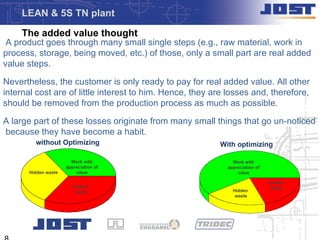
The document outlines an agenda and objectives for a 5S training for shop floor employees, describing the five S's of 5S (Sort, Set In Order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain) and how to implement them to organize the workplace, eliminate waste, improve safety and quality, and establish standards and habits to maintain the 5S system. The 5S methodology is presented as a tool to help make operations more lean by reducing waste and non-value added activities.