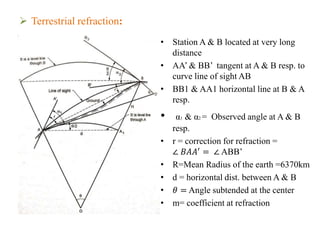
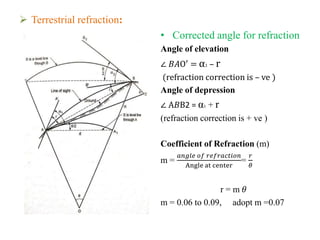
Trigonometric leveling is a surveying method to determine vertical distances between two points by taking vertical angle measurements and known distances. It accounts for refraction and curvature of the Earth. Refraction makes points appear higher, while curvature makes them appear lower, so their combined effect is that points appear lower. Refraction corrections are negative for elevation angles and positive for depression angles. Curvature corrections are positive for elevations and negative for depressions. The total corrections combine these and consider the distance between points, Earth's radius, and coefficient of refraction.