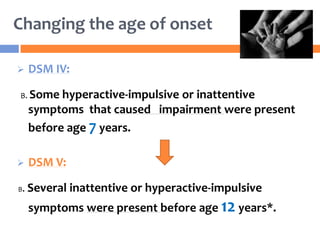
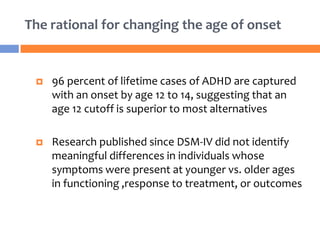
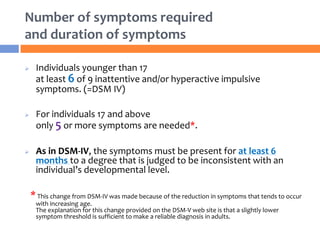
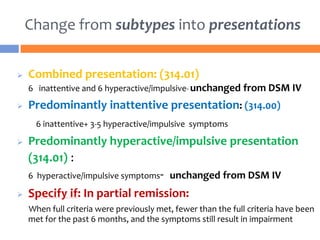
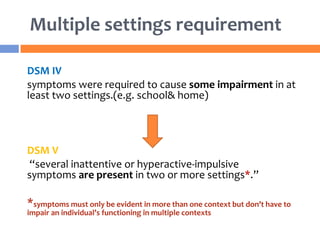
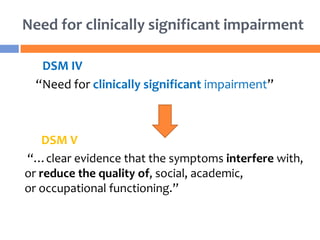
The document summarizes key changes to the diagnostic criteria for ADHD in the DSM-5. Some of the major changes include: expanding the age of onset for symptoms from 7 to 12 years old; reducing the number of required symptoms for adults from 6 to 5; changing the subtypes to presentations; removing the requirement for impairment in multiple settings; and allowing an ADHD diagnosis to be made comorbid with autism spectrum disorder. The changes are aimed at better capturing the presentation of ADHD across the lifespan but may increase prevalence rates, especially in adolescents and adults. There is concern that the DSM lacks biological validity and the NIMH is pursuing the Research Domain Criteria initiative to develop a classification system grounded in neuro