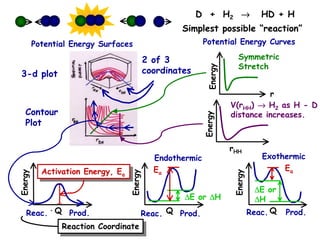
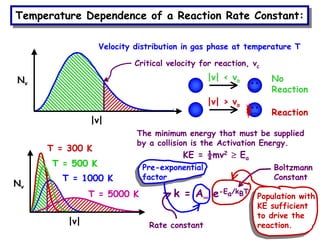
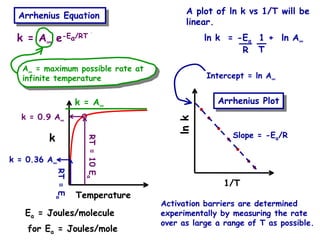
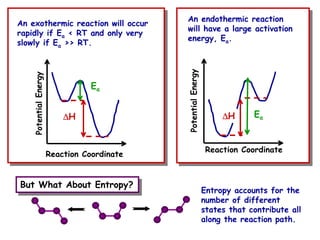
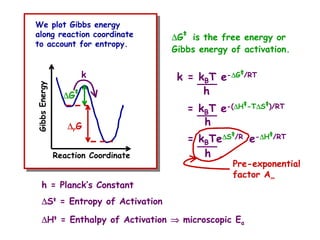
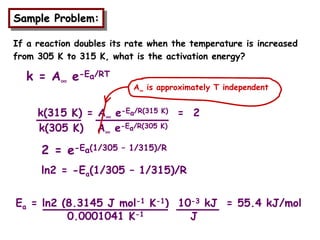
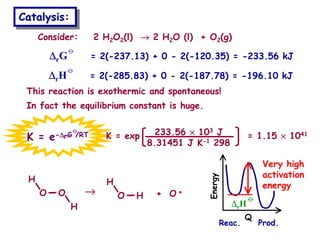
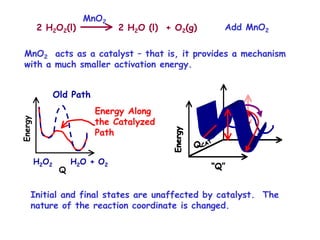
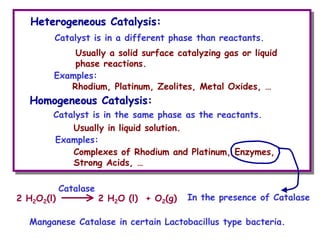
The document discusses reaction kinetics and catalysis. It defines catalysis as lowering the activation energy of a reaction by providing an alternative reaction pathway. A catalyst is unchanged by the reaction but alters the reaction coordinate to reduce the energy needed to reach the transition state. Heterogeneous catalysis involves a solid catalyst and liquid/gas reactants, while homogeneous catalysis uses catalysts in the same phase as reactants, such as metal complexes in solution. Examples of catalysts mentioned include enzymes, metal oxides, rhodium, and platinum.