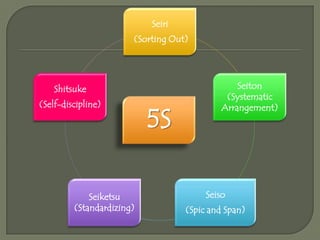
5S is a workplace organization method originating from Japan that involves sorting, systematic arrangement, sweeping, standardizing, and sustaining cleanliness and order. It was developed to improve efficiency and effectiveness in manufacturing. The method involves five Japanese words translated to English starting with "S": sort, systematize, sweep, standardize, and sustain. It aims to clearly identify necessary items, store them properly, maintain a clean work area, set clear standards, and ensure best practices are followed consistently.