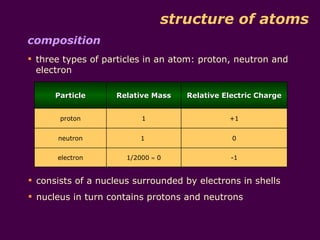
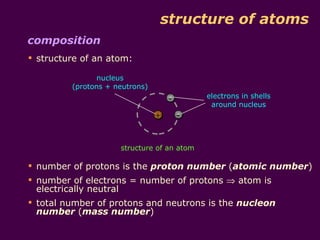
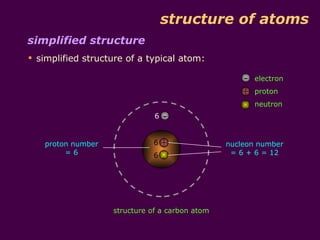
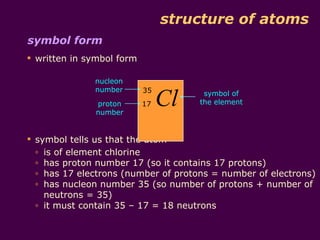
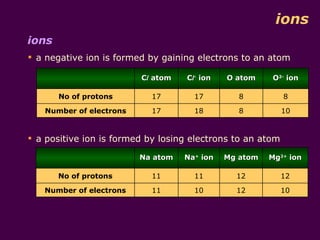
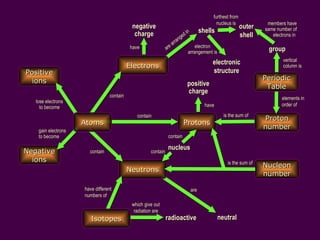
1) Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus, while electrons orbit the nucleus in shells.
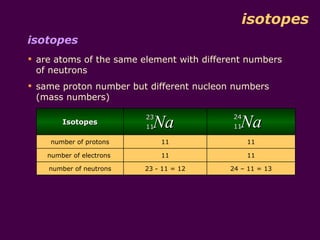
2) Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons, giving them different mass numbers but the same chemical properties.
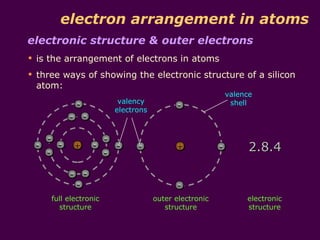
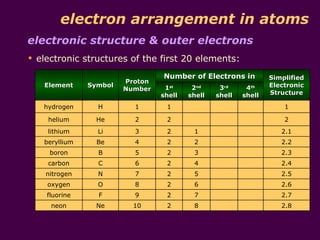
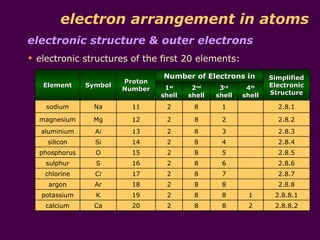
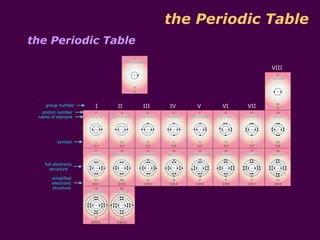
3) Electrons fill the lowest available shell around the nucleus. The arrangement of electrons is shown in an element's electronic structure.