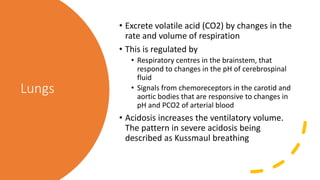
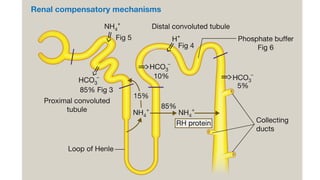
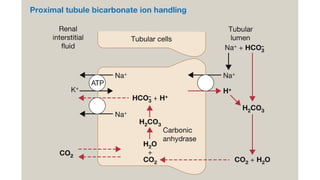
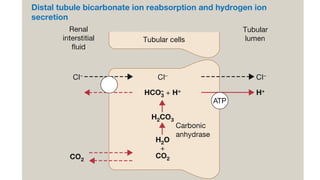
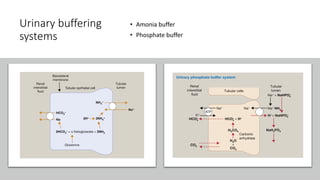
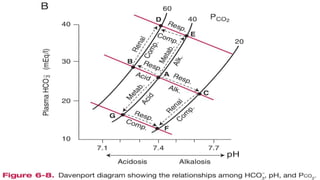
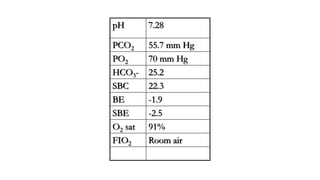
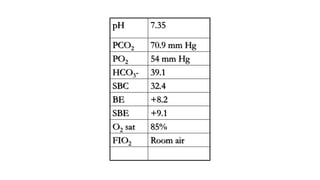
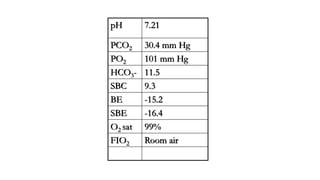
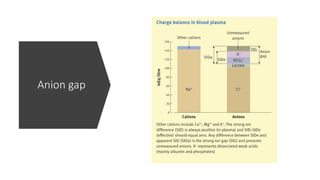
The document discusses the importance of maintaining acid-base balance in the body, highlighting the roles of pH, buffers, and the mechanisms for excretion of acids by the lungs and kidneys. It outlines various sources and types of acids from metabolism and food, as well as the physiological effects of acidaemia and disturbances in acid-base balance, such as respiratory and metabolic acidosis. The document also describes the compensation mechanisms the body employs in response to these disturbances, including the roles of bicarbonate and other buffers.


![pH
pH is the negative logarithm to
the base 10 of the hydrogen
ion concentration
pH= -log [H+]
Normal PH of arterial blood
gas sample= 7.35-7.45](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbasebalance-220729072718-3f8cd29e/85/Acid-base-balance-pptx-3-320.jpg)