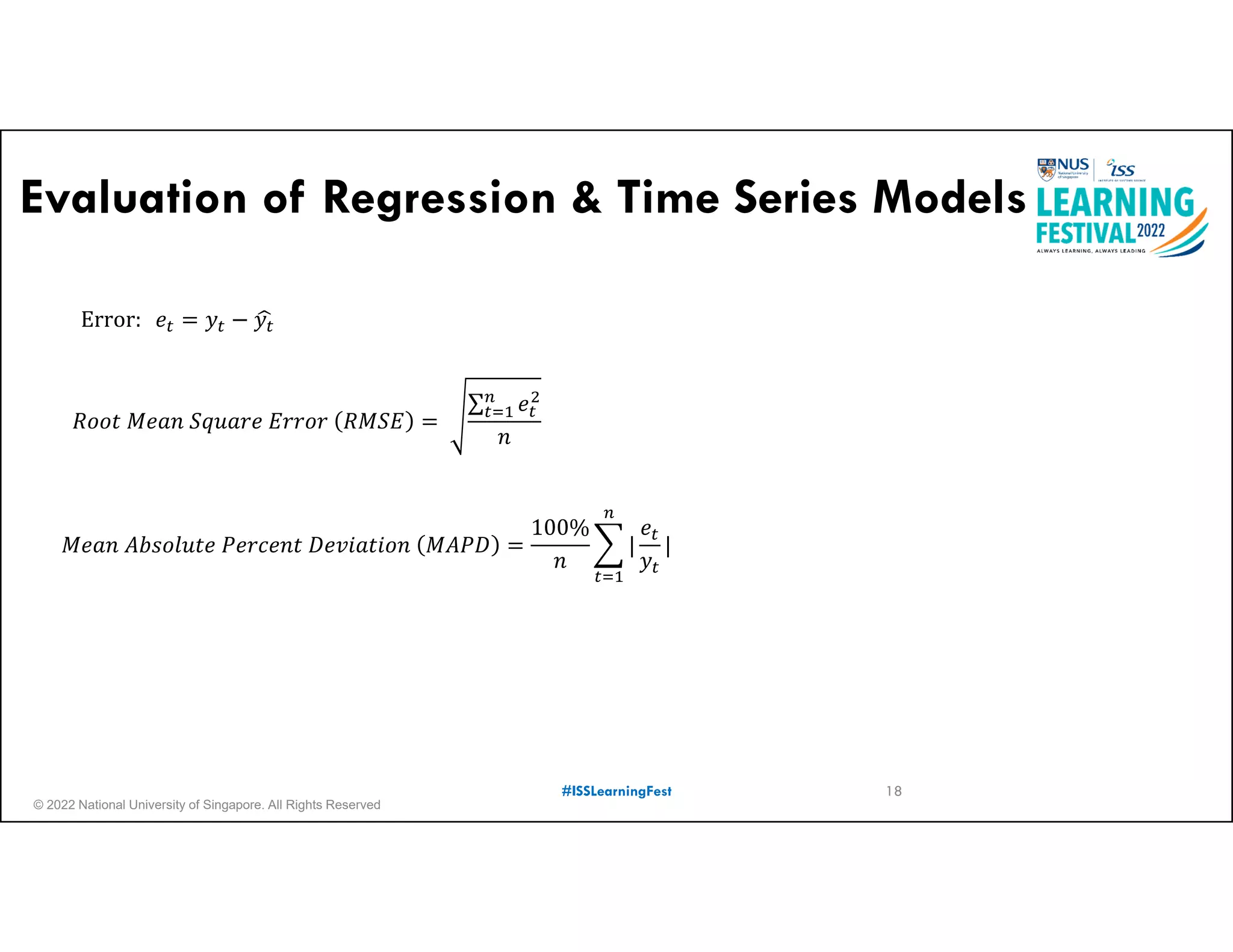
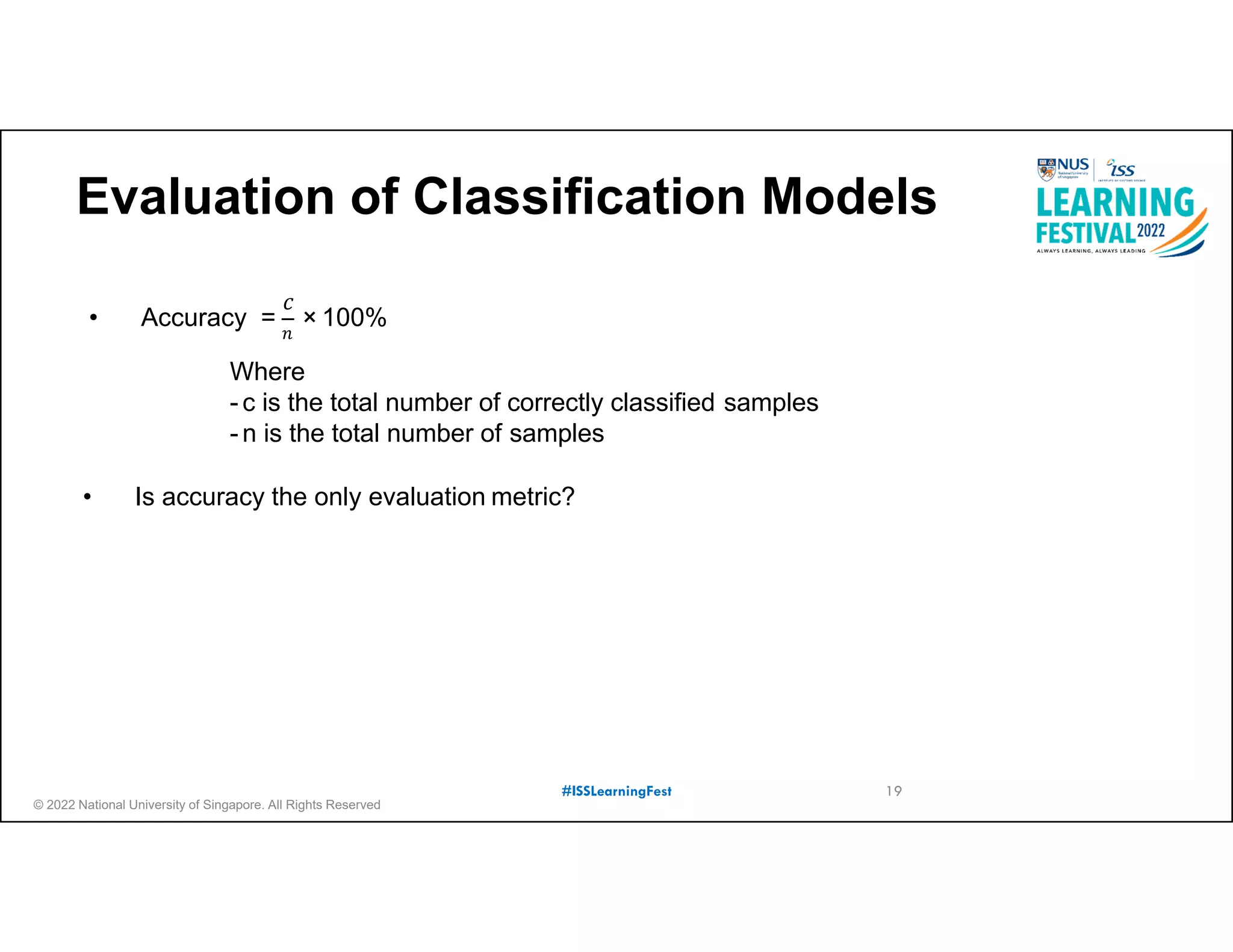
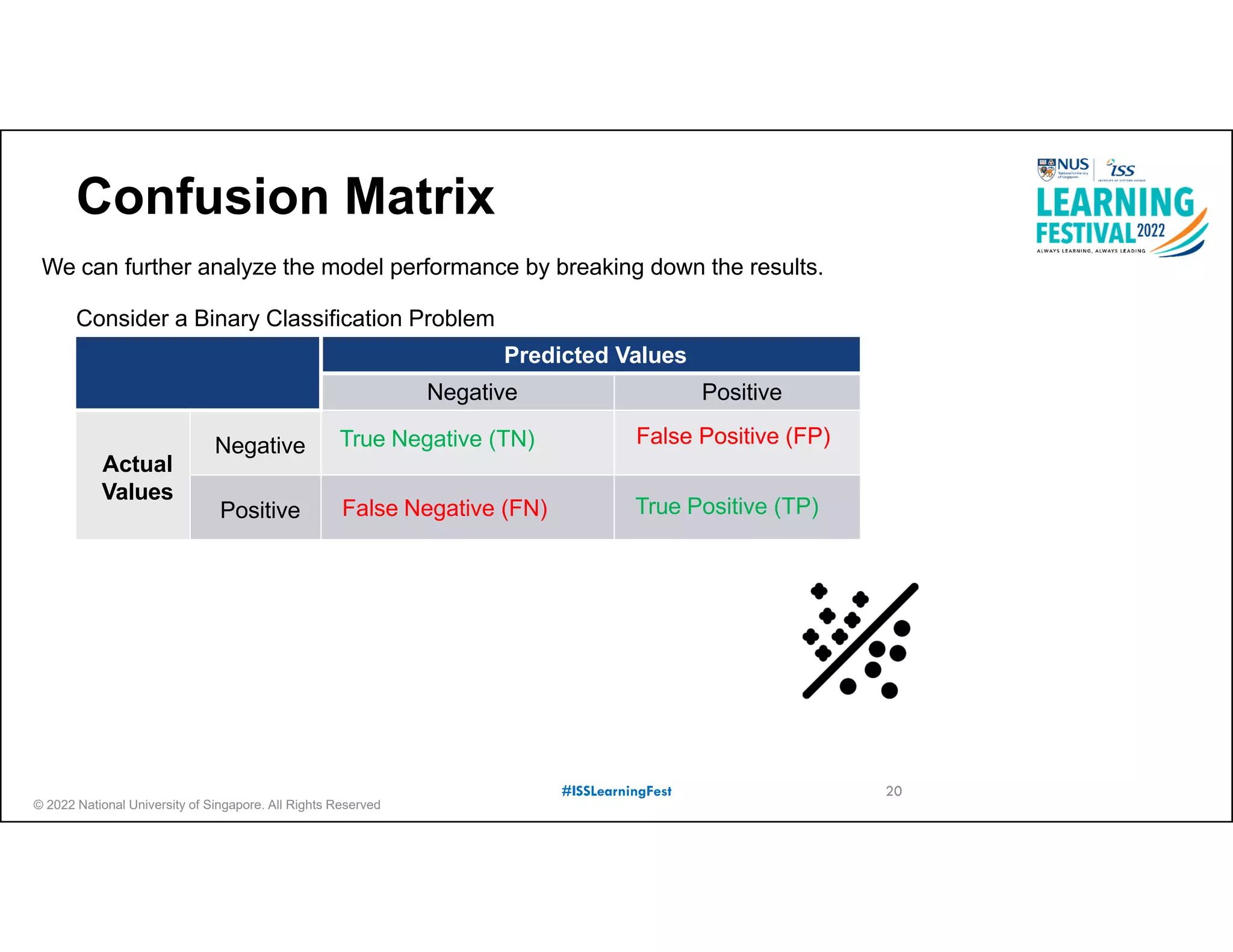
