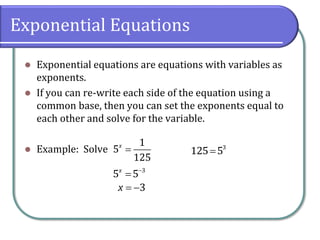
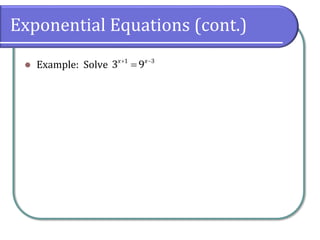
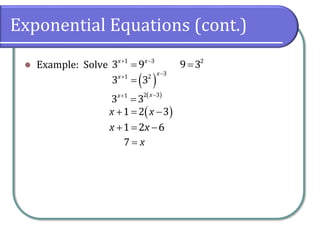
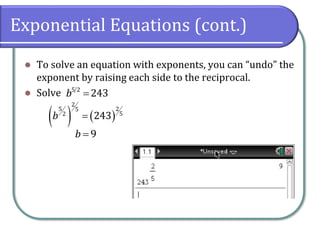
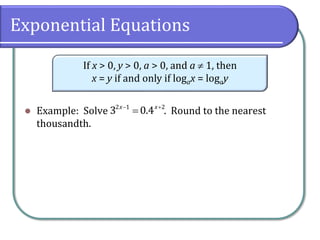
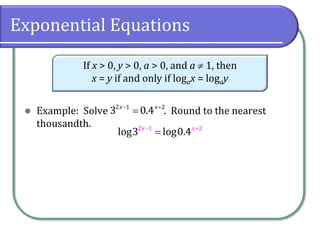
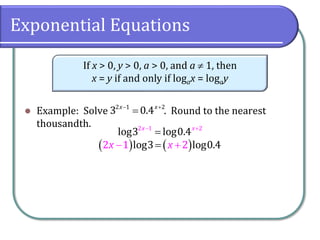
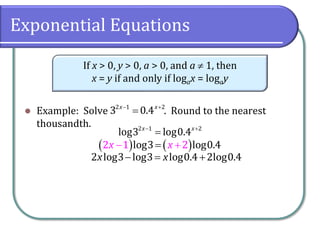
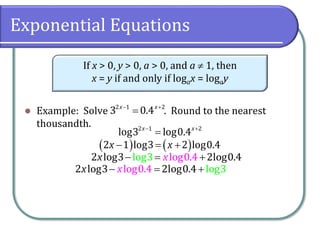
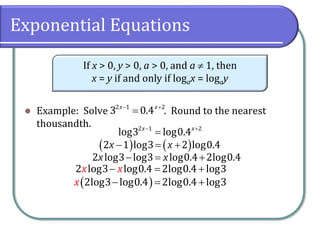
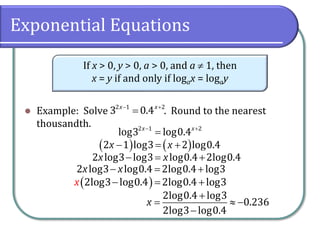
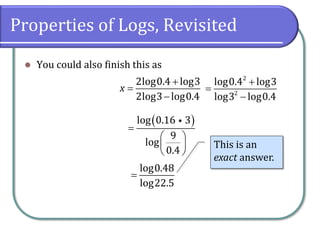
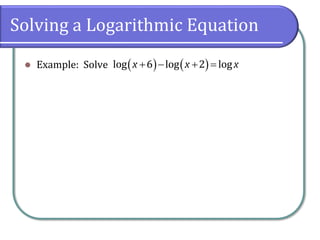
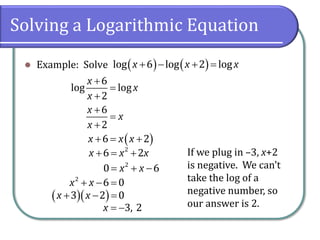
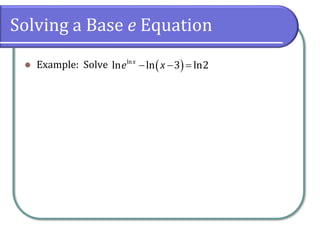
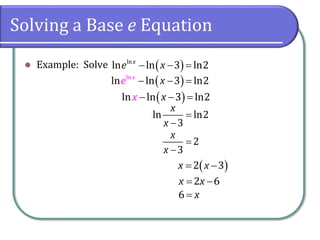
This document covers the concepts and objectives of solving exponential and logarithmic equations, including using like bases, logarithms, and properties of logarithms. It provides examples of solving these equations using various methods, such as rewriting equations to a common base, using logarithmic properties, and applied problem-solving. Additionally, it outlines classwork assignments related to the material.