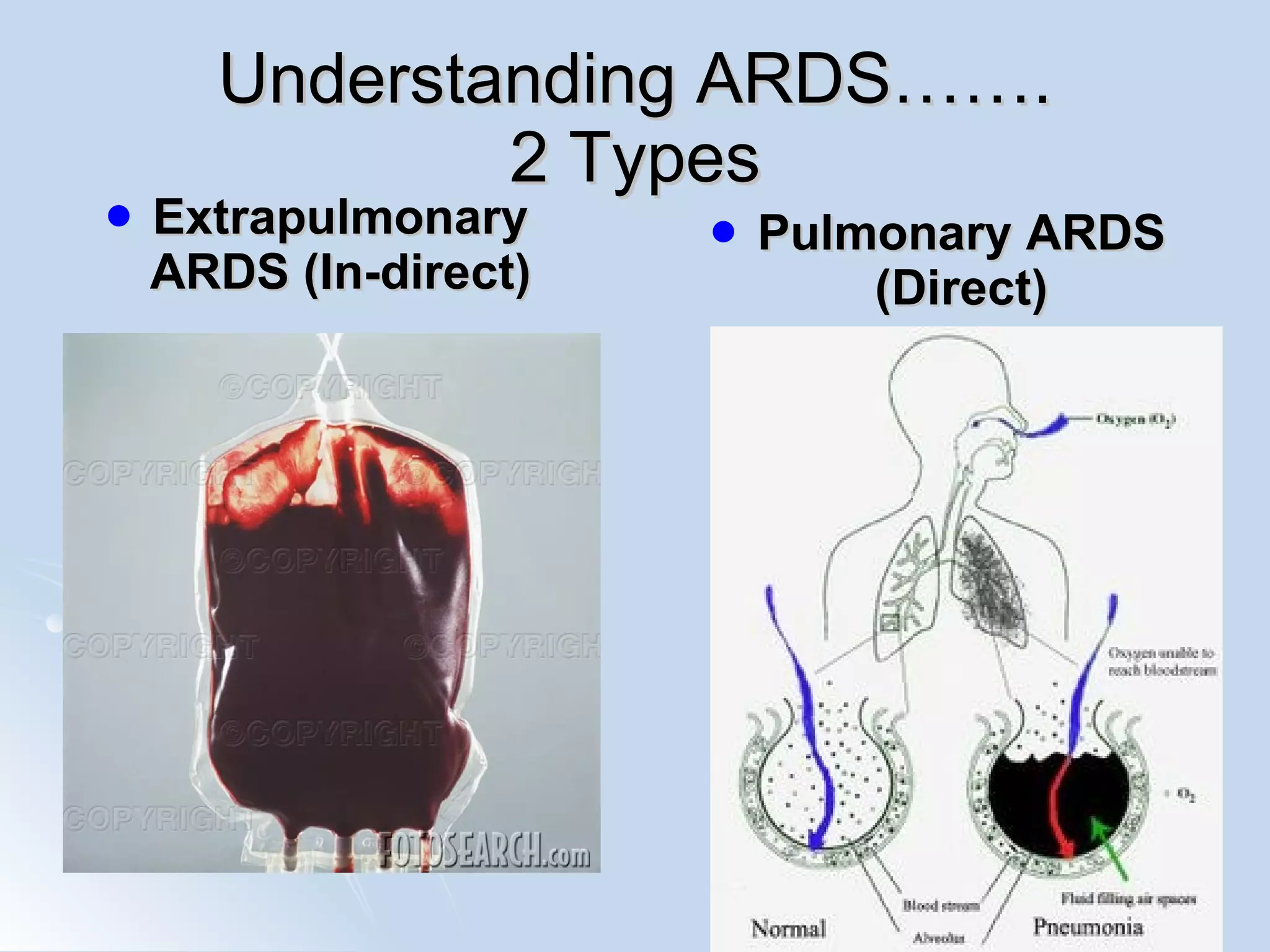
