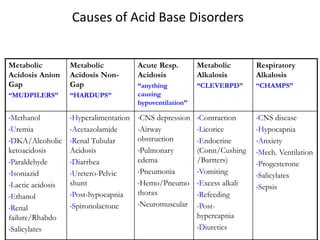
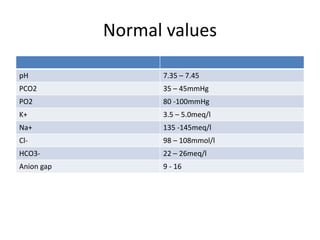
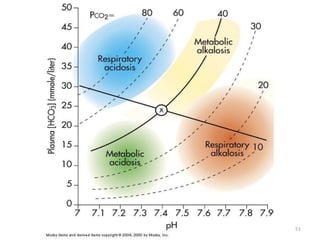
This document provides an overview of acid-base abnormalities and their management. It defines key terms, outlines regulatory mechanisms like buffers and respiration, and describes different acid-base disorders including their causes and treatments. An example case is presented of a patient with metabolic and respiratory acidosis on admission, resolving to metabolic acidosis and respiratory alkalosis after treatment. Overall it reviews acid-base physiology and the approach to diagnosing and managing common acid-base imbalances.



![Introduction
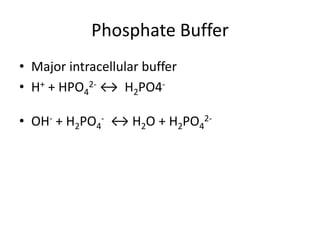
• Balance assessed in terms of bicarbonate-carbon
dioxide buffer system, Henderson-Hasselbalch
equation
– pH = 6.10 x log ([HCO3] / [0.03 x pCO2])
• Acid-base homeostasis critically affects tissue and
organ performance
• Both acidosis and alkalosis can have severe
and life threatening consequences
• It is the nature of the responsible condition
that determines the prognosis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbaseabnormalitiescausesandtreatment-170109125326/85/Acid-base-abnormalities-causes-and-treatment-4-320.jpg)


![Definitions
• At equilibrium, the rate of dissociation of an
acid , and the rate of association of H+ and A-
to form HA, are equal. the acid dissociation
constant, (Ka), is
• Ka = [H+]x[A-]
[HA]
pKa = -log10Ka (logarithmic expression of Ka)
• The higher Ka the more an acid dissociates
and the stronger the acid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbaseabnormalitiescausesandtreatment-170109125326/85/Acid-base-abnormalities-causes-and-treatment-7-320.jpg)
![Definitions
• pH is a logarithmic measure of hydrogen ion
concentration.
pH= -log10 [H+]
• pH is inversely proportional to [H+] . Each
whole number on the pH scale represents a
10fold (logarithmic) change in acidity.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbaseabnormalitiescausesandtreatment-170109125326/85/Acid-base-abnormalities-causes-and-treatment-8-320.jpg)
![Definitions
• The pH of a solution is determined by the pKa
of the acid and the ratio of the concentration
of the conjugate base to acid.
pH= pKa + log [A-]
[HA]
(Henderson-Hasselbalch equation)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbaseabnormalitiescausesandtreatment-170109125326/85/Acid-base-abnormalities-causes-and-treatment-9-320.jpg)


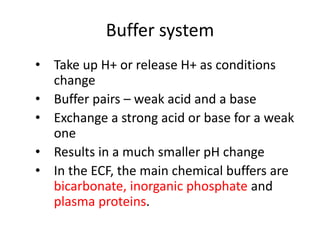



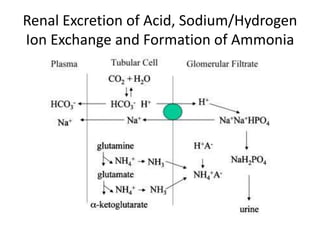
![Respiratory Mechanisms
• Arterial PCO2 stimulates chemorecptors in the
medulla oblongata
• An elevated arterial blood PCO2 is a stimulus
to increase ventilation leading to increased
expiration of CO2 hence increase blood pH
• Conversely, a drop in blood PCO2 inhibits
ventilation; the consequent rise in blood
[H2CO3] reduces the alkaline shift in blood pH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbaseabnormalitiescausesandtreatment-170109125326/85/Acid-base-abnormalities-causes-and-treatment-17-320.jpg)


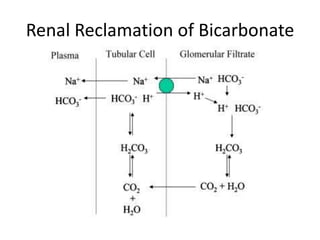

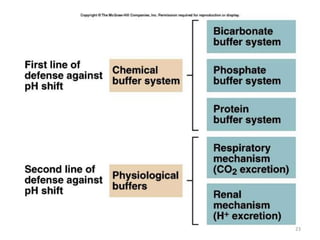



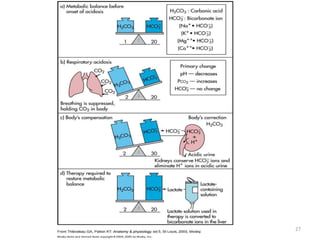



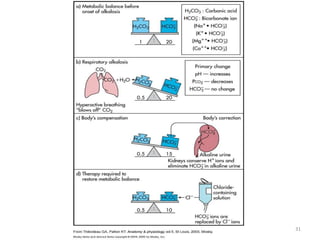
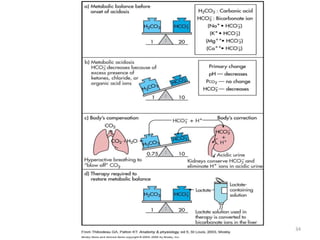
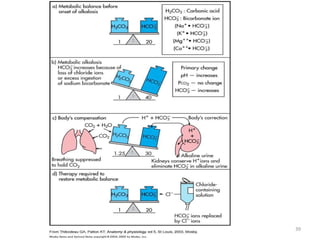
![Metabolic Acidosis
• Hallmark is [HCO3
-]
• Acid production net acid intake
above net renal excretion
(ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, ammonium chloride
loading)
• failure of renal net excretion
(chronic renal failure, renal tubular acidosis)
• Bicarbonate loss via the gastroinestinal tract
(diarrhea, gastrointestinal fistula)
• Nonbicarbonate solutions added to ECF
(dilutional acidosis)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbaseabnormalitiescausesandtreatment-170109125326/85/Acid-base-abnormalities-causes-and-treatment-32-320.jpg)





![Anion Gap
• The anion gap is the difference in the
measured cations (positively charged ions)
and the measured anions (negatively charged
ions) in serum or urine.
• It is calculated as :
([Na+] + [K+]) − ([Cl−] + [HCO3−])
• Anion gap is calculated when attempting to
identify the cause of metabolic acidosis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbaseabnormalitiescausesandtreatment-170109125326/85/Acid-base-abnormalities-causes-and-treatment-40-320.jpg)