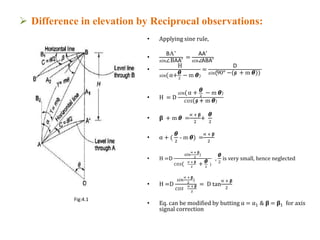
1) The document describes the method of determining the difference in elevation between two stations using reciprocal observations. Observations of vertical angles are made simultaneously from both stations to eliminate the effect of refraction.
2) The mean of the observed vertical angles is used in trigonometric formulas along with the horizontal distance between stations to calculate the difference in elevation.
3) The coefficient of refraction is defined as the ratio of the radius of curvature of the earth to the radius of curvature of the line of sight. A formula is provided to calculate the coefficient of refraction based on the vertical angles observed and the curvature of the earth.



![ Difference in elevation by Reciprocal observations:
• H= Difference in elevation bet. A &B
• ∝ & 𝛃 = Angle observed simultaneously
• D = Horizontal distance = AB
• 𝛾 & C = Angle of refraction & curvature
• ∝1 & 𝛃1 = Corrected vertical angle for axis
signal
• The mean vertical angle =
∝ + 𝛃
2
• ∠B AA’ = [ α + (
ᆈ
2
- m ᆈ) ]
• ∠ ABB’ = [ 𝛃 - (
ᆈ
2
- m ᆈ) ]
• The sign of correction being +ve for angle of
elevation & -ve for angle of depression
• Since the chords AA’ & BB’ are parallel, ∠BAA’
=∠ABB’
• α + (
ᆈ
2
- m ᆈ) = 𝛃 - (
ᆈ
2
- m ᆈ) =
∝ + 𝛃
2
….. .1
Fig.3.1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trigonometricleveling04-200410060009/85/Trigonometric-leveling-04-4-320.jpg)