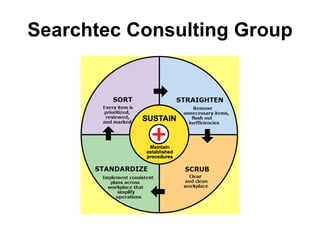
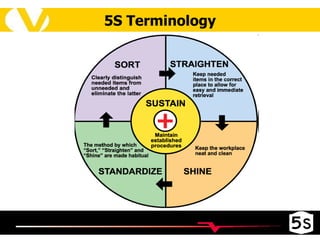
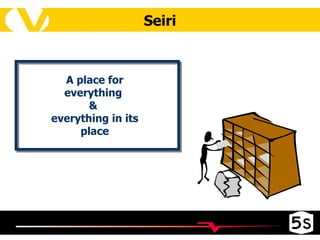
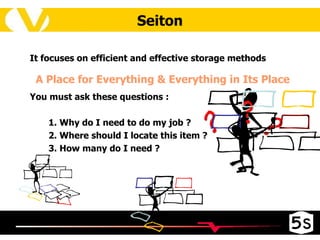
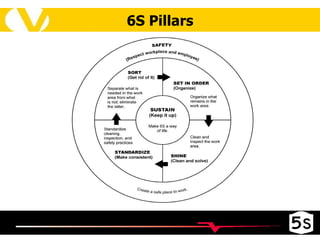
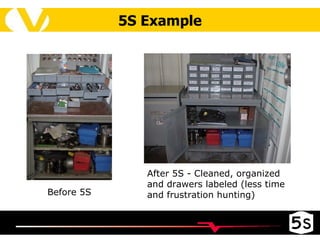
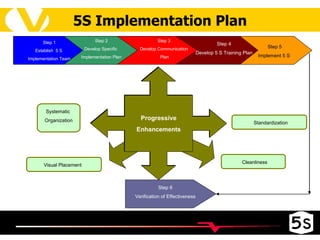
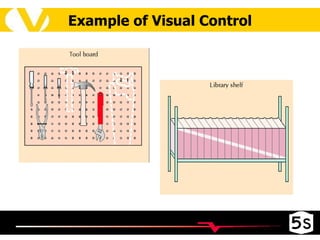
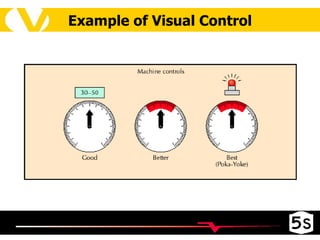
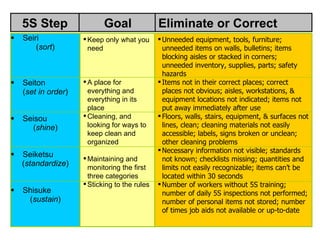
The document discusses the 5S methodology for organizing and managing workspaces. 5S stands for five Japanese words that start with "S" and represent techniques for sorting, setting in order, shining, standardizing, and sustaining a organized workspace. Implementing 5S in a systematic way through training and teamwork can increase efficiency, quality, safety and morale by eliminating waste and ensuring everything has a clear place.