This document contains a lecture outline on trigonometric leveling with examples of numerical problems. It includes:
- An introduction to trigonometric leveling and the lecturer's contact information.
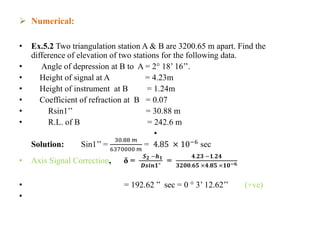
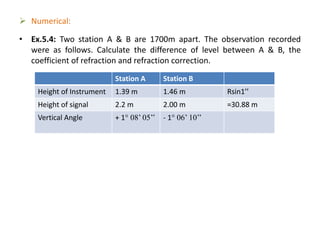
- Four example problems demonstrating calculations for corrected vertical angles, central angles, curvature and refraction corrections, and determining height differences or reduced levels between stations using trigonometric leveling methods and accounting for instrument heights, signal heights, and refraction.