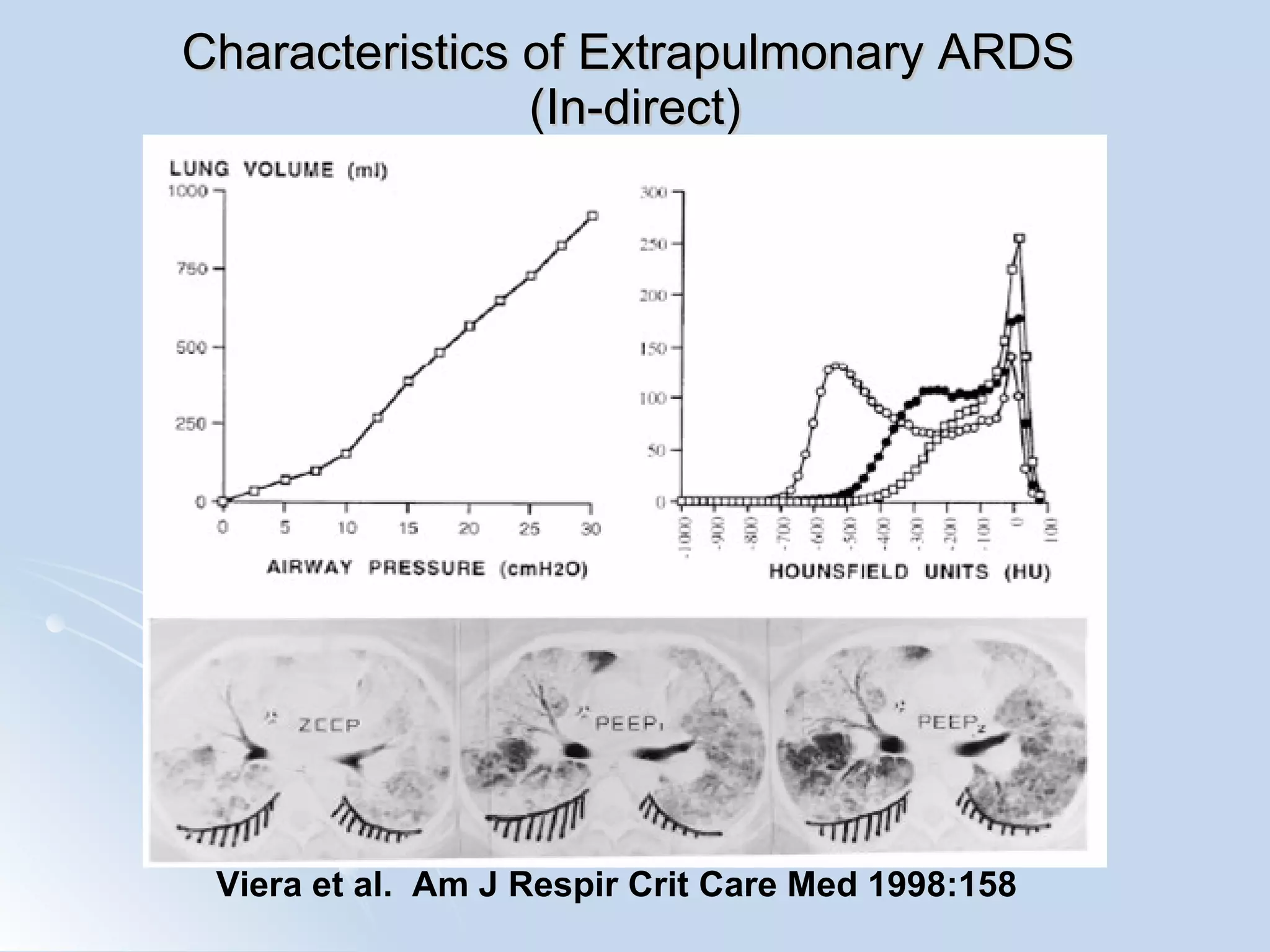
