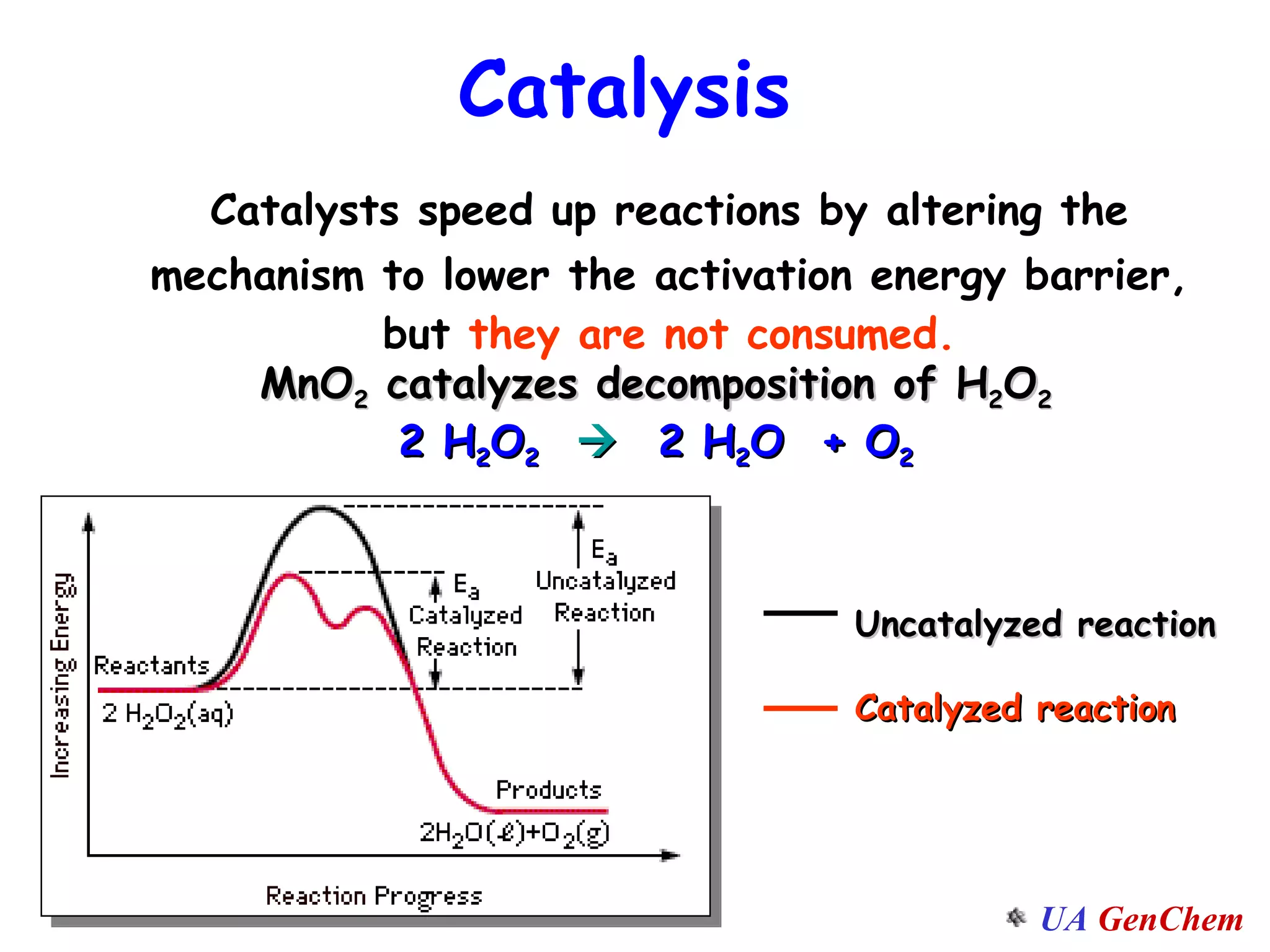
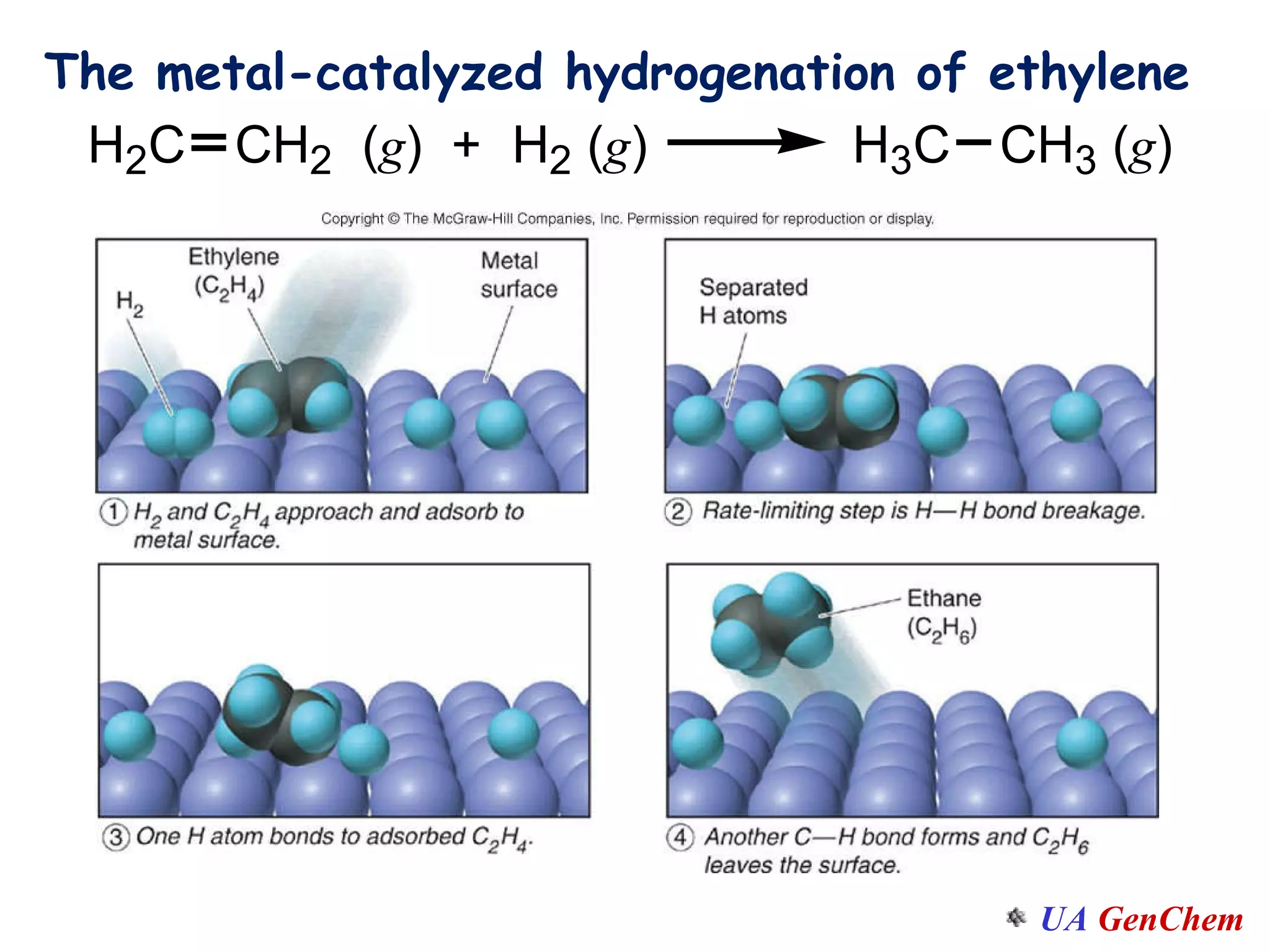
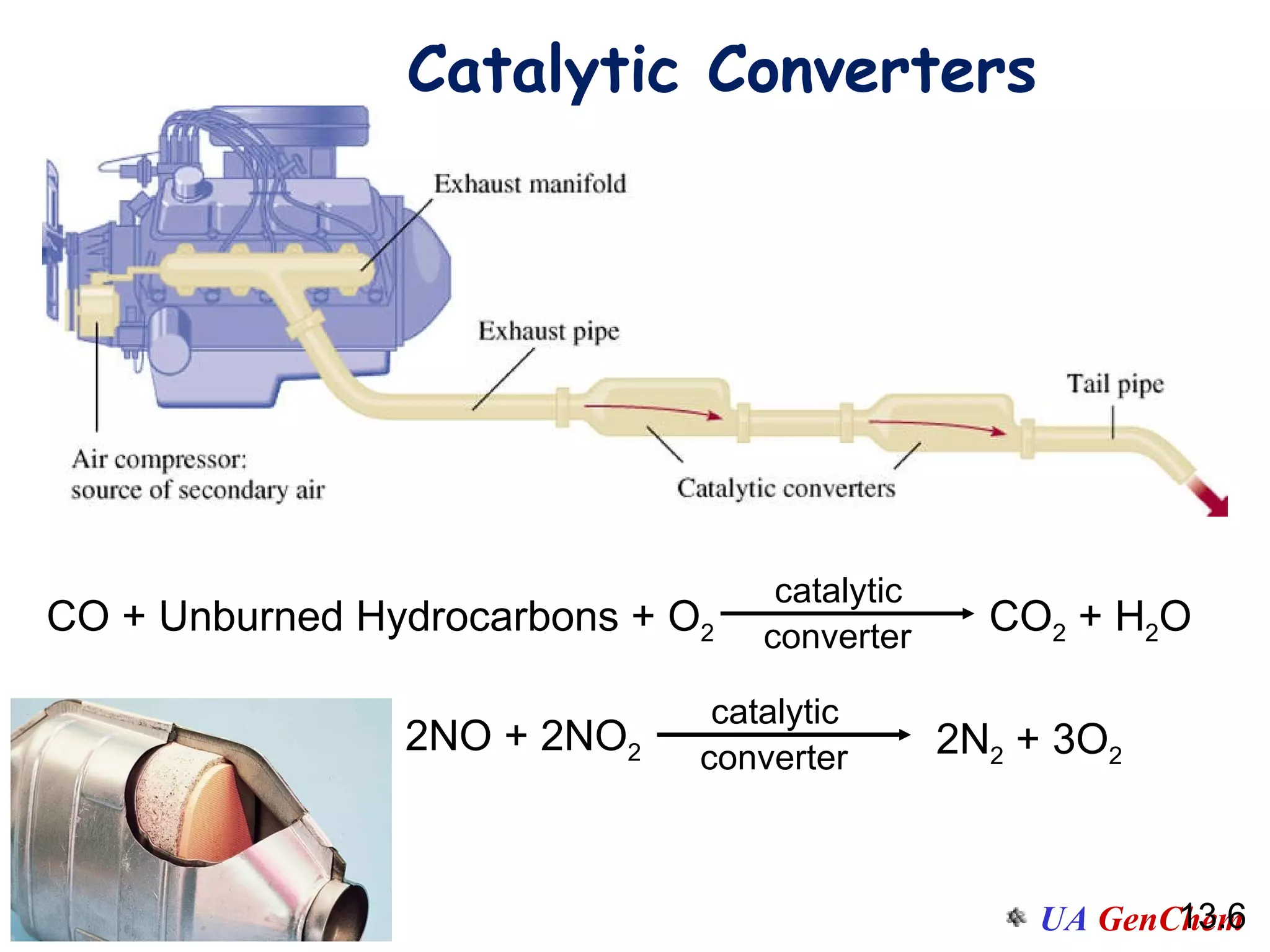
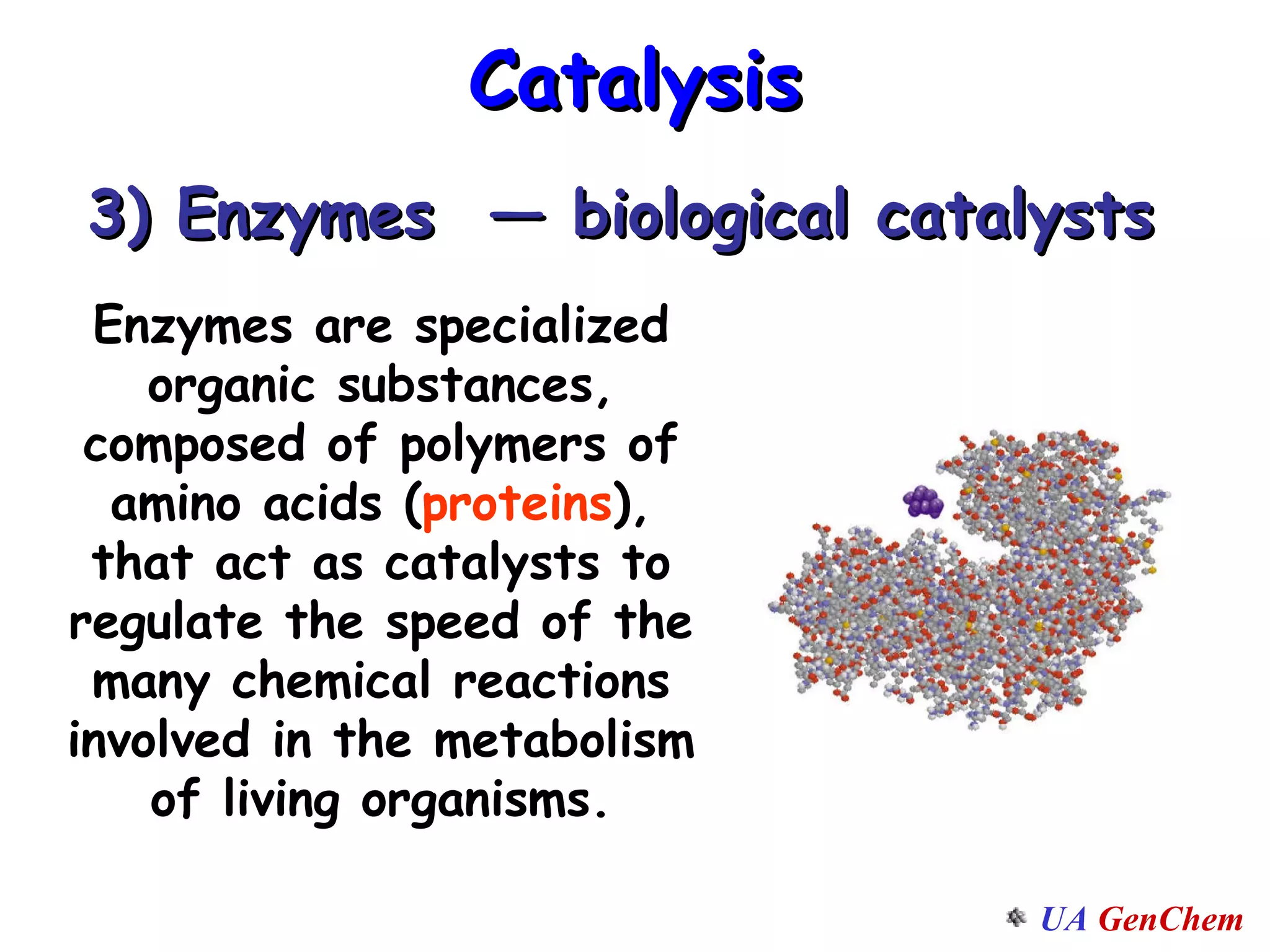
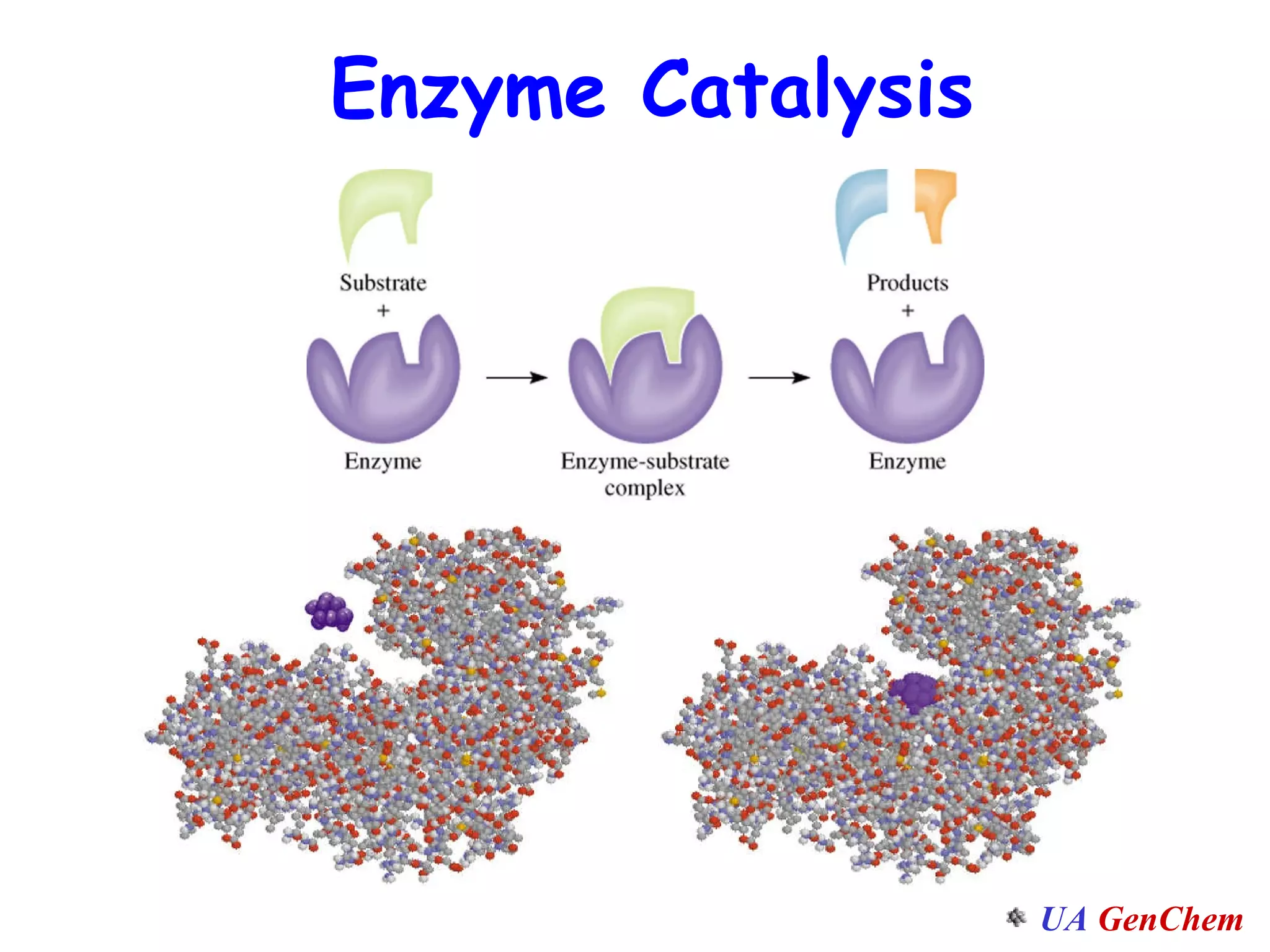
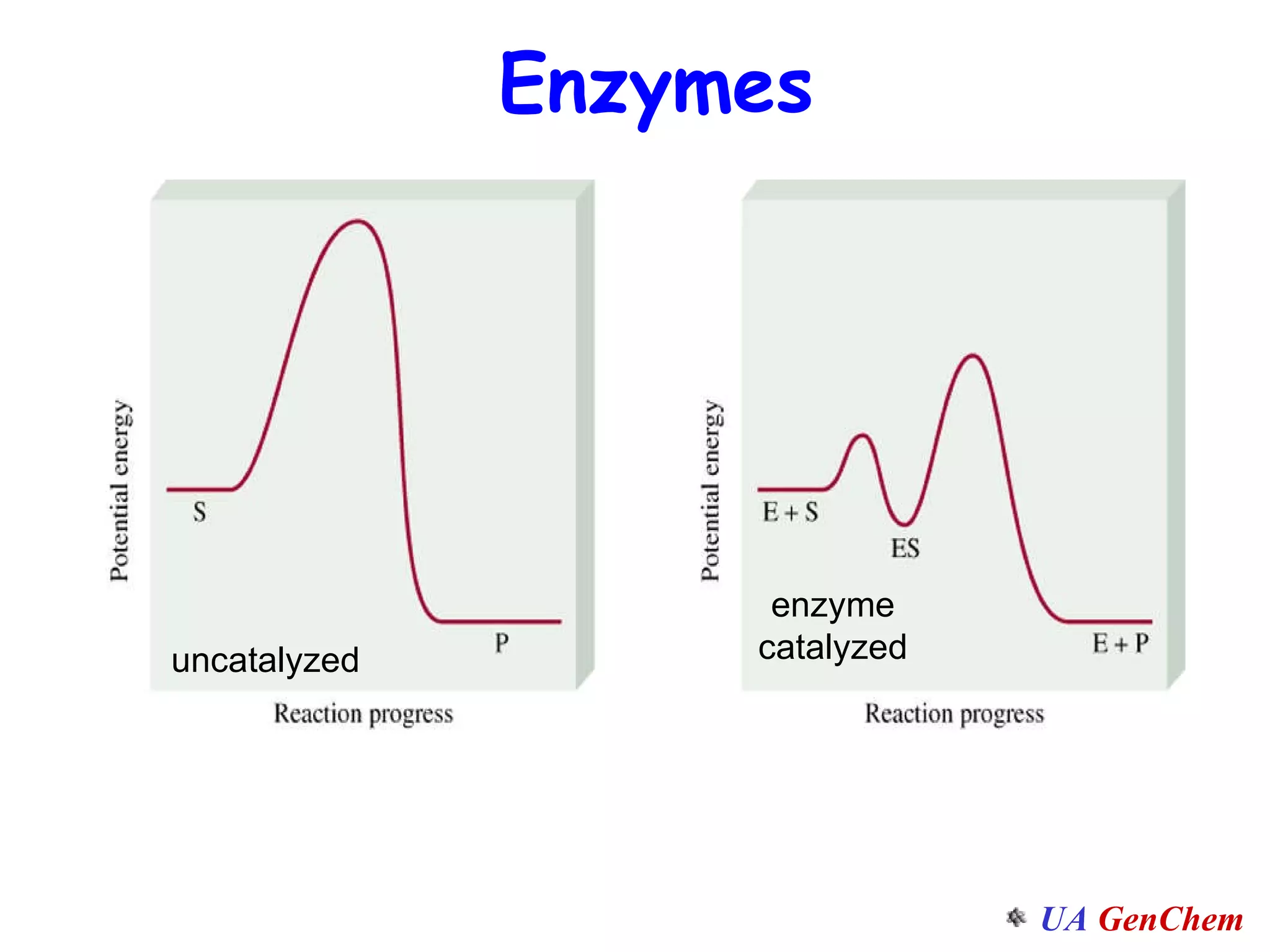
