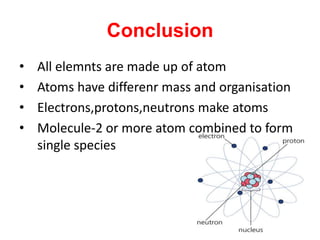
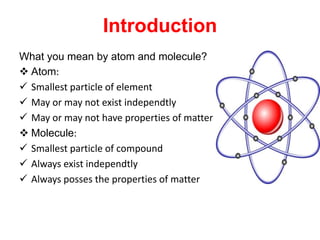
This document defines key concepts in chemistry including atoms, molecules, and laws of chemical combination. It states that atoms are the smallest particle of an element and may exist independently or combined with other atoms. Molecules are the smallest particle of a compound made of two or more atom types bonded together. The document also summarizes the laws of conservation of mass and constant proportion, and defines atomic and molecular mass, ions, and the mole concept in chemistry.


![MOLECULE
• Molecular mass: mass of the molecules of a chemical compound.
Expressed in amu
Determined by adding the individual atomic mass
Eg:molecular mass of NH3 =atomic mass of N + 3 * atomic mass of H
= 14+[3*1]
=17 amu
• Gram molecular mass: molecular mass expressed in grams
Numericlly equal to molecular mass in amu
Eg: I g molecule of H20 =18g](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullppt-141010052935-conversion-gate01/85/atoms-and-molcules-9-320.jpg)
![MOLE CONCEPT
• 1 Mole = 6.023 * 1023 number of particles
• 1 mole of any substance contain avagrado
number[6.023*1023] of particles which have weight
equvalent to atomic mass
• Number of moles = total mass
molecular mass
N= W
M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullppt-141010052935-conversion-gate01/85/atoms-and-molcules-10-320.jpg)