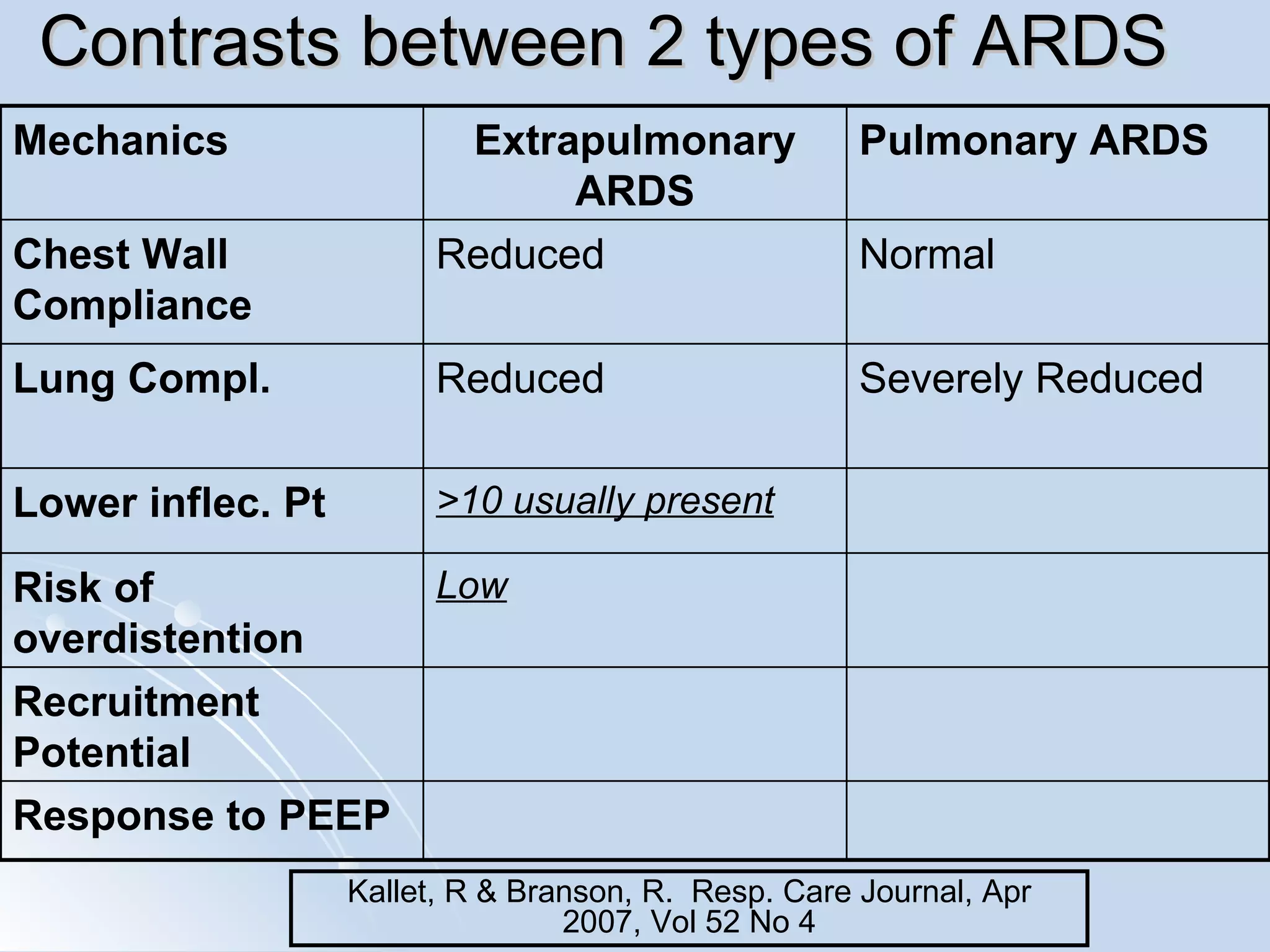