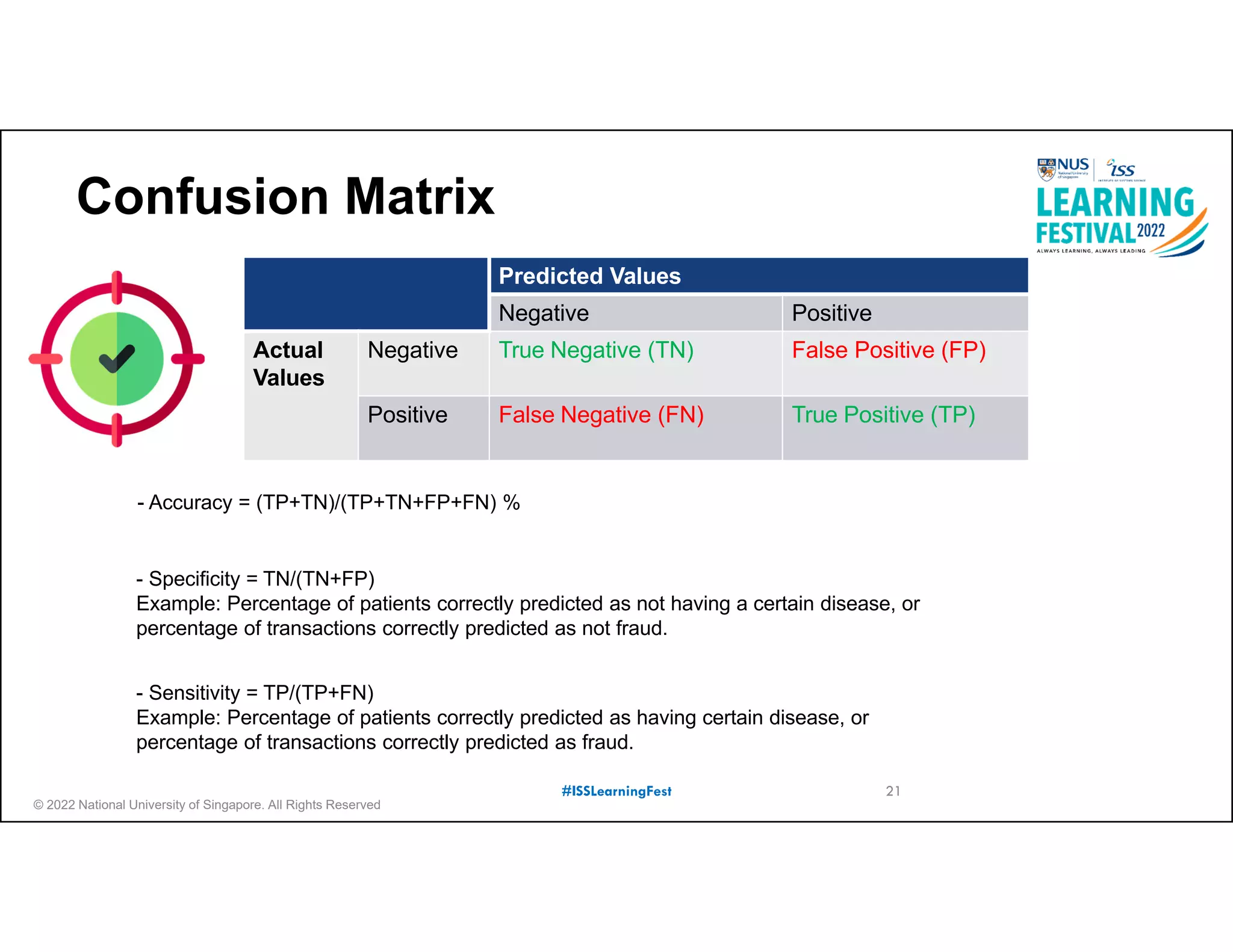
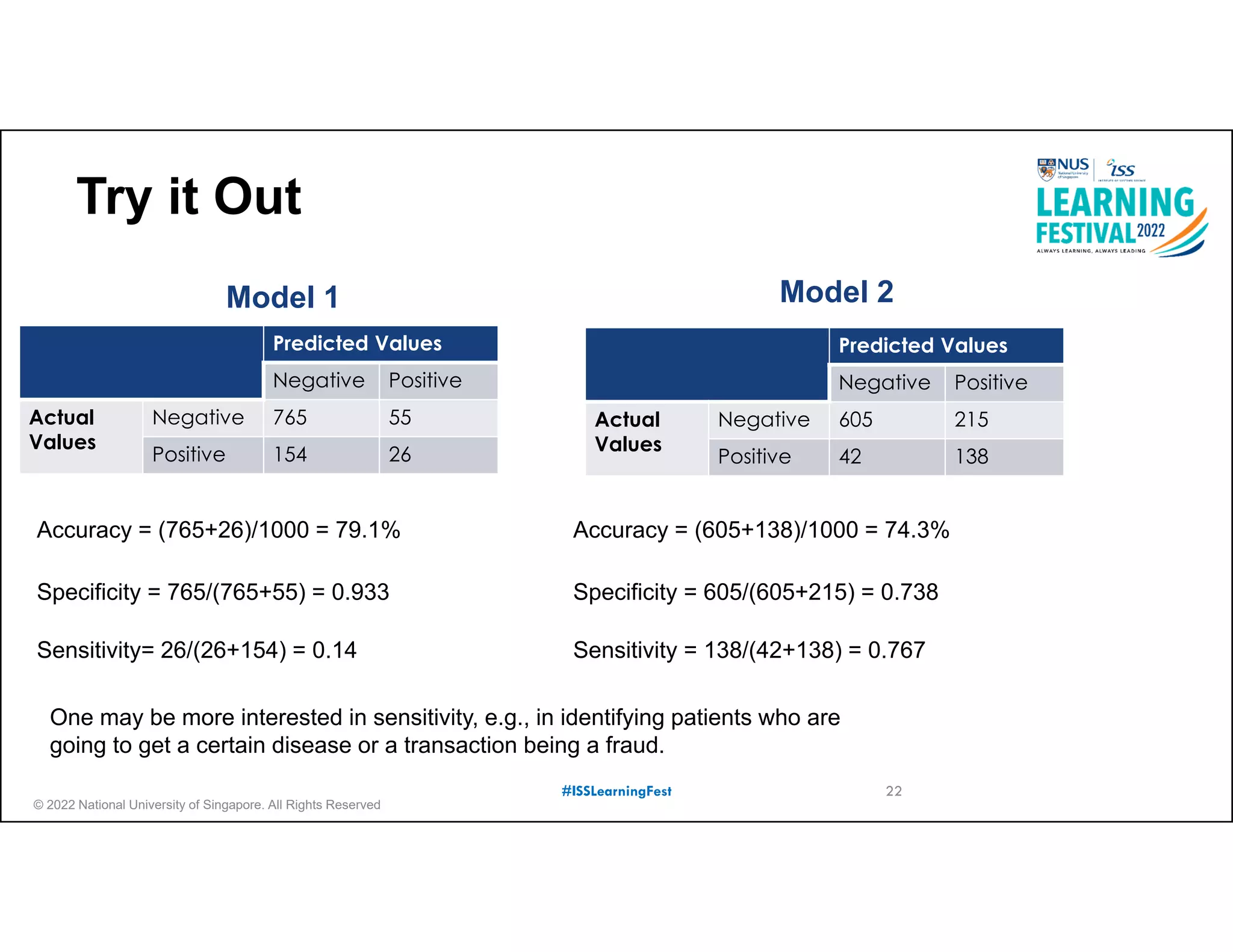
