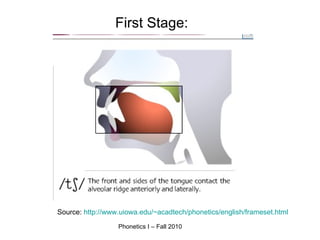
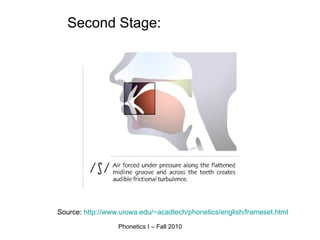
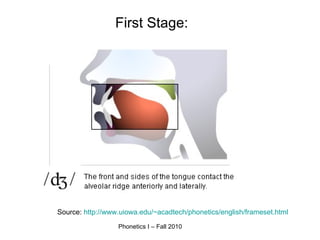
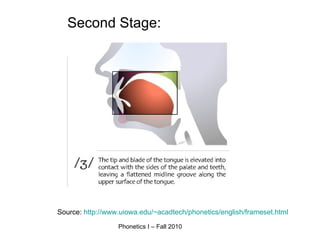
An affricate sound is a consonant sound that is a combination of a plosive sound followed immediately by a fricative sound produced with the same articulators. There are two affricate sounds in English: /tʃ/ as in "chip" and /dʒ/ as in "judge". Both involve an initial plosive sound (/t/ or /d/) followed by a fricative sound produced in the post-alveolar region. For a sound to be considered an affricate, the plosive and fricative components must be homorganic or use the same place of articulation in the vocal tract.