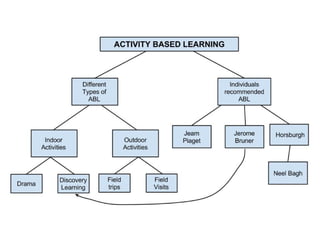
Activity based learning involves using activities as the base for the educational process to actively engage students in learning. Some key points:
- It began gaining popularity during World War 2 with pioneers like David Horsburgh incorporating activities like music, carpentry and gardening into the curriculum.
- There are different types of activities used in ABL like role playing, debates, experiments, field trips and discovery learning to explore concepts hands-on.
- ABL is beneficial for students as it allows them to learn better through direct experience in their environment and when they participate and learn on their own.