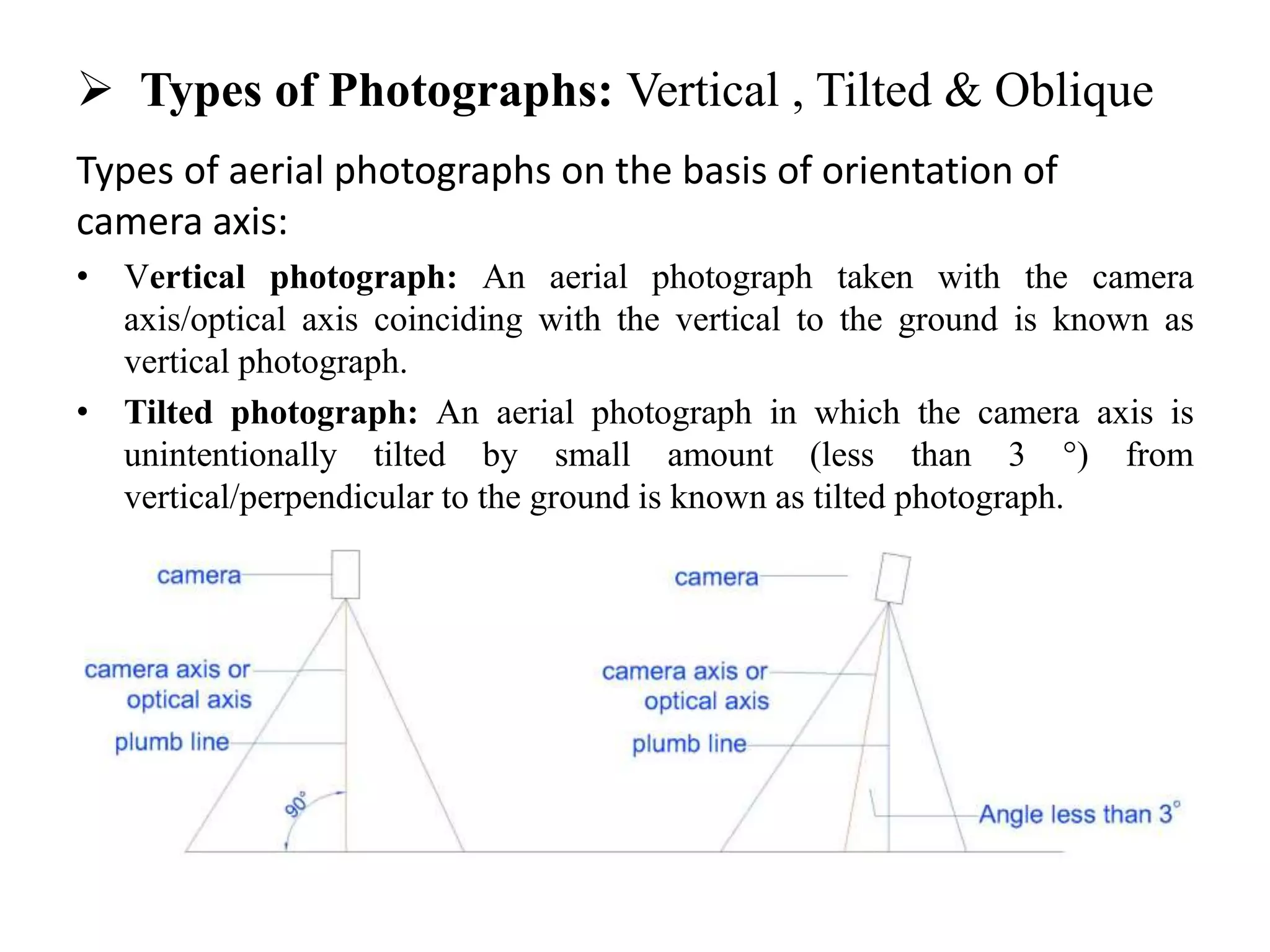
The document presents an outline of aerial photogrammetry, defining it as an advanced technique for obtaining information about objects or areas without physical contact. It discusses objectives such as mapping, reconnaissance, military intelligence, and environmental assessments, and distinguishes between terrestrial and aerial photogrammetry based on investment, technical skill, and land size. The document also compares maps with aerial photographs and describes types of aerial photographs, including vertical, tilted, and oblique orientations.