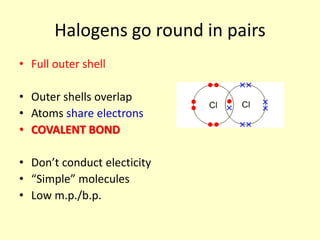
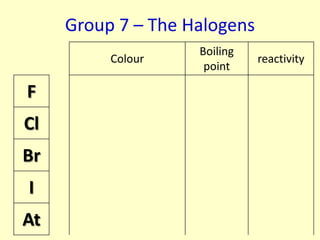
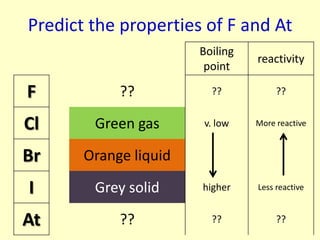
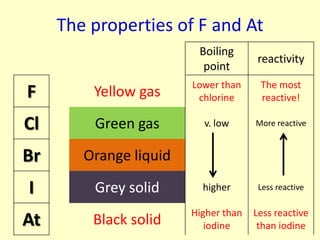
The document compares the properties of the halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, At). It shows that fluorine has the lowest boiling point and is the most reactive, while iodine has the highest boiling point and is the least reactive. Fluorine forms a yellow gas, chlorine forms a green gas, bromine forms an orange liquid, and iodine forms a grey solid. Astatine is predicted to have a higher boiling point than iodine and be less reactive. Displacement reactions are discussed, where more reactive halogens can displace less reactive ones from their compounds.


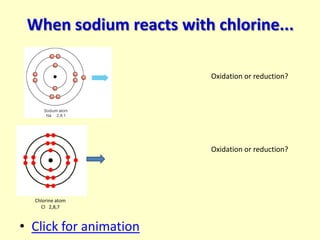
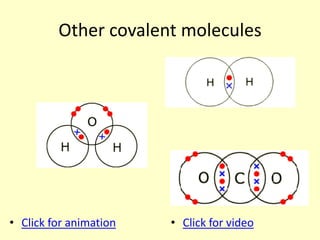
![Ionic bonding in NaCl
Na → Na+ + e-
Oxidation Is Loss
(OIL)
Cl + e- → Cl-
Reduction Is Gain
(RIG)
Chlorine atom Chloride ion
Cl 2,8,7 Cl - [2,8,8]-
• Click for animation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group7thehalogens-lesson-130407112349-phpapp02/85/Group-7-the-halogens-lesson-7-320.jpg)