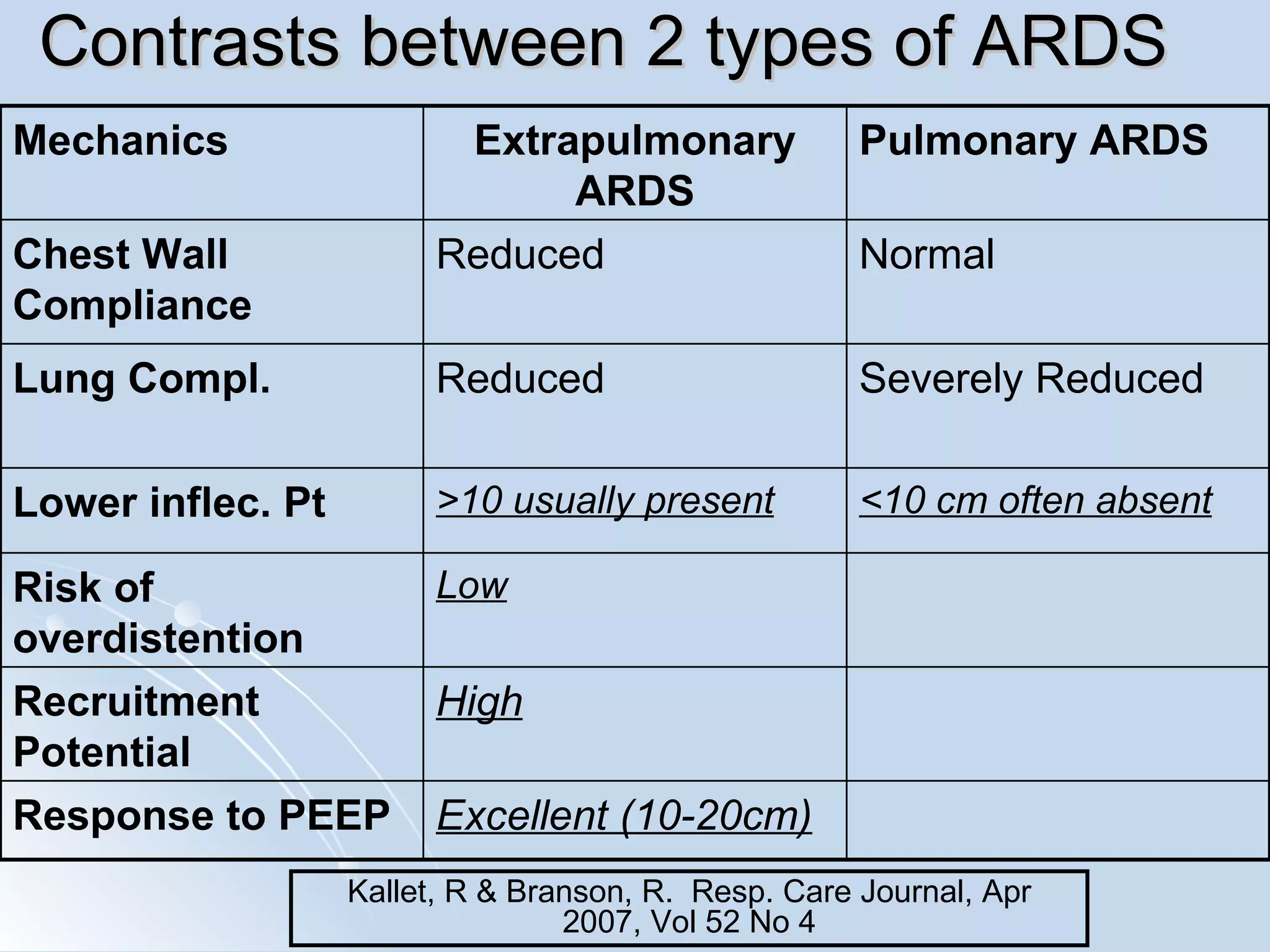
