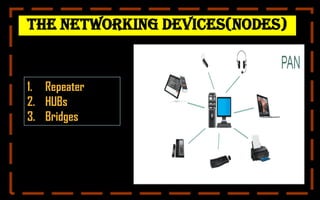
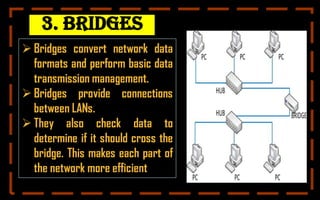
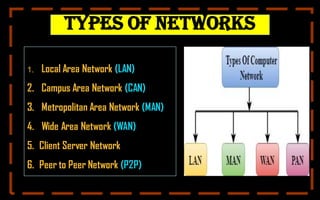
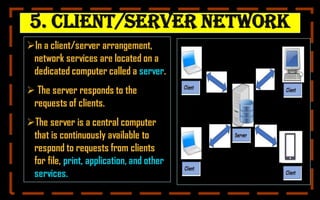
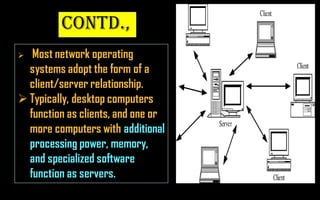
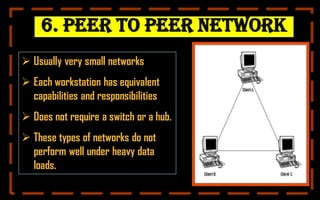
This document provides a comprehensive overview of computer networking, covering topics such as networking devices, types of networks, and wireless networks. Key devices include repeaters, hubs, and bridges, while various network types are detailed, including LAN, WAN, and client/server networks. It also explains wireless technologies like Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, emphasizing their importance in modern networking.