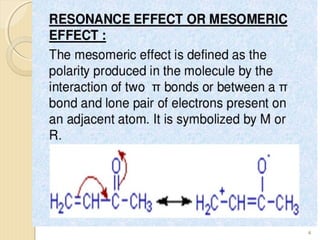
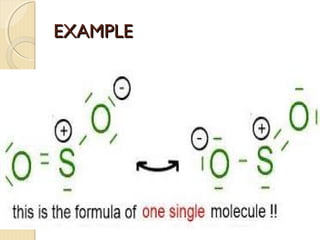
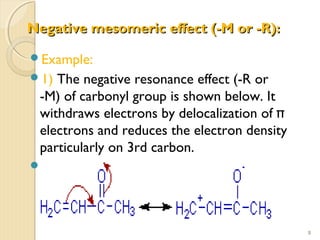
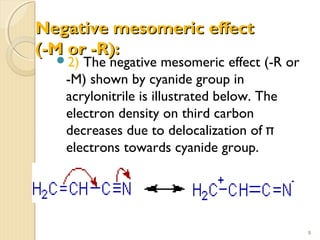
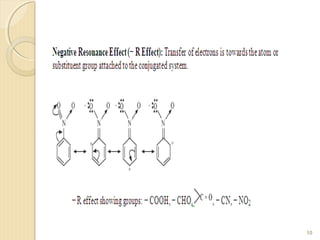
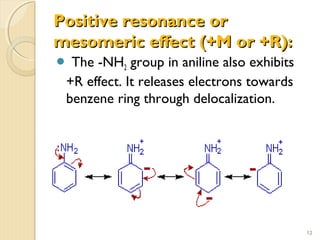
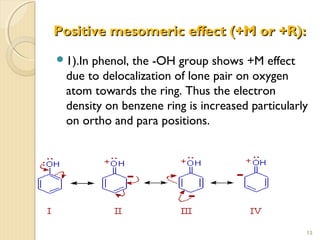
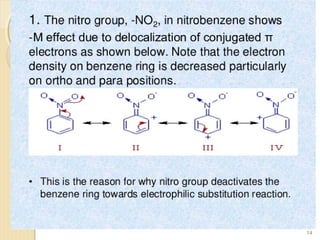
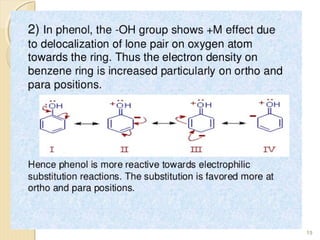
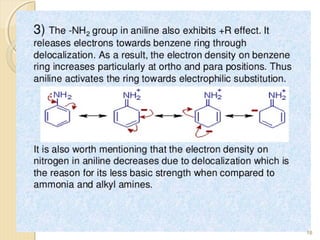
Mesomeric (or resonance) effect refers to the polarity produced in a molecule through delocalization of pi electrons between bonds or a bond and lone pair. This effect can increase or decrease electron density in different parts of a molecule. Negative mesomeric effects are shown by groups like nitro (-NO2) that withdraw electron density, while positive effects are shown by groups like hydroxyl (-OH) that release electron density. Understanding mesomeric effects helps explain a molecule's reactivity toward electrophiles and nucleophiles by determining where electron density is increased or decreased.