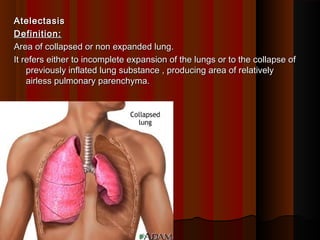
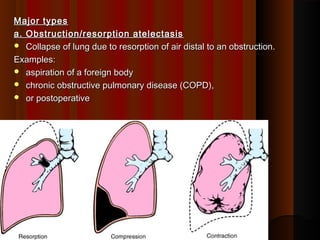
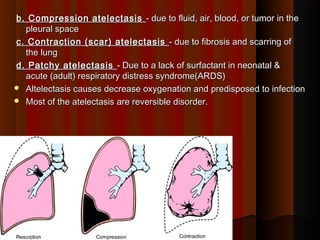
Atelectasis is defined as an area of collapsed or non-expanded lung. There are four major types of atelectasis: (1) obstruction/resorption atelectasis caused by obstruction distal to the lung, such as from aspiration or COPD; (2) compression atelectasis caused by fluid, air, blood or tumor in the pleural space; (3) contraction (scar) atelectasis caused by fibrosis and scarring of the lung; and (4) patchy atelectasis caused by a lack of surfactant as seen in neonates and ARDS patients. Atelectasis causes decreased oxygenation and an increased risk of infection, though most cases are reversible disorders.