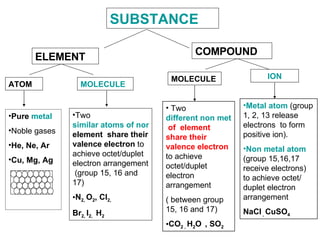
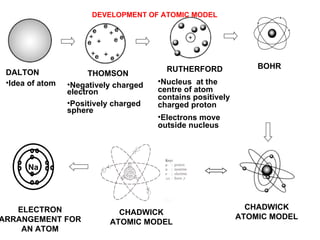
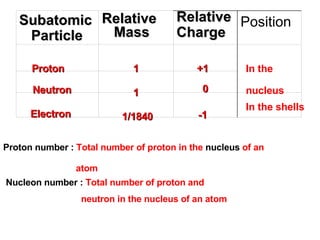
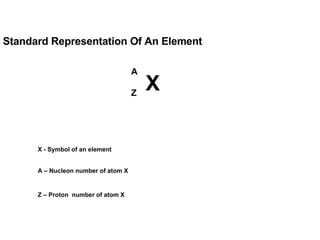
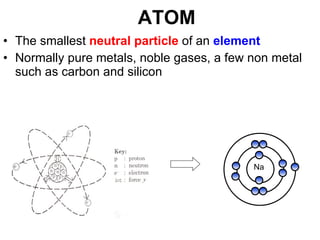
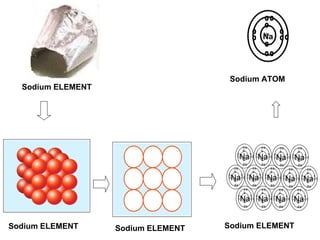
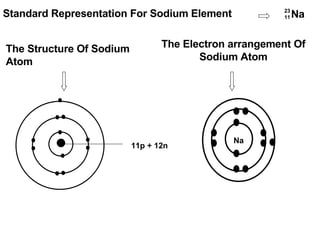
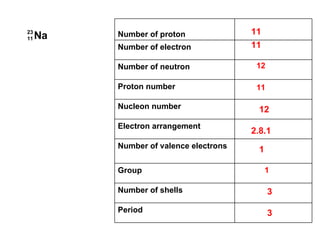
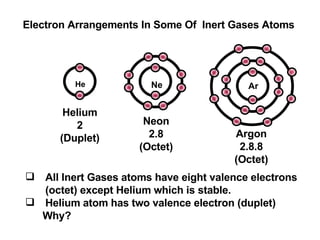
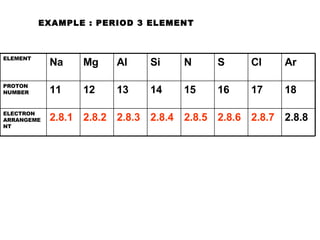
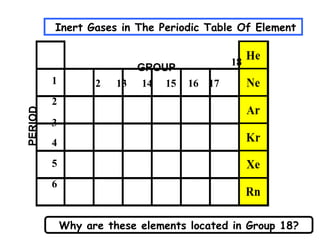
The document discusses the key concepts of elements, compounds, atoms, and molecules. It defines elements as pure substances that cannot be broken down further, and compounds as substances made of two or more elements bonded chemically. Atoms are the smallest particles of an element, with a nucleus containing protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons. Molecules are formed when two or more atoms of elements share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.