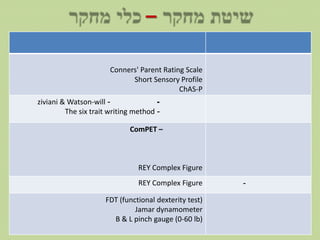
Children with ADHD demonstrate motor coordination difficulties (DCD) at higher rates than children without ADHD. This study examined the relationship between ADHD symptoms and motor skills in 25 children with ADHD compared to 25 control children without ADHD ages 8-11. Results indicated moderate to strong correlations between ADHD symptom severity and poorer performance on motor tests, with worse scores on tests of visual-motor integration, dexterity, handwriting and complex figure copying among children with more severe ADHD. The findings suggest that motor coordination should be assessed in children with ADHD, as difficulties may be linked to ADHD symptom severity levels.