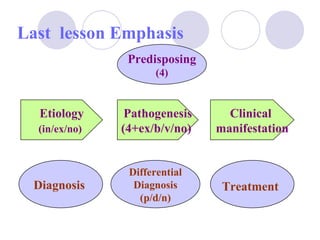
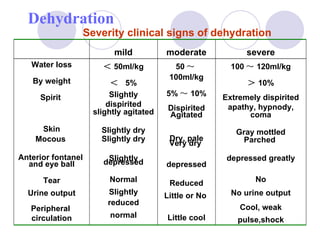
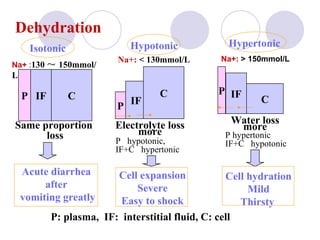
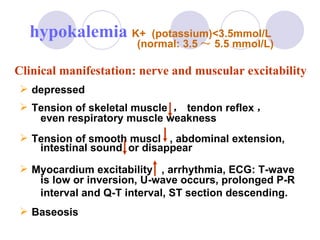
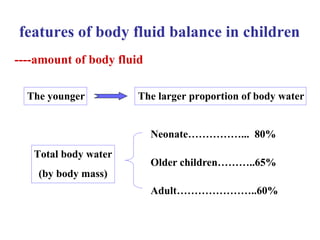
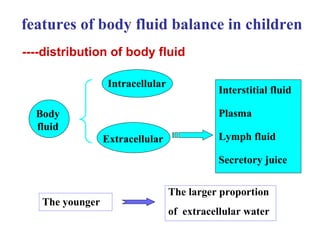
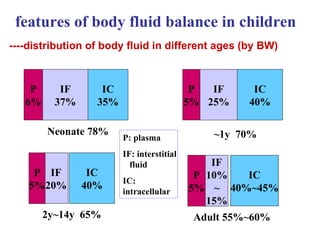
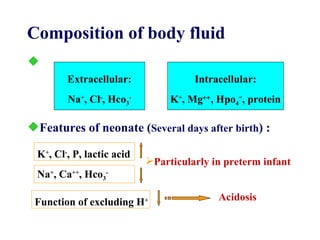
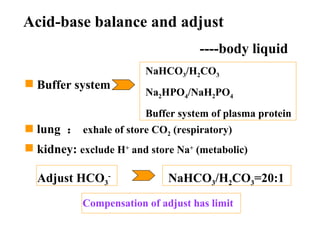
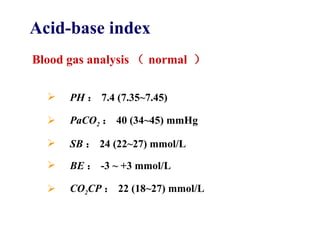
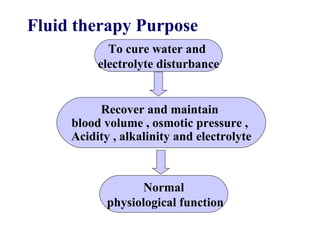
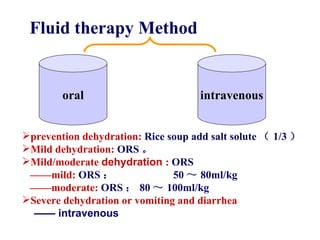
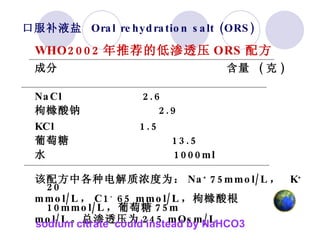
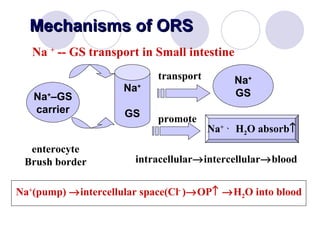
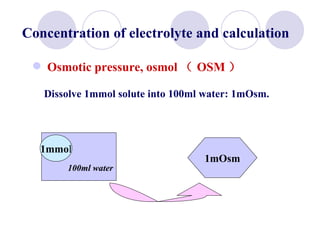
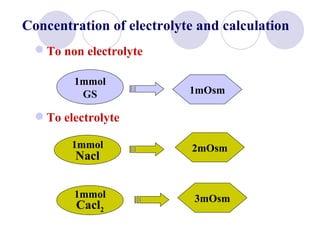
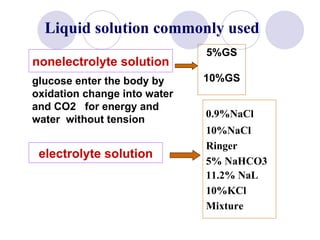
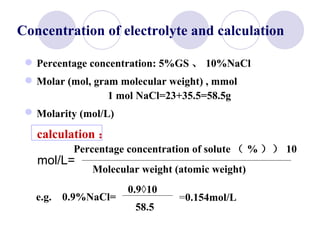
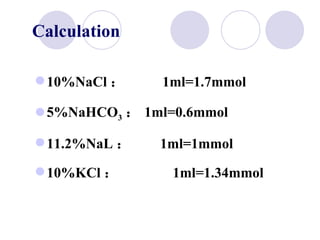
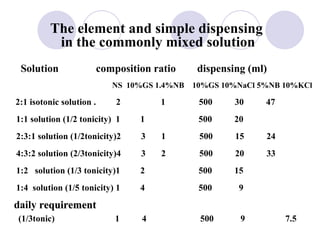
