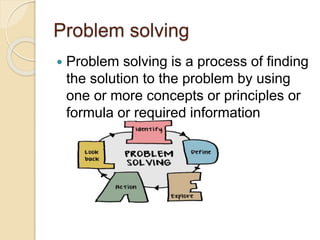
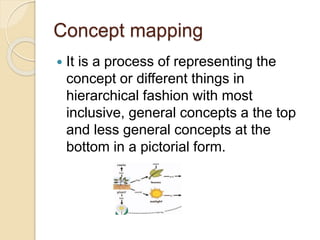
This document discusses activity-based learning (ABL). It begins by defining activities and activity-based learning as using activities as the basis for learning. The history of ABL is then outlined, tracing it back to its origins in the 1940s in British schools. Examples of different types of activities used in ABL are provided, such as role plays, games, debates, and experiments. The needs and benefits of ABL are described as helping students learn and retain information through active participation. Steps for organizing ABL and its uses, such as reinforcing concepts and providing feedback, are also summarized.