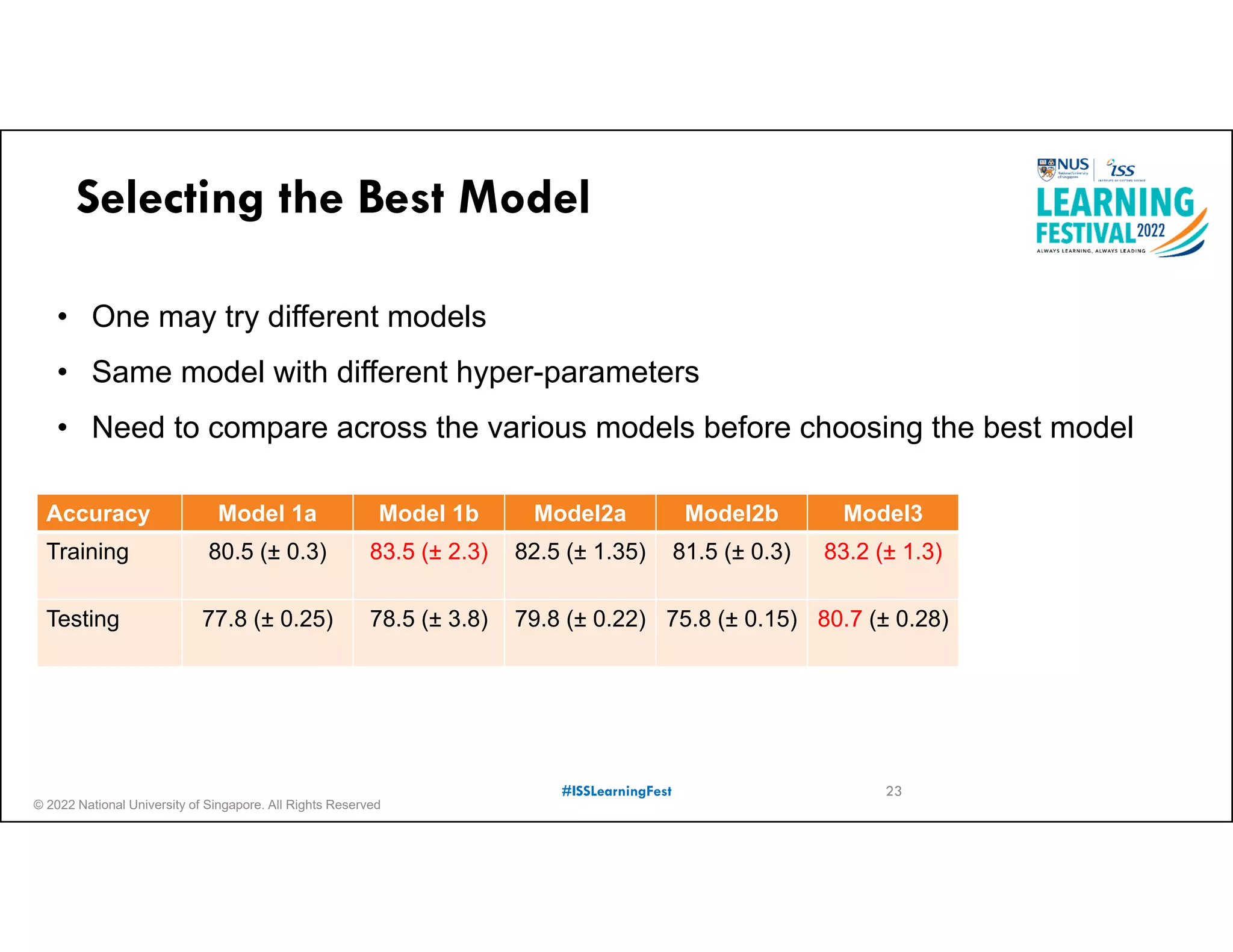
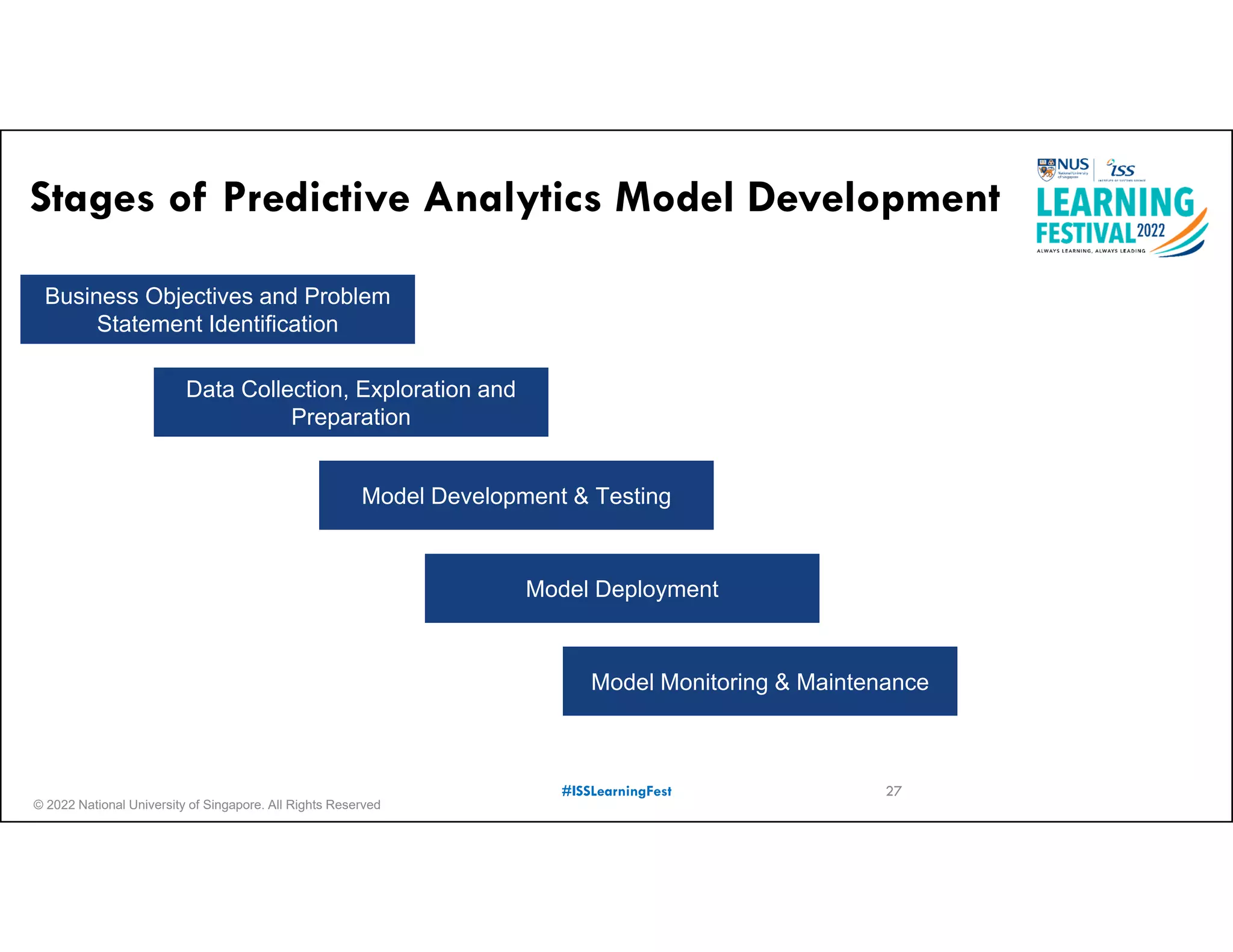
The document outlines the concept of predictive analytics, which involves using current data to forecast future trends and events. It details the stages of model development, including identifying business objectives, data collection, model testing, and monitoring, as well as the importance of stakeholder engagement and cost-benefit analysis. Additionally, various predictive model types, evaluation metrics, and deployment considerations are discussed.