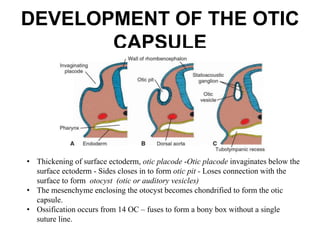
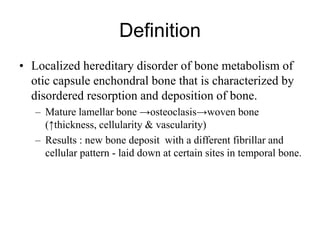
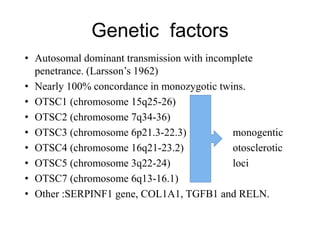
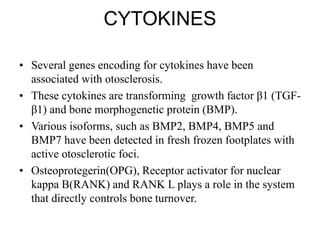
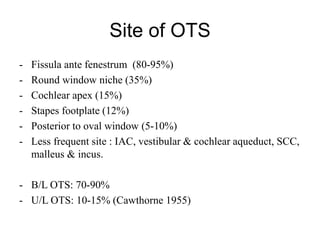
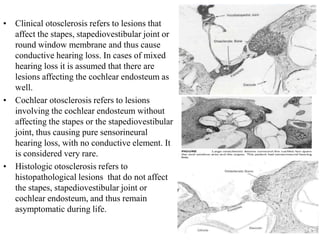
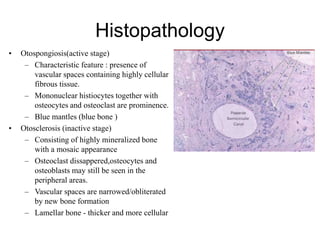
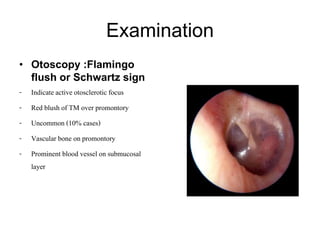
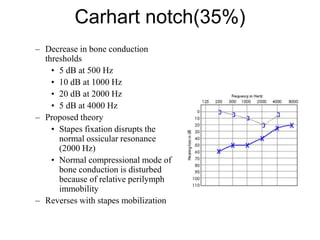
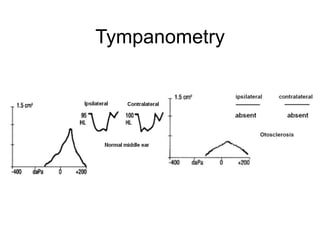
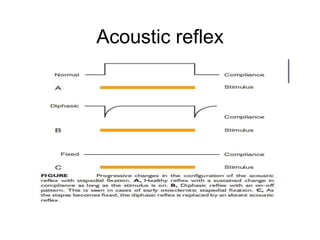
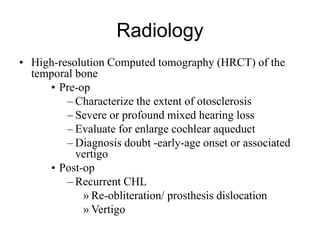
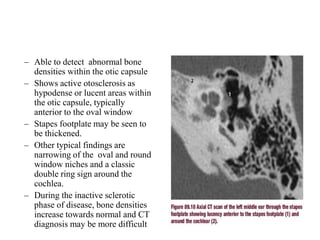
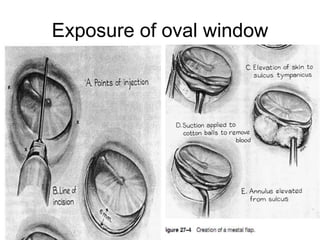
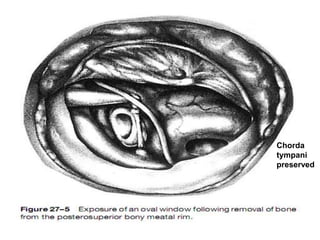
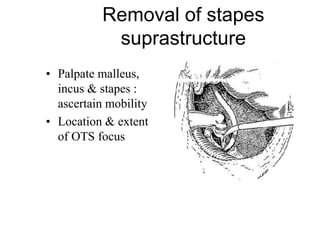
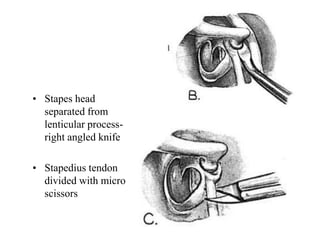
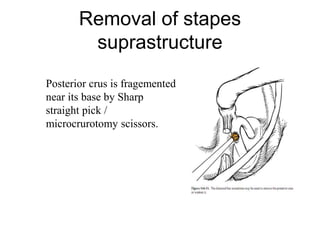
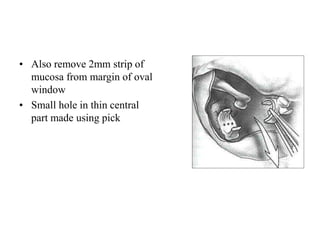
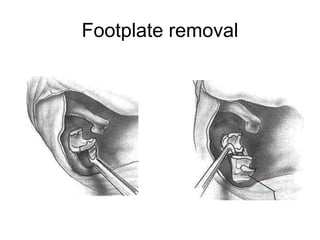
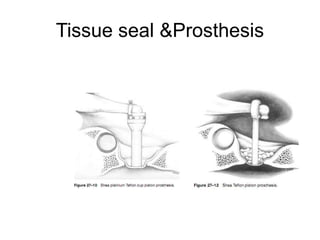
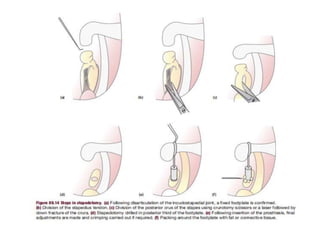
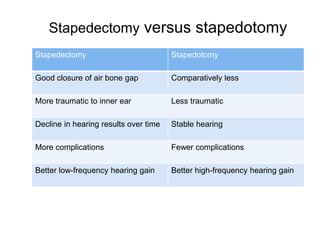
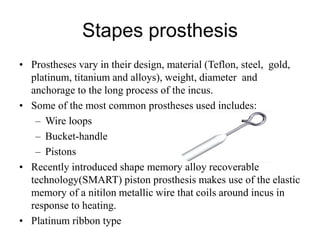
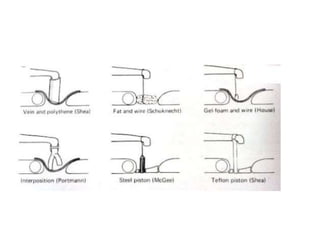
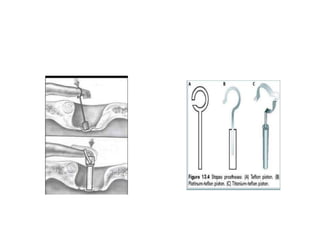
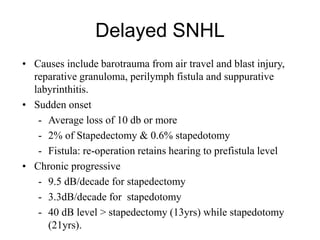
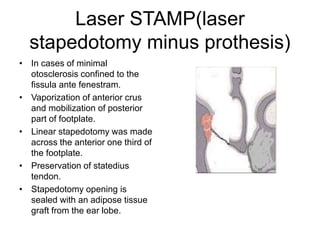
The document discusses otosclerosis, a hereditary disorder affecting the bone of the inner ear. It causes thickening and fusion of the bones of the middle ear, most commonly the stapes footplate. This leads to conductive hearing loss or mixed hearing loss. Treatment options include medical management with sodium fluoride or bisphosphonates, hearing aids, and surgery to mobilize or replace the stapes bone. Stapedectomy is the most common surgical procedure, where the stapes bone is removed and replaced with a prosthesis to restore hearing. Precise techniques and graft materials are discussed. Risks include dizziness, facial nerve injury and sensorineural hearing loss.