Embed presentation
Downloaded 1,425 times





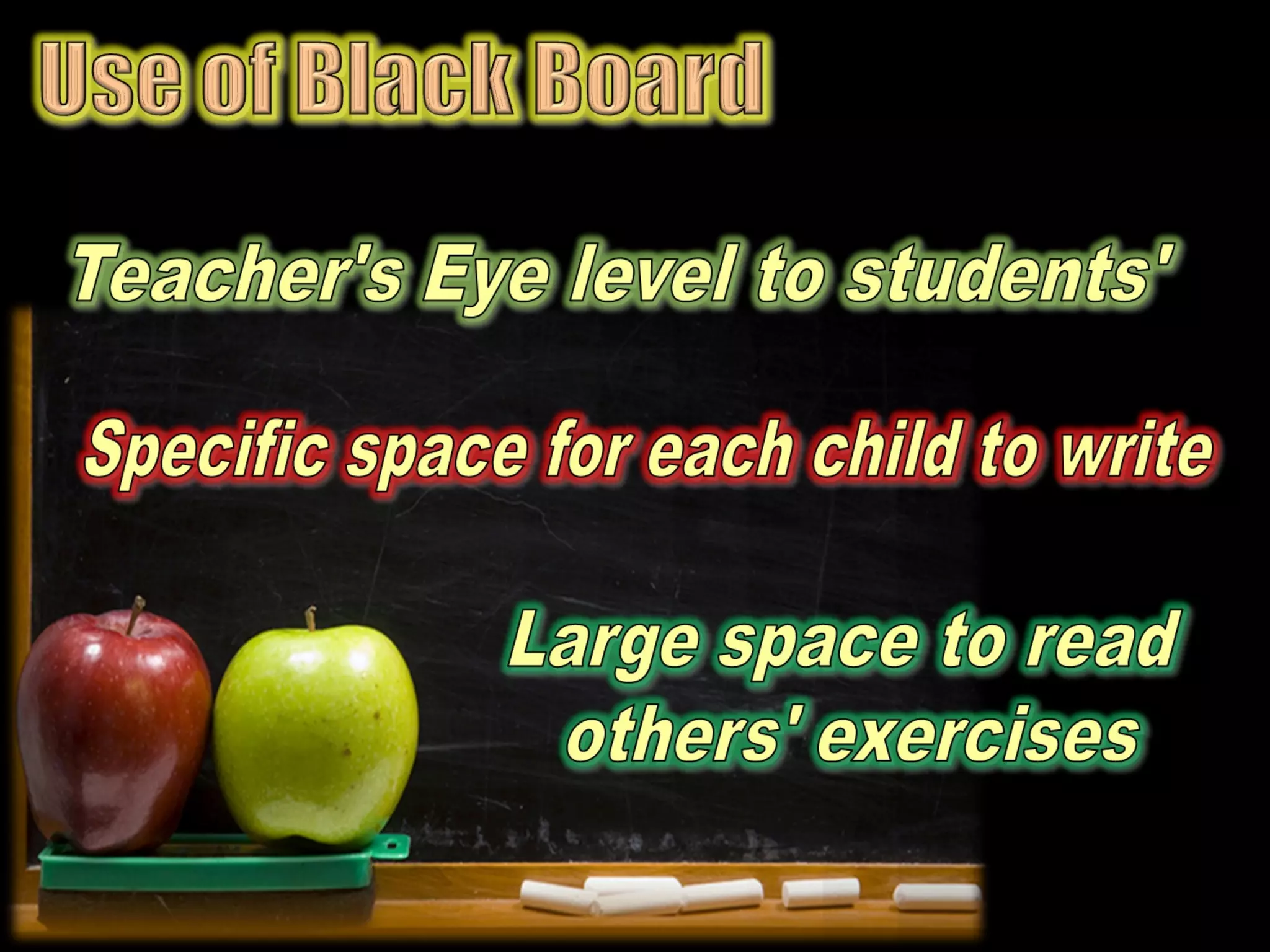







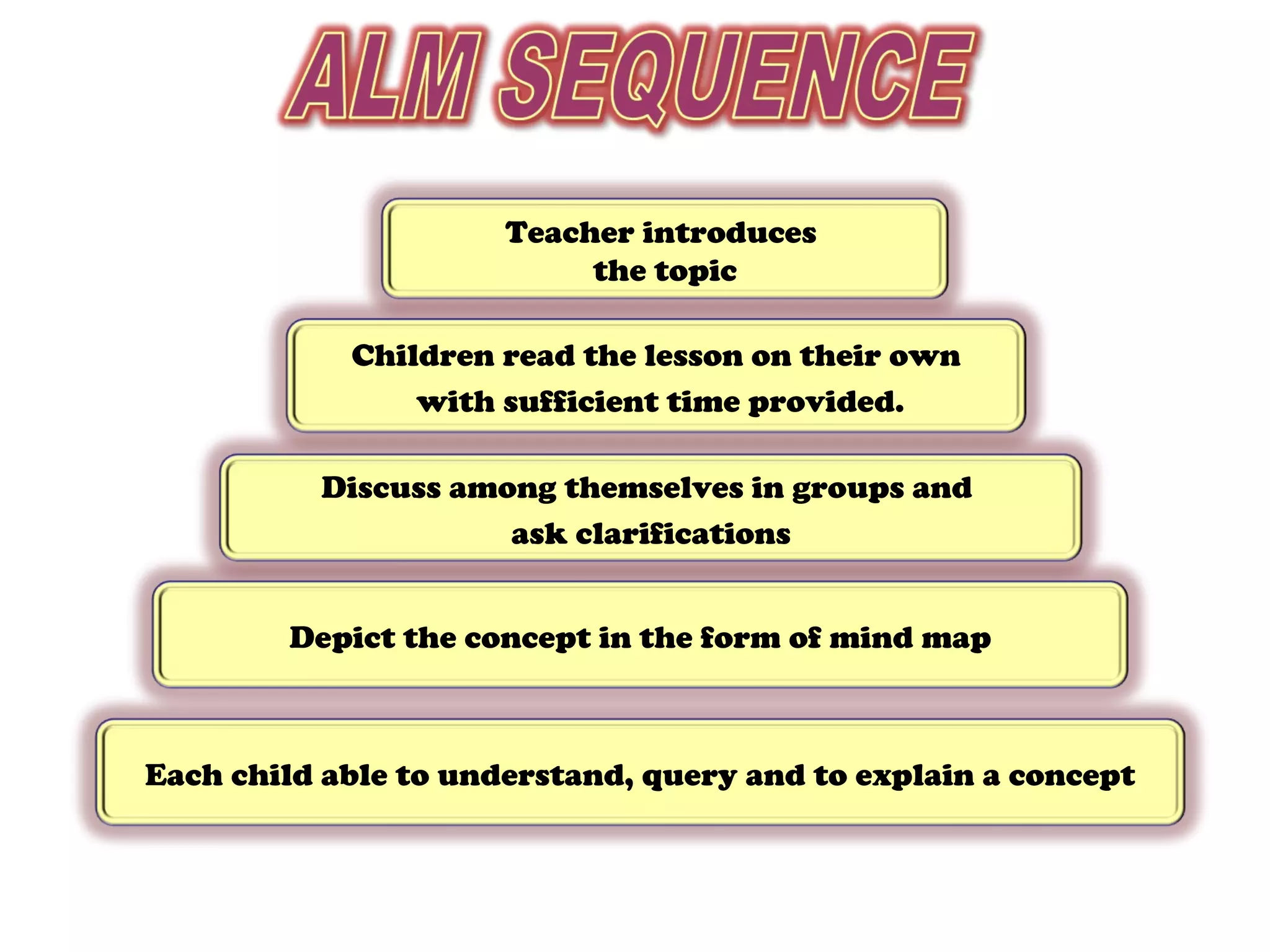


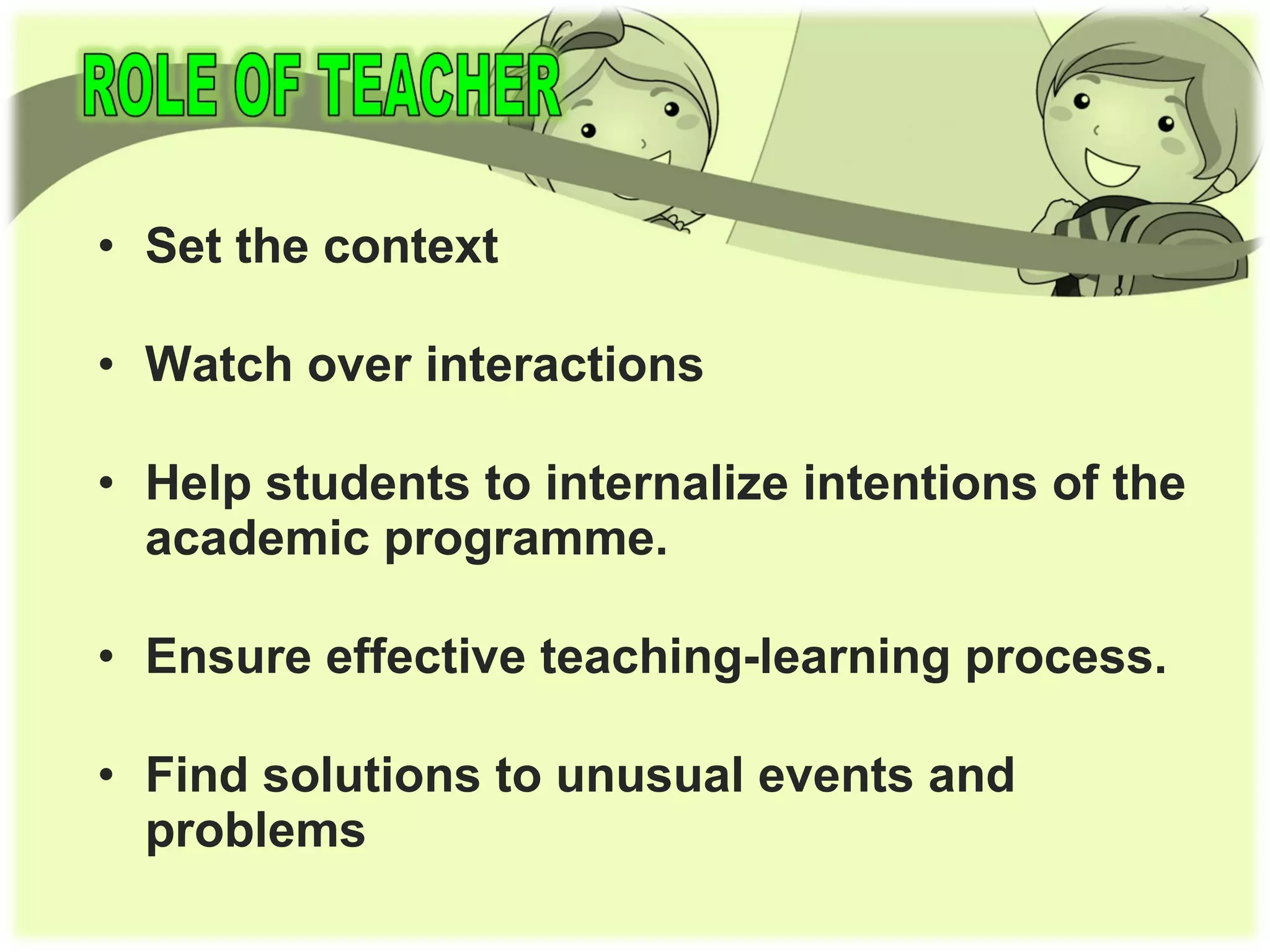





The document discusses a new teaching method introduced in Tamilnadu that involves grouping children vertically with 4 students each from grades 1 through 4. This vertical grouping has advantages such as older children helping younger ones, encouraging cooperation over competition, and providing a solution for multi-grade classrooms. The method involves teachers introducing topics and then having children read independently, discuss in groups, create mind maps to depict concepts, and ensure each child can understand and explain the ideas with the teacher acting as a facilitator rather than conveyor of information.





















