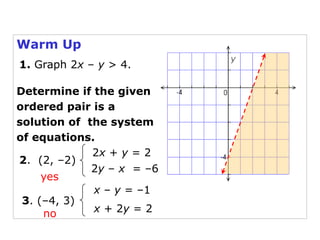
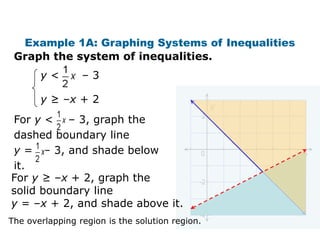
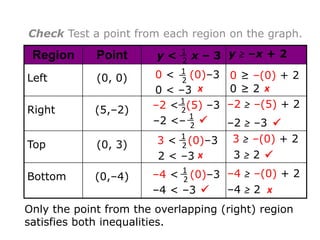
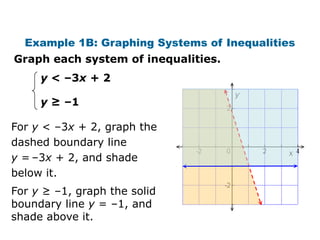
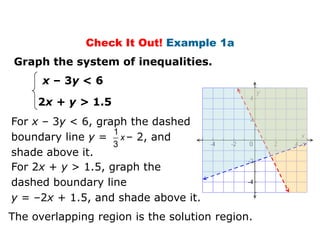
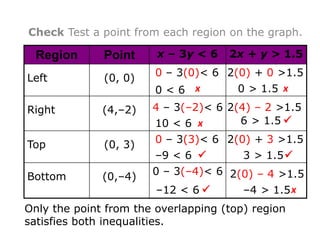
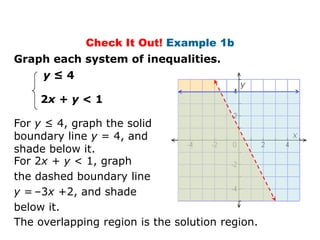
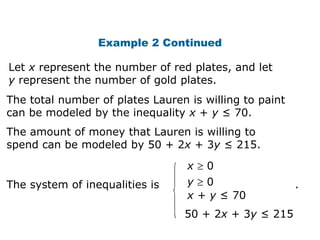
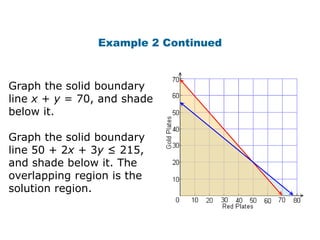
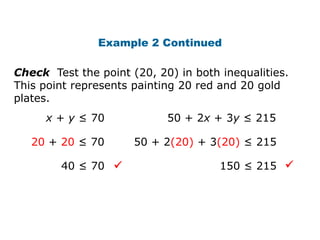
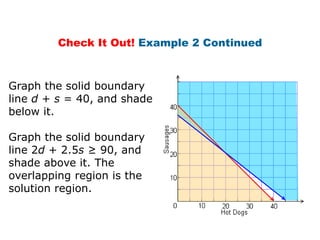
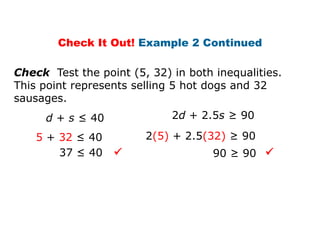
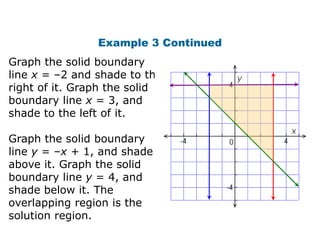
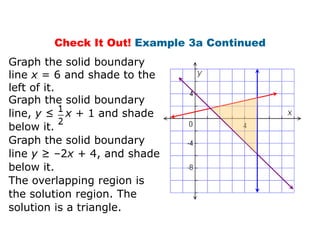
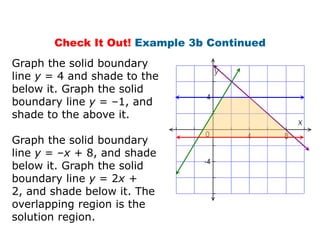
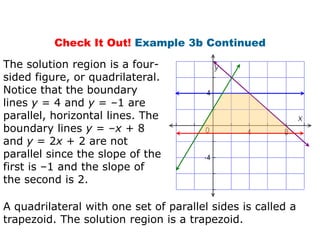
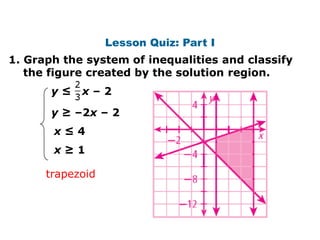
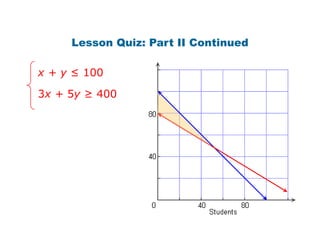
Here is the system of inequalities for the cross-country team problem:
Let x = number of water bottles sold to students
Let y = number of water bottles sold to others
x + y ≤ 100 (they have 100 bottles total)
3x + 5y ≥ 400 (they need at least $400)
Graph the regions defined by these inequalities and the overlapping region is the solution.