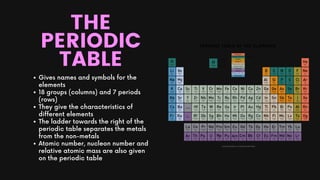
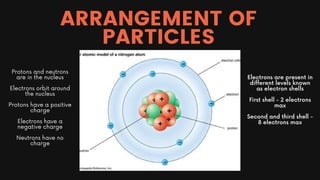
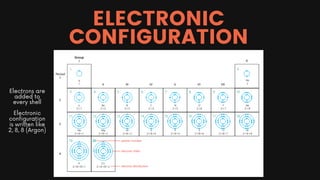
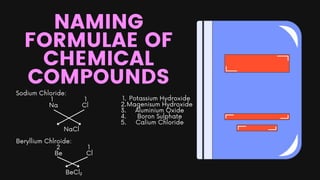
Chapter 2 of the chemistry document covers the concepts of atoms, elements, compounds, and the periodic table. Atoms are the fundamental particles of matter, while elements consist of only one type of atom; compounds are formed from two or more different elements. The periodic table organizes elements by atomic number and provides information on their characteristics, including atomic and nucleon numbers, electron configuration, and valency.