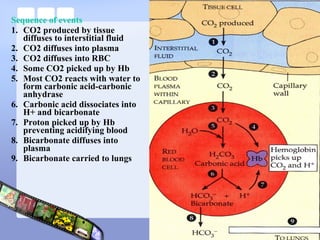
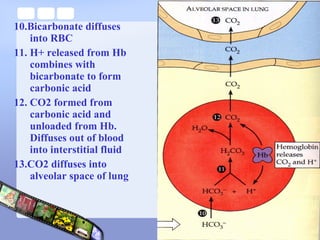
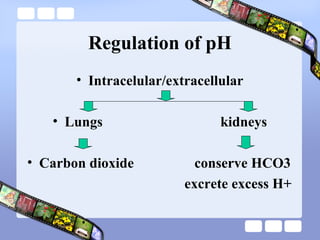
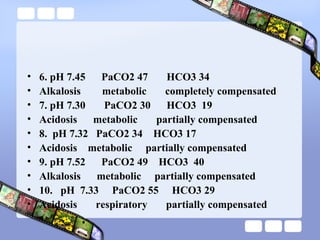
This document provides an overview of acid-base imbalances. It defines acids and bases and describes the body's buffer systems that help regulate pH, including the roles of the lungs, kidneys, and hemoglobin. Causes of metabolic acidosis and alkalosis as well as respiratory acidosis and alkalosis are outlined. The document explains how to interpret arterial blood gas results based on pH, pCO2, and bicarbonate levels to determine the acid-base imbalance and extent of compensation.