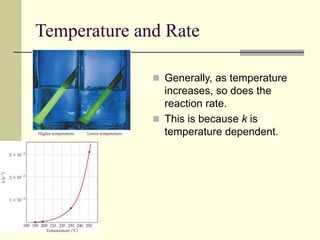
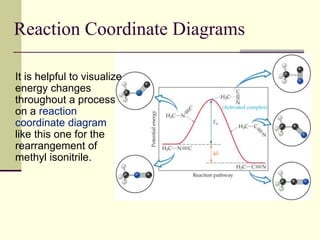
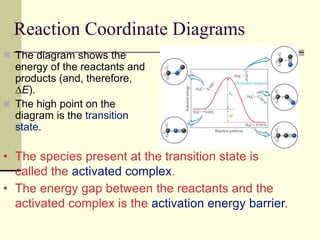
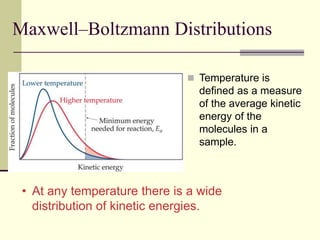
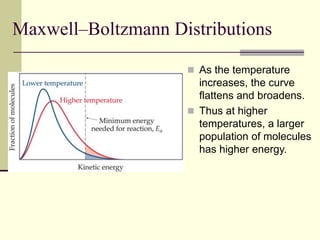
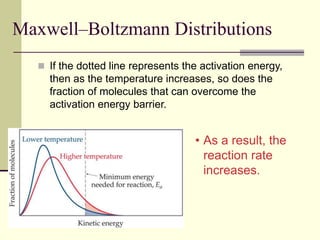
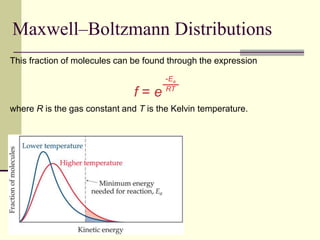
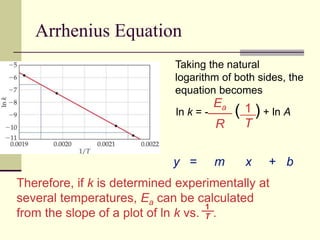
1) Reactions require a minimum amount of energy called the activation energy to occur. As temperature increases, more molecules have sufficient energy to overcome this barrier and reaction rate increases.
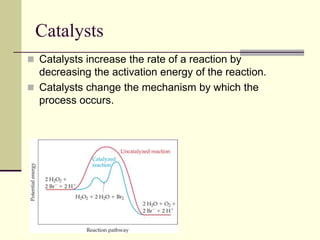
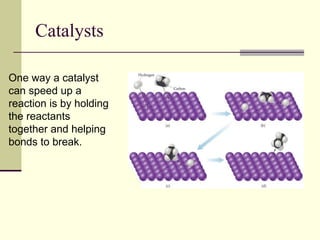
2) Catalysts decrease the activation energy needed for a reaction, allowing more molecules to react at a given temperature and increasing reaction rate.
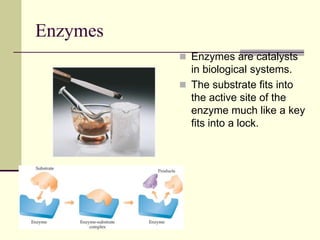
3) Enzymes are biological catalysts that hold substrates in their active sites, facilitating bond breaking and formation to speed up biochemical reactions.