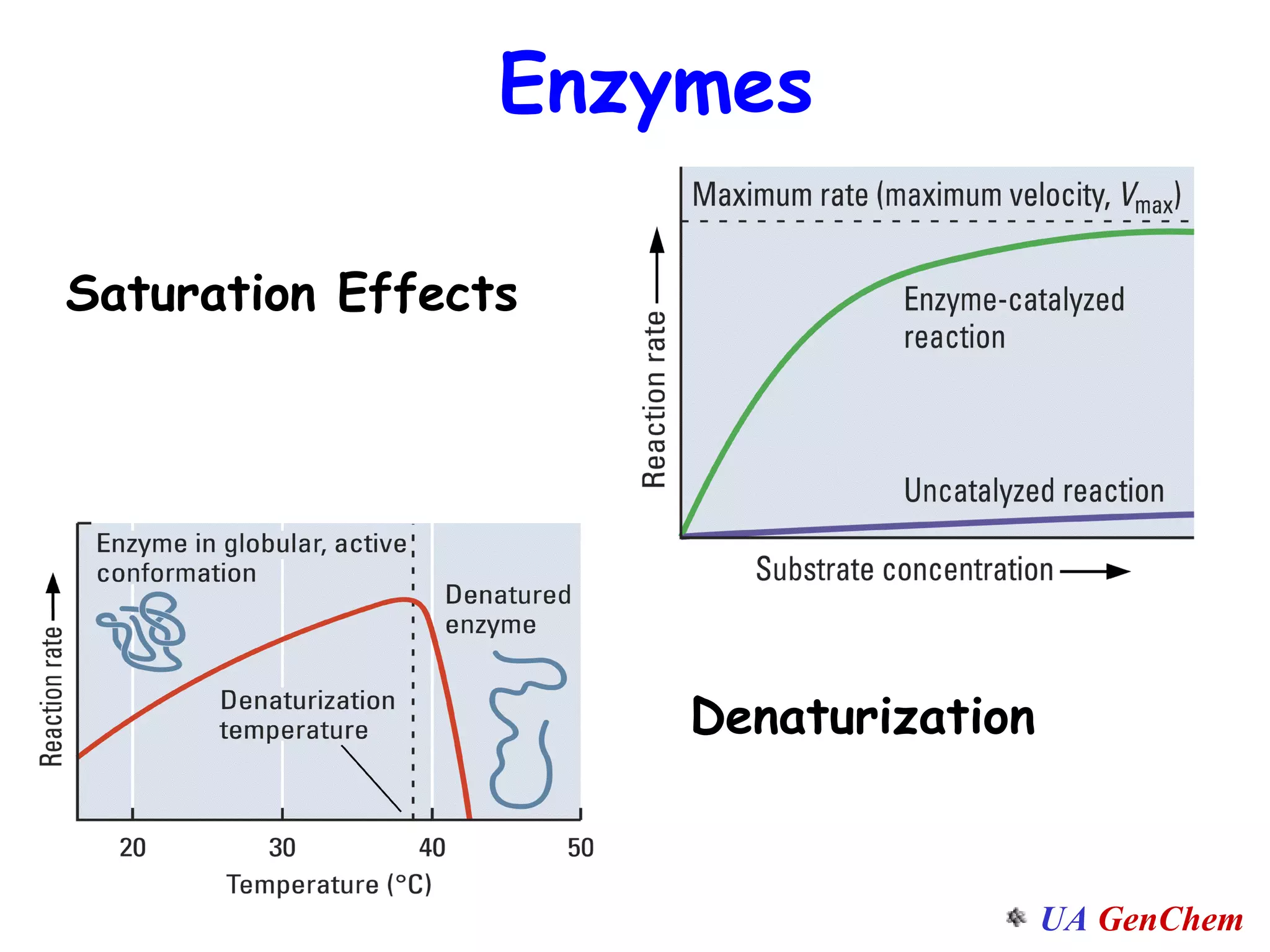
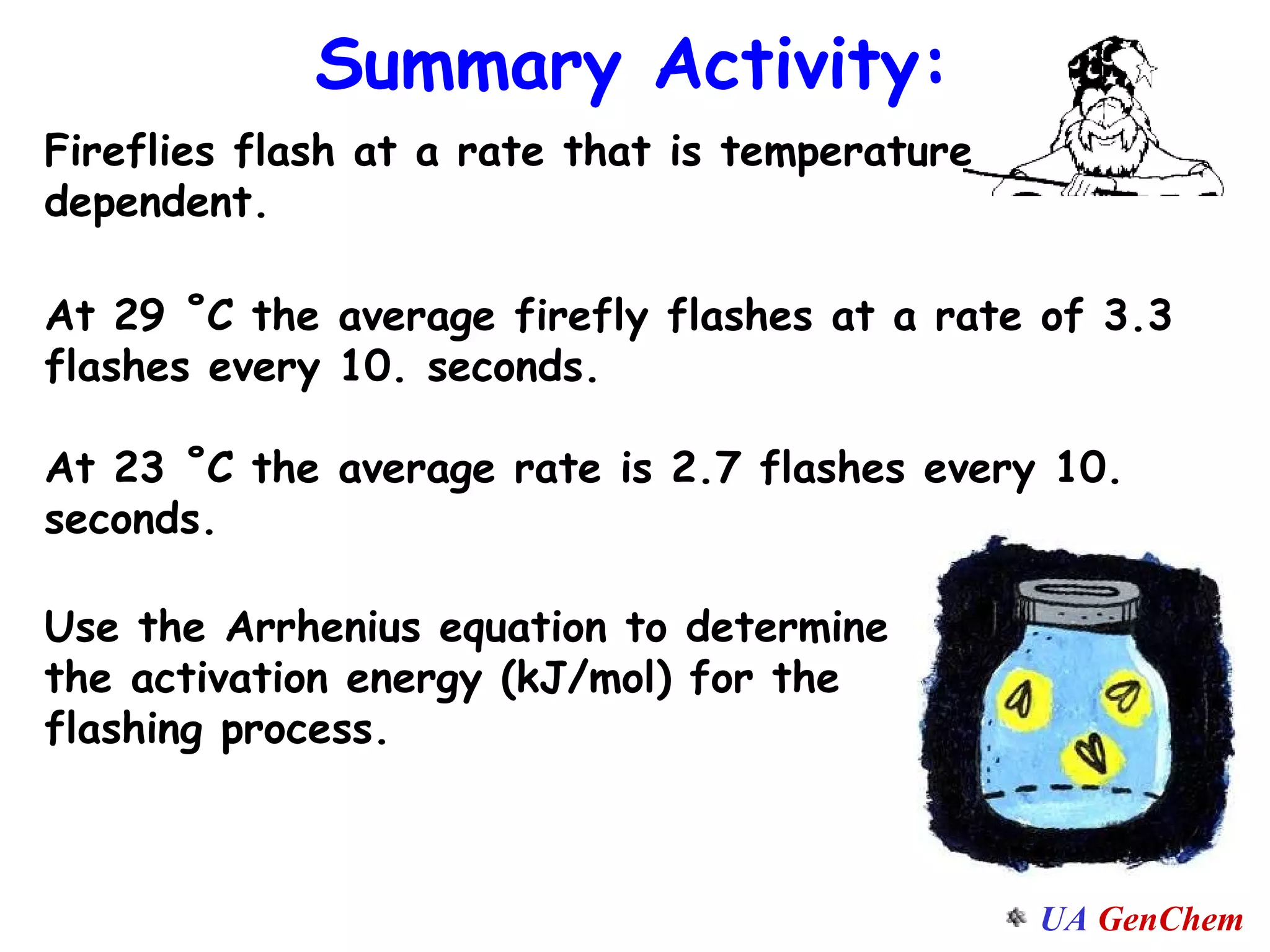
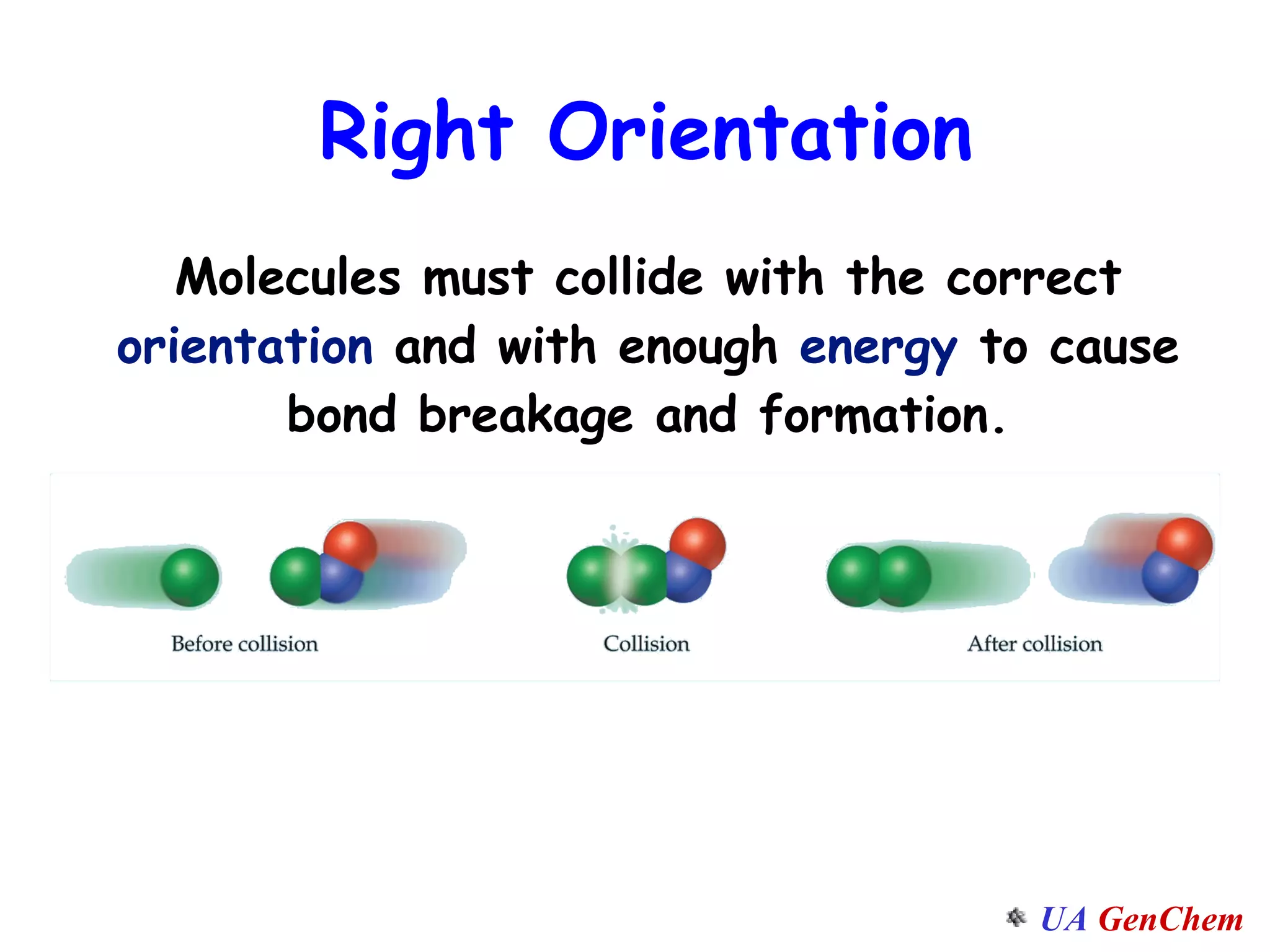
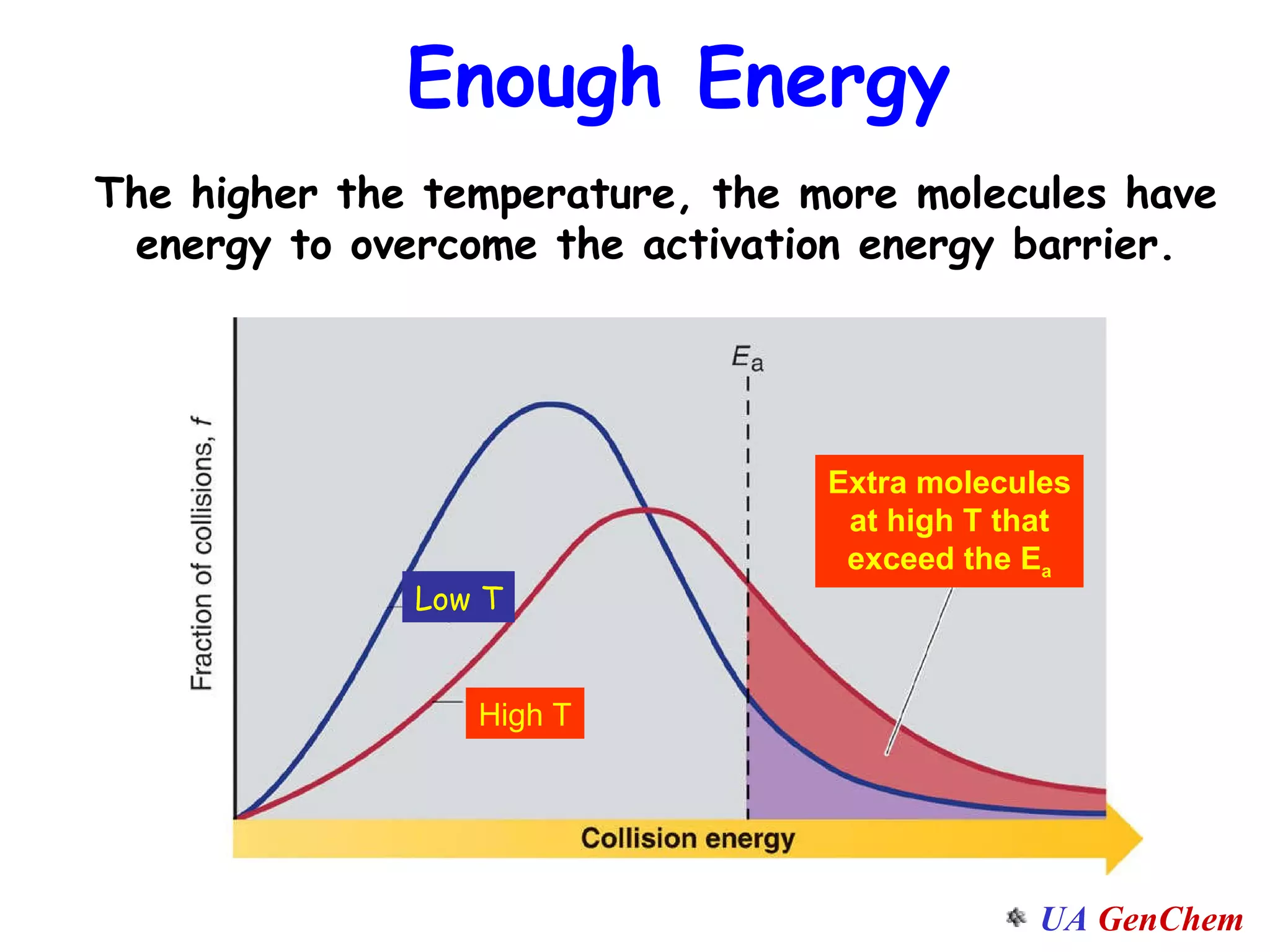
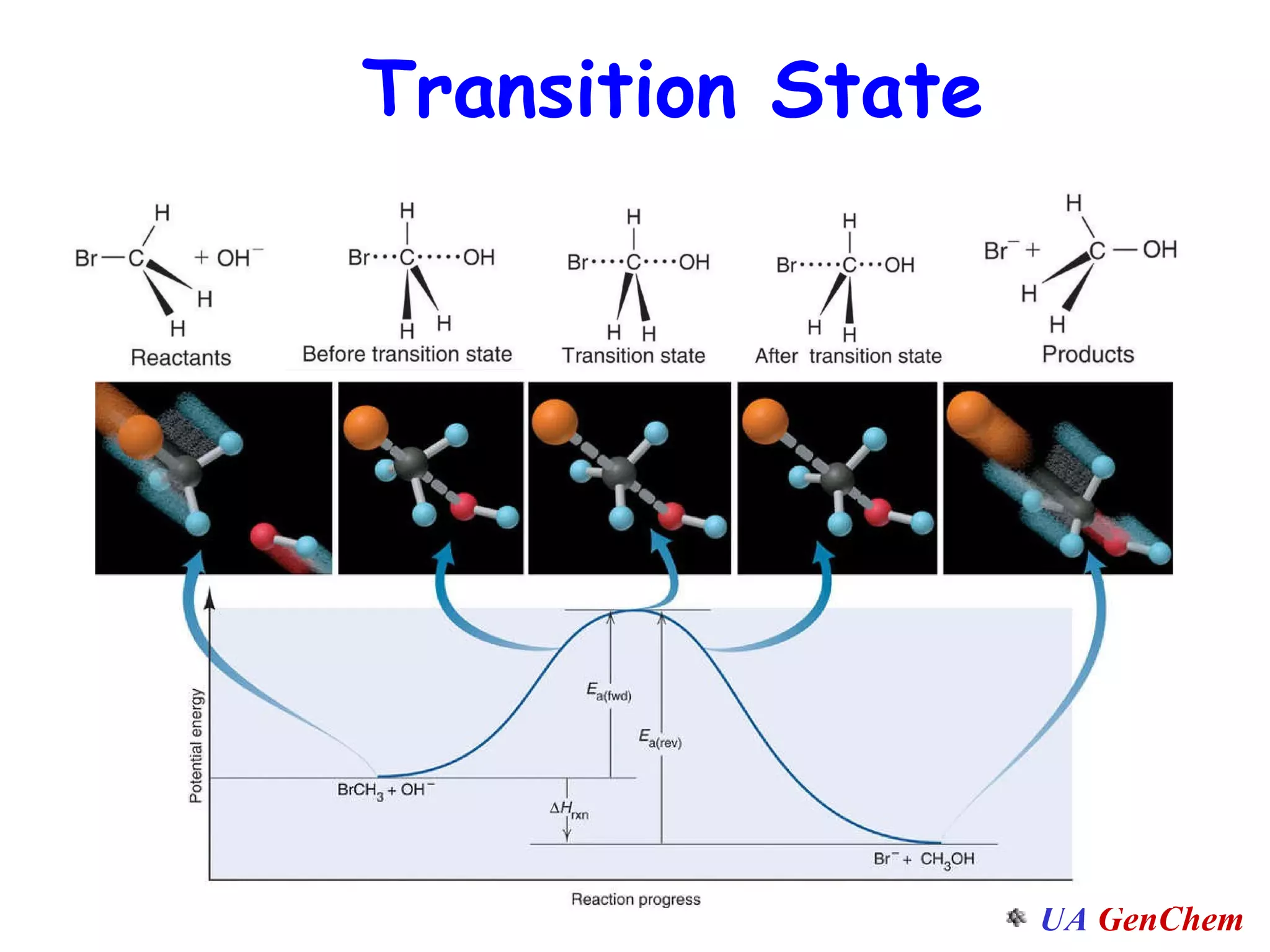
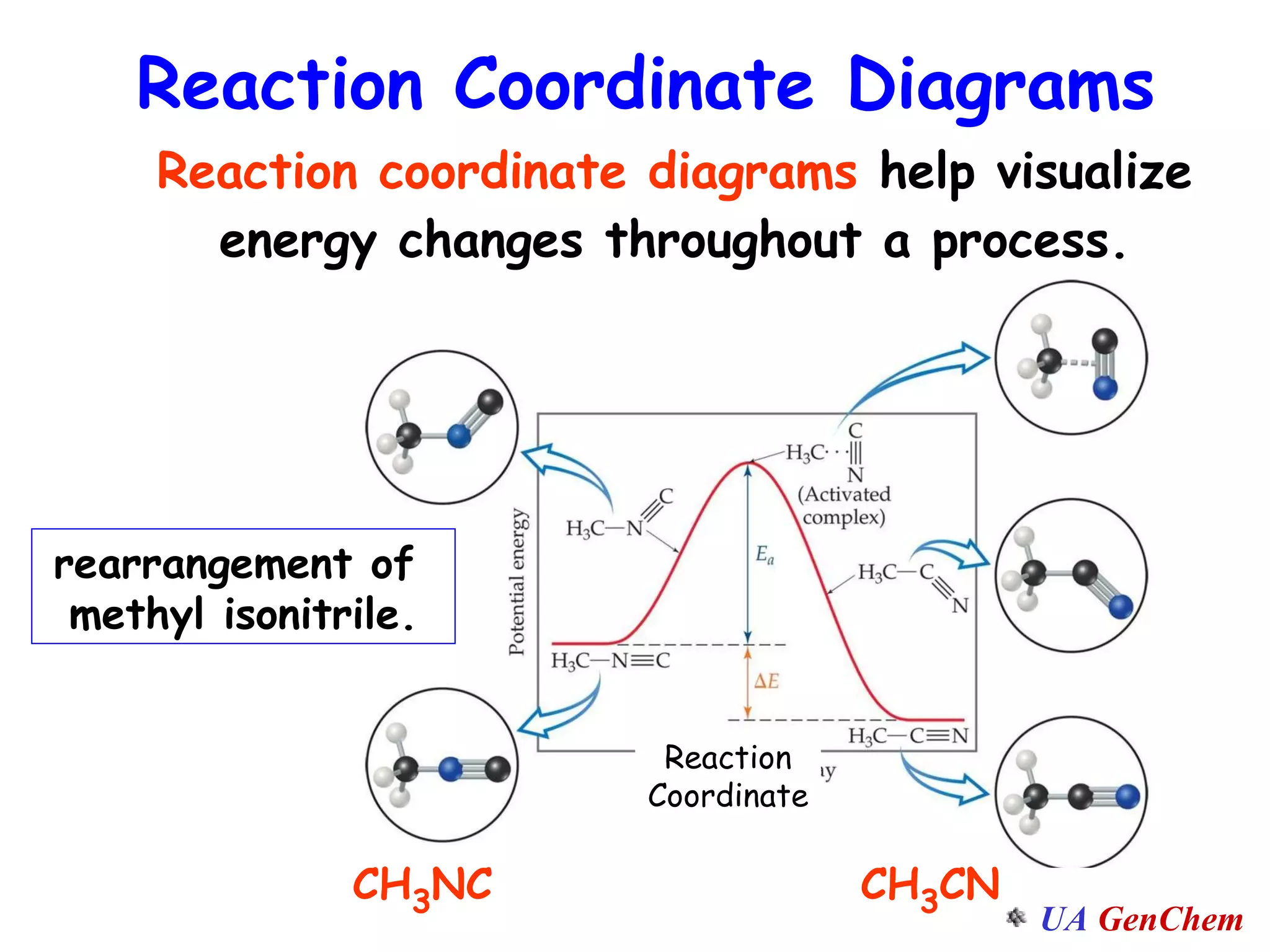
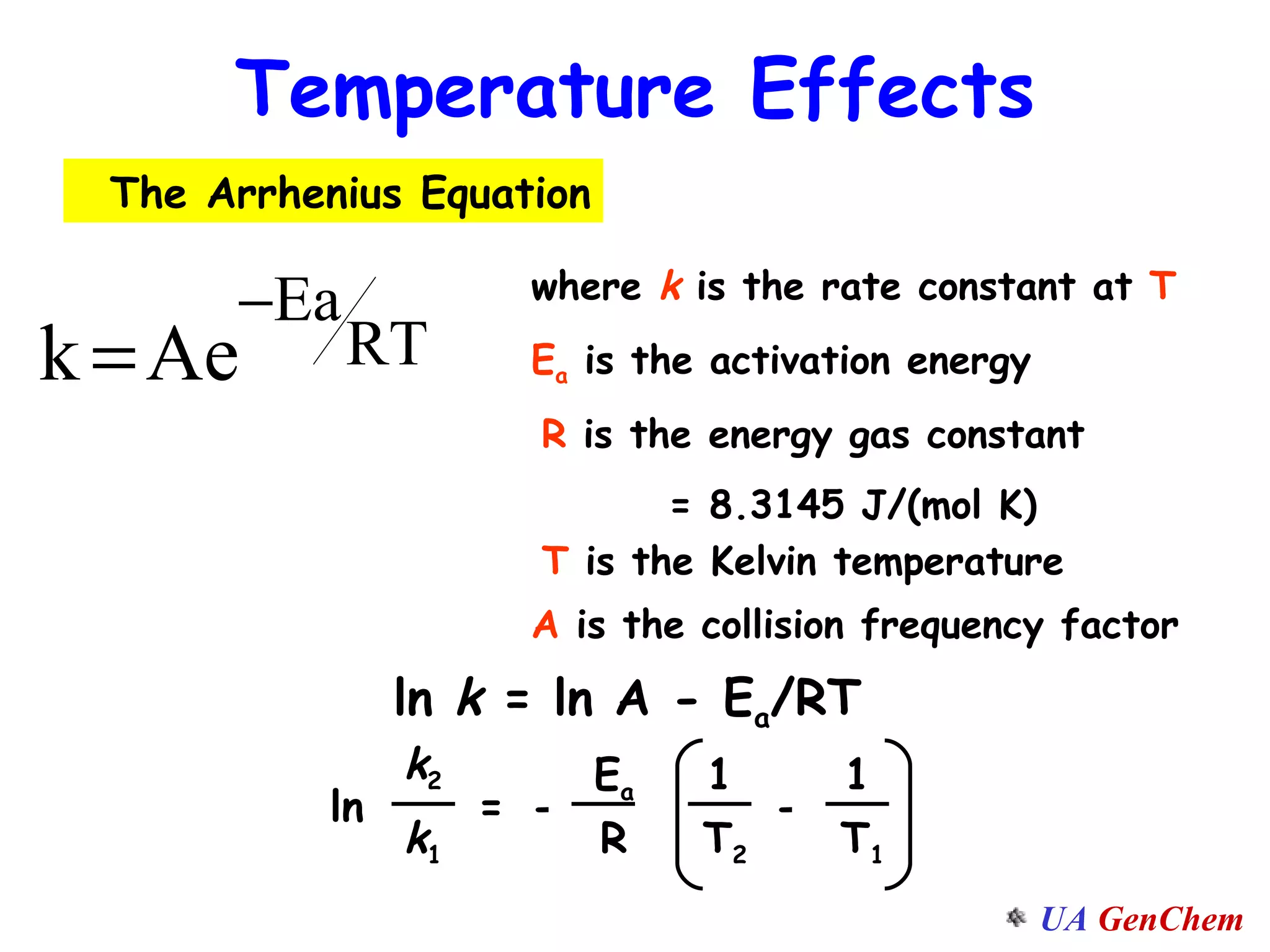
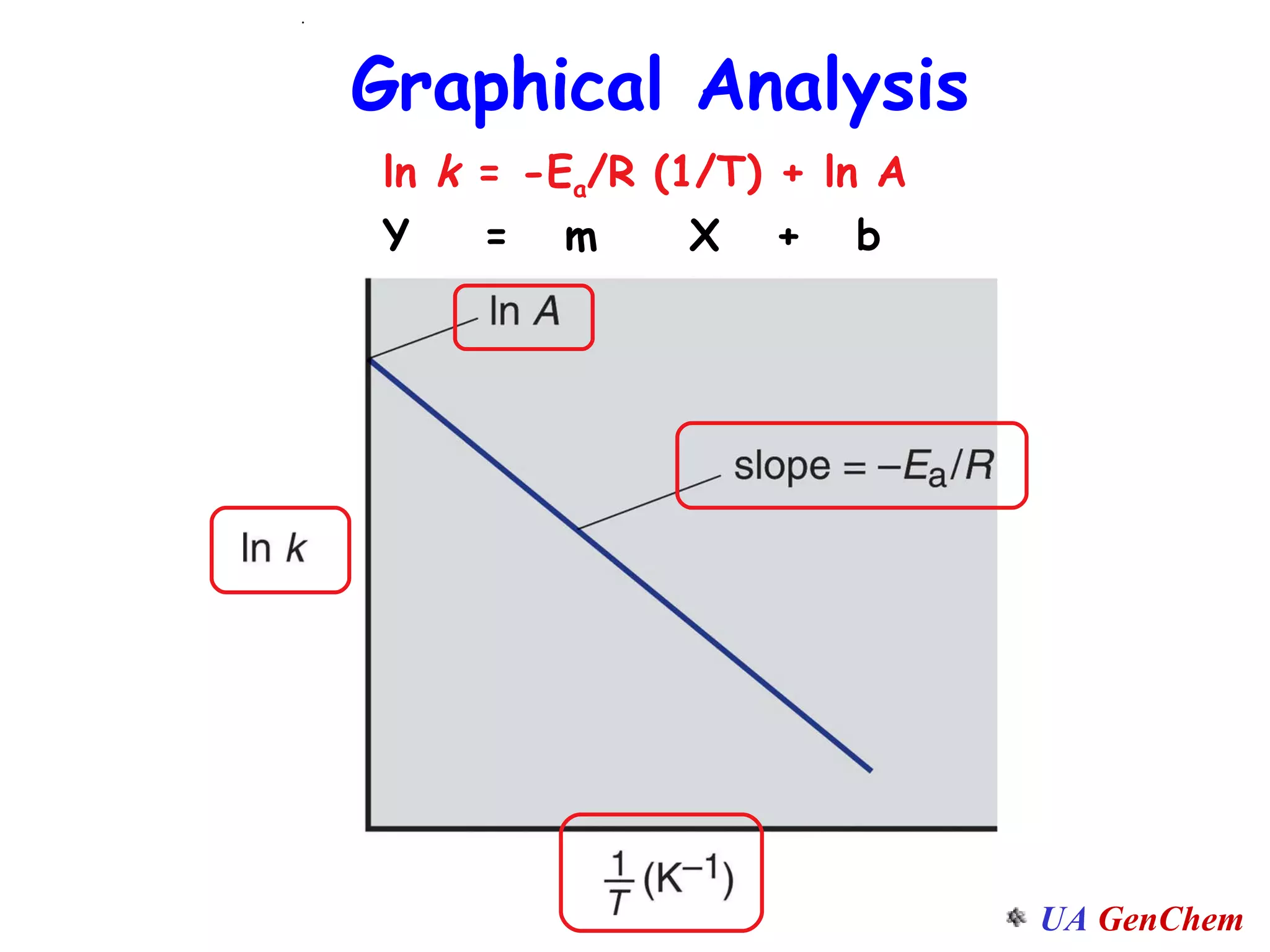
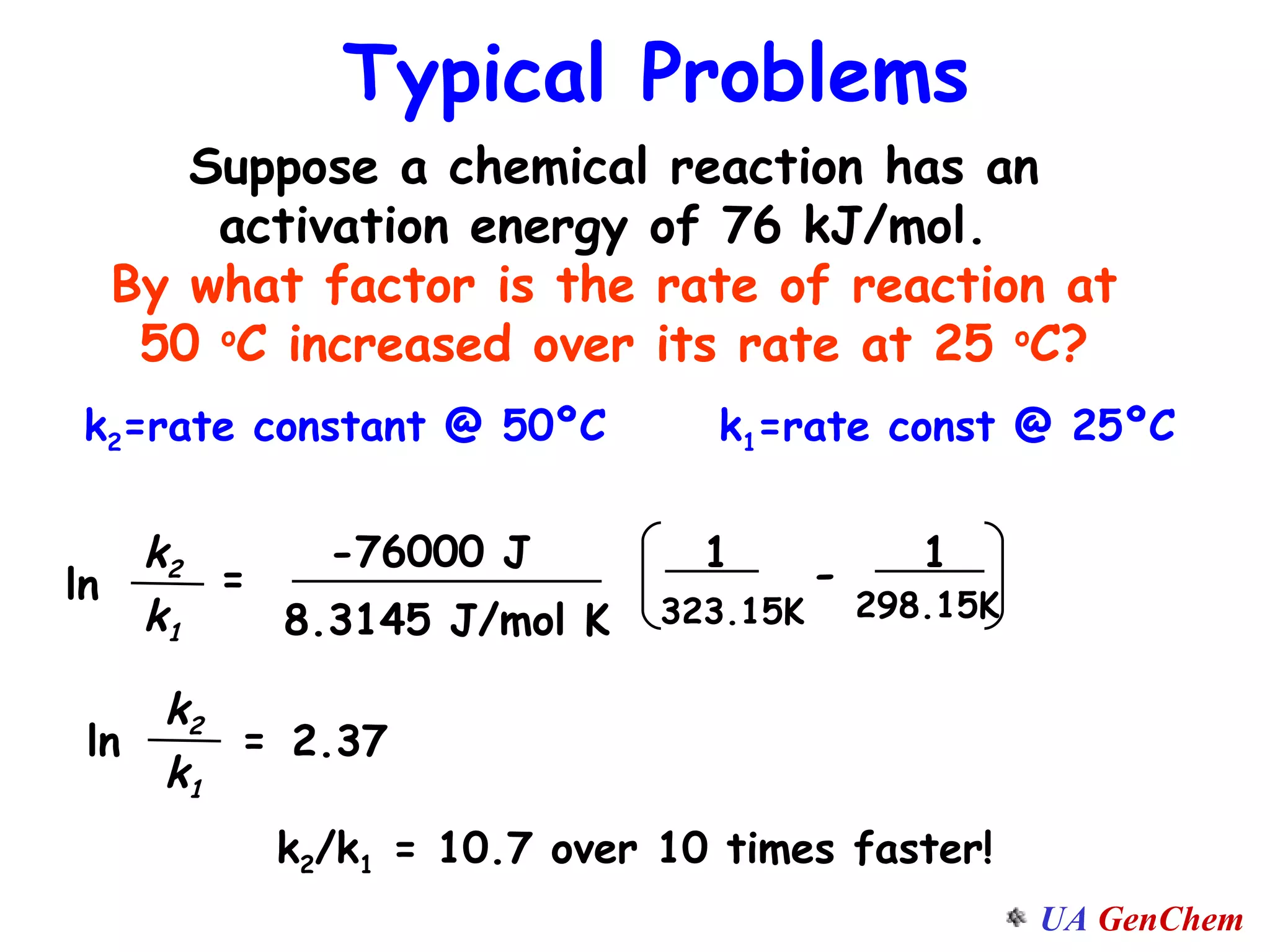
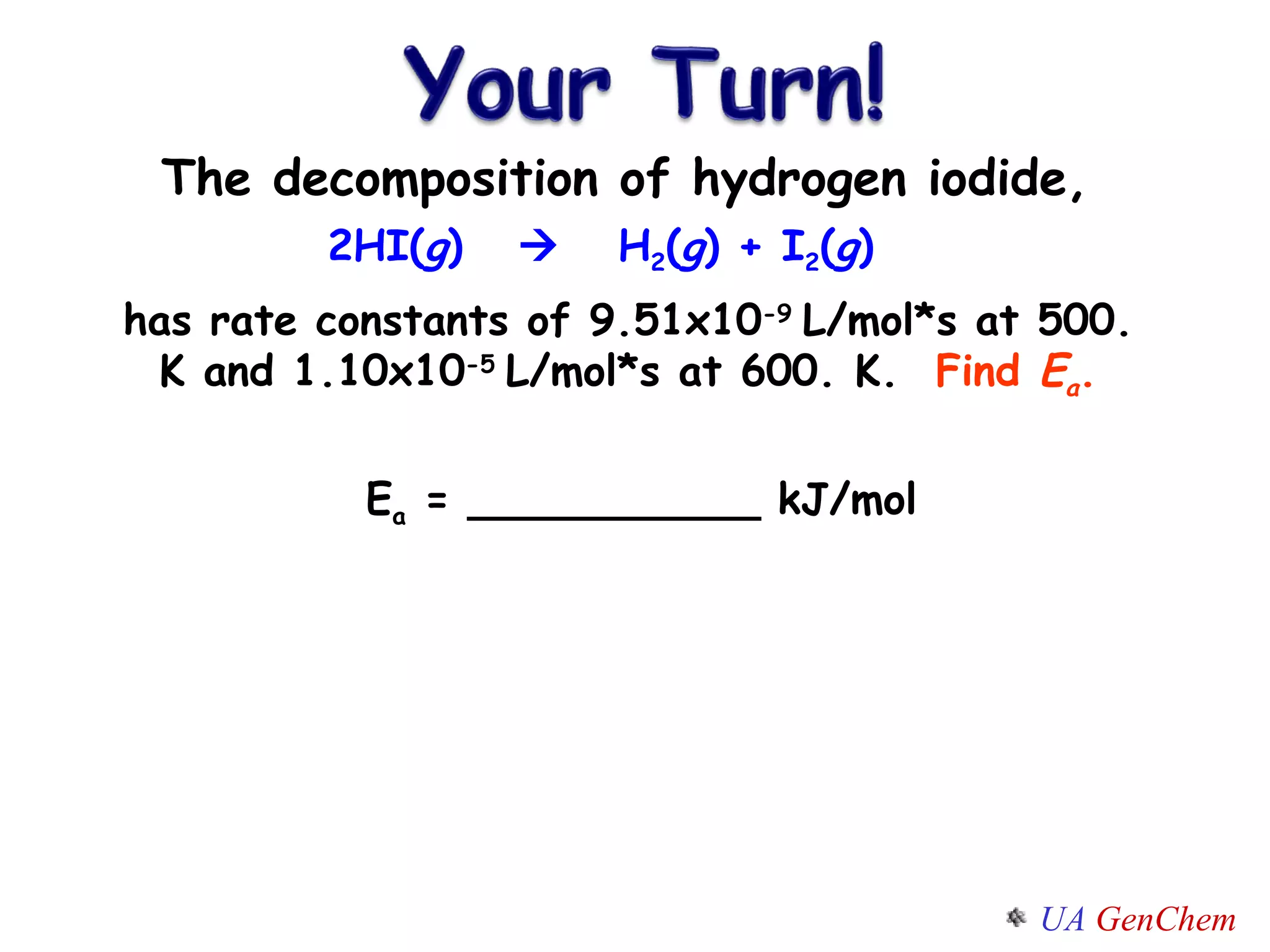
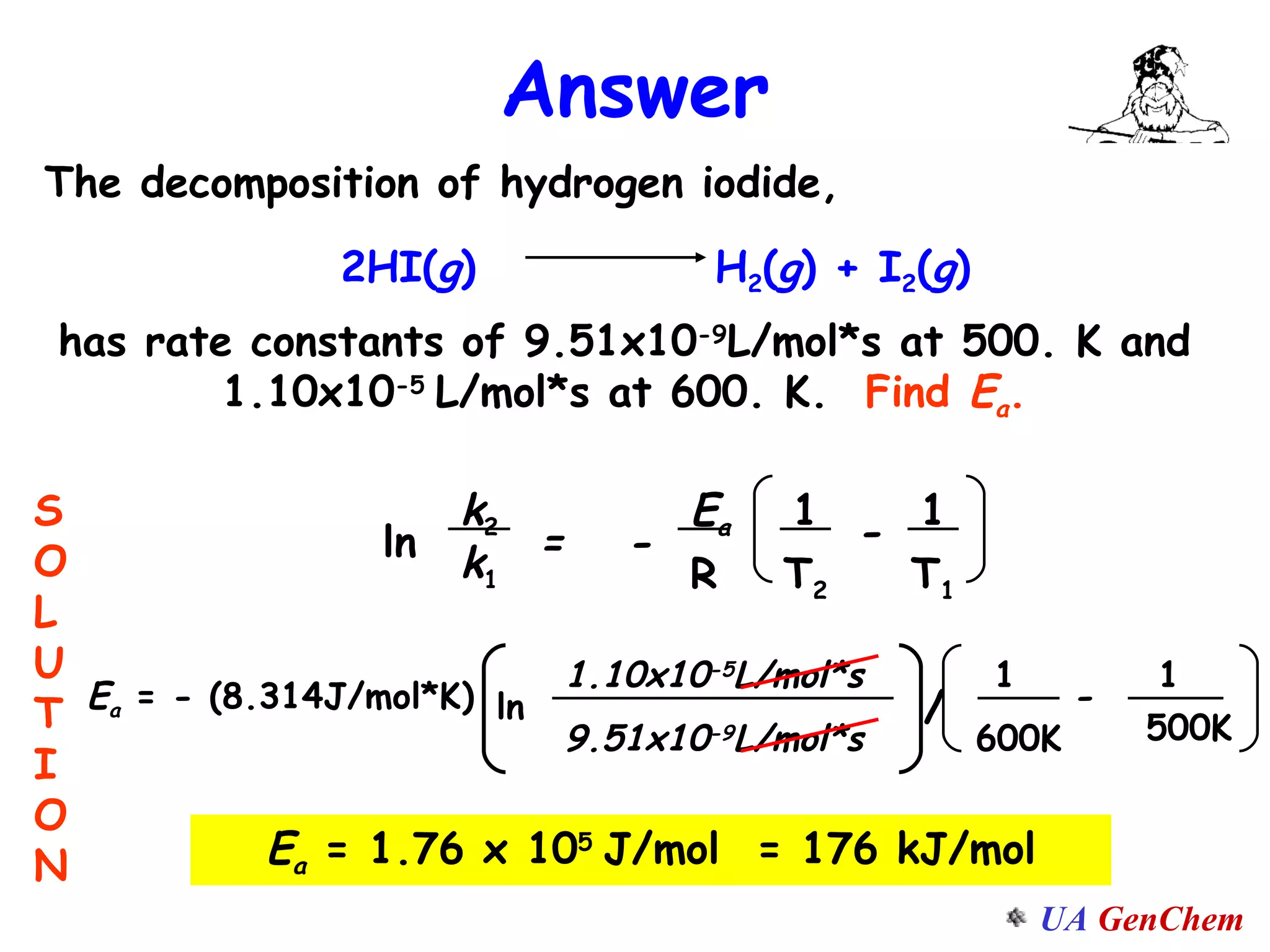
This document discusses the effects of temperature on reaction rates and provides an explanation using collision theory and activation energy. It introduces the Arrhenius equation and shows how to use it to determine activation energy from rate constants measured at different temperatures. Catalysts are discussed as lowering the activation energy of reactions without being consumed. Enzymes are described as biological catalysts that regulate metabolic reaction speeds. An example problem determines activation energy for a temperature-dependent firefly flashing process using rate data.


![Series of plots of concentra-tion vs. time Initial rates Reaction orders Rate constant ( k ) and actual rate law Integrated rate law (half-life, t 1/2 ) Rate constant and reaction order Activation energy, E a Plots of concentration vs. time Overview Find k at varied T Determine slope of tangent at t 0 for each plot Compare initial rates when [A] changes and [B] is held constant and vice versa Substitute initial rates, orders, and concentrations into general rate law: rate = k [A] m [B] n Use direct, ln or inverse plot to find order Rearrange to linear form and graph Find k at varied T](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/d07abbrevarrheniusandcatalystsalg-110302112611-phpapp02/75/D07-abbrev-arrhenius-and-catalysts_alg-18-2048.jpg)