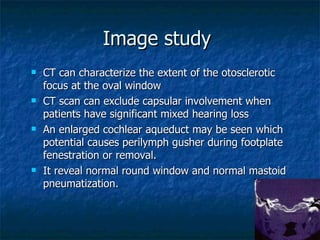
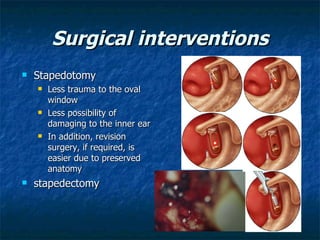
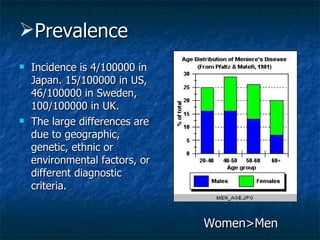
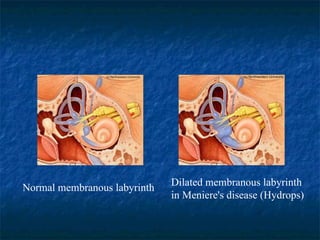
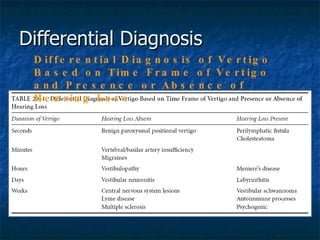
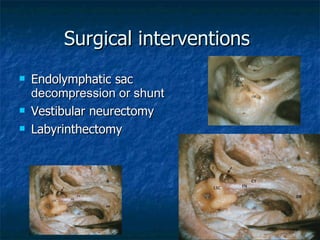
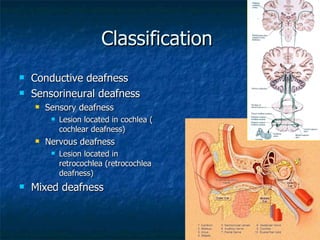
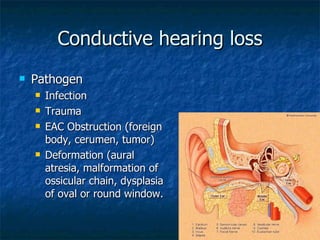
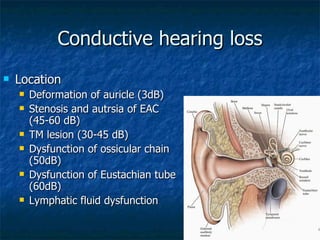
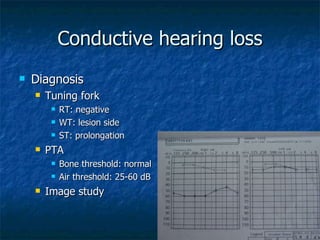
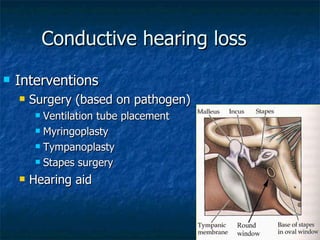
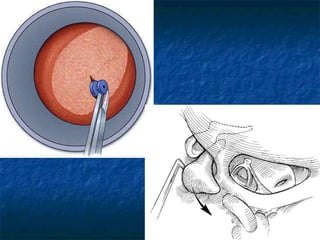
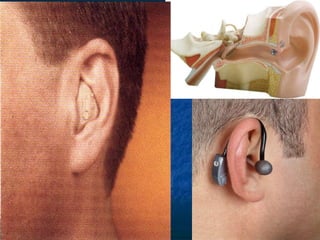
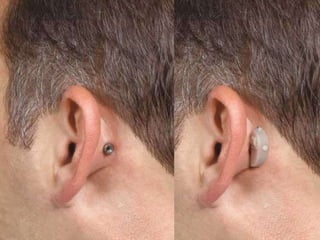
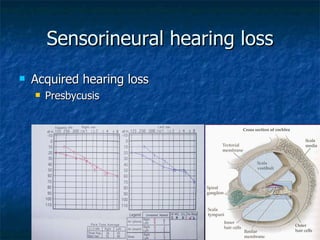
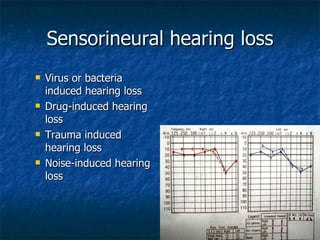
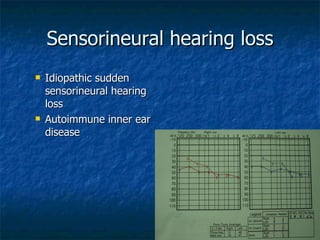
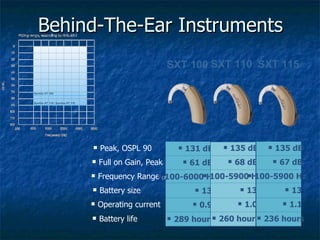
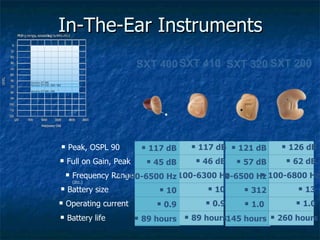
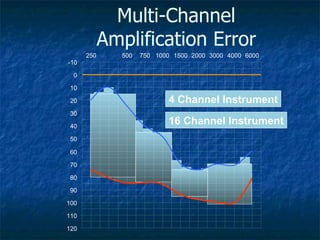
Otosclerosis is a metabolic bone disease that causes fixation of the ossicles, resulting in conductive or mixed hearing loss. It has a higher prevalence in Caucasians and affects women more commonly than men. The most common age of presentation is 15-45 years old. While the exact etiology is unknown, genetic and hormonal factors likely play a role. Surgical interventions like stapedotomy or stapedectomy can improve hearing for patients, while non-surgical options include hearing aids or medical treatments like fluoride. Differential diagnoses include other causes of conductive hearing loss.