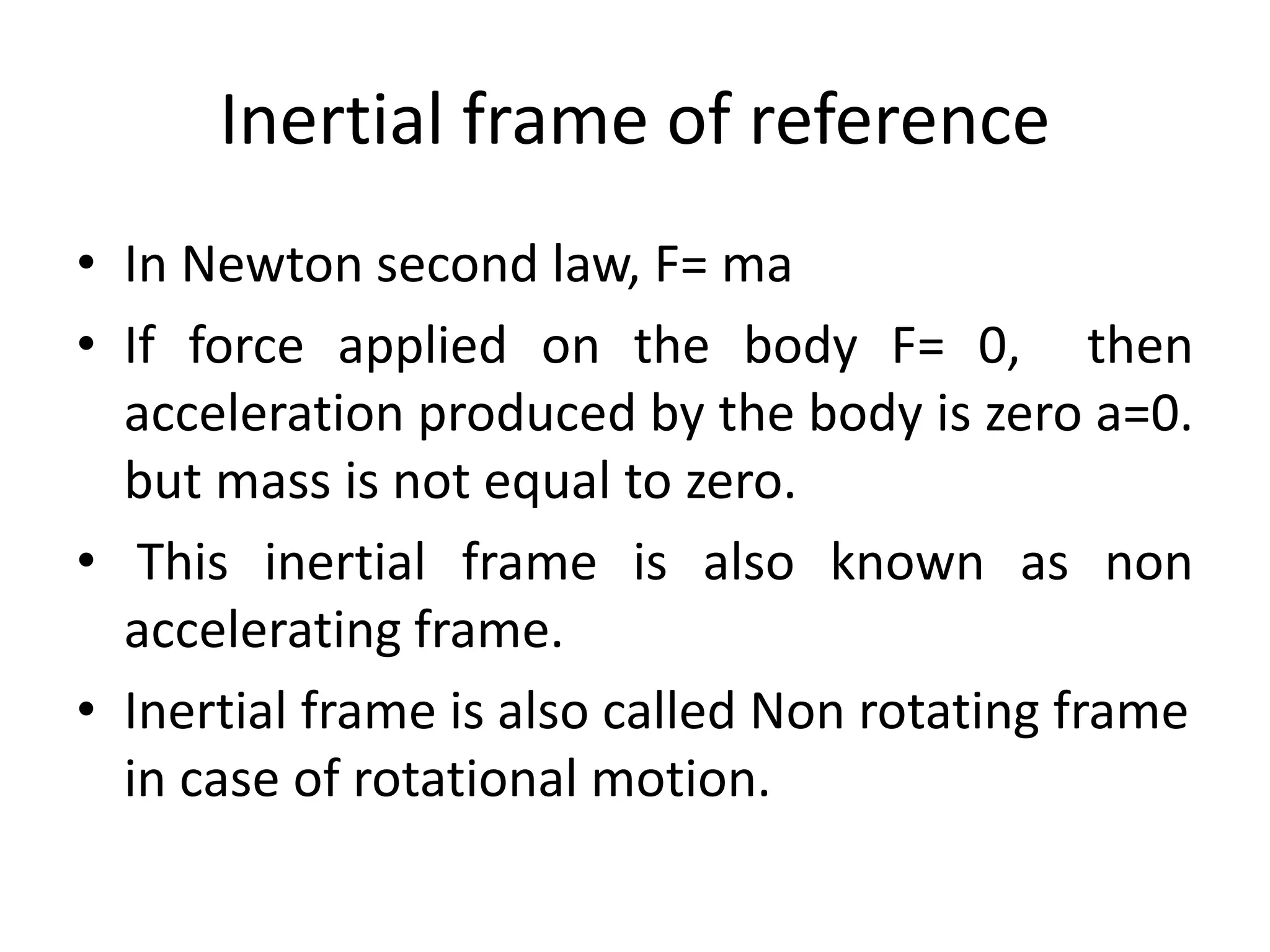
- There are two types of reference frames: inertial and non-inertial frames. Inertial frames obey Newton's laws of motion while non-inertial frames do not.
- The Earth is considered an inertial frame even though it rotates and revolves because the accelerations produced are small enough to be negligible.
- In non-inertial frames, pseudo or fictitious forces appear even when no real forces are acting on an object. These forces arise due to the acceleration of the non-inertial reference frame.