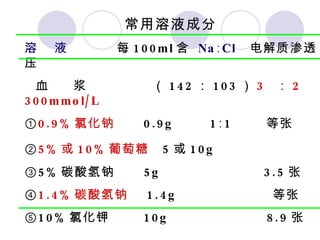
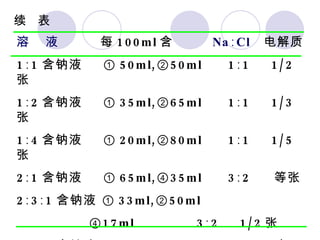
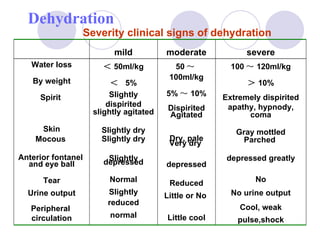
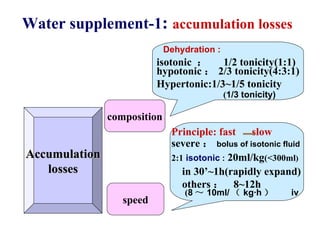
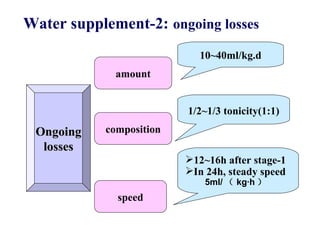
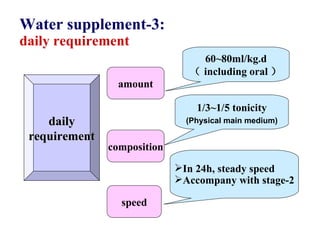
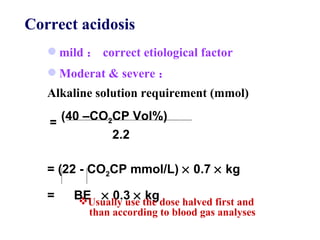
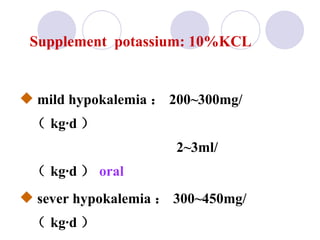
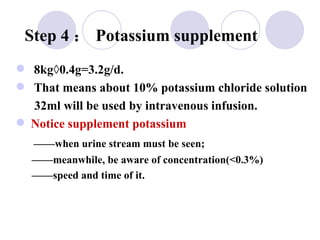
This document discusses fluid therapy for acute diarrhea and dehydration in children. It describes the assessment of dehydration severity based on clinical signs. For mild to moderate dehydration, oral rehydration solution (ORS) is recommended. For severe dehydration, intravenous fluids are needed. The document provides formulas for ORS and intravenous fluids and guidelines for calculating fluid volumes based on the degree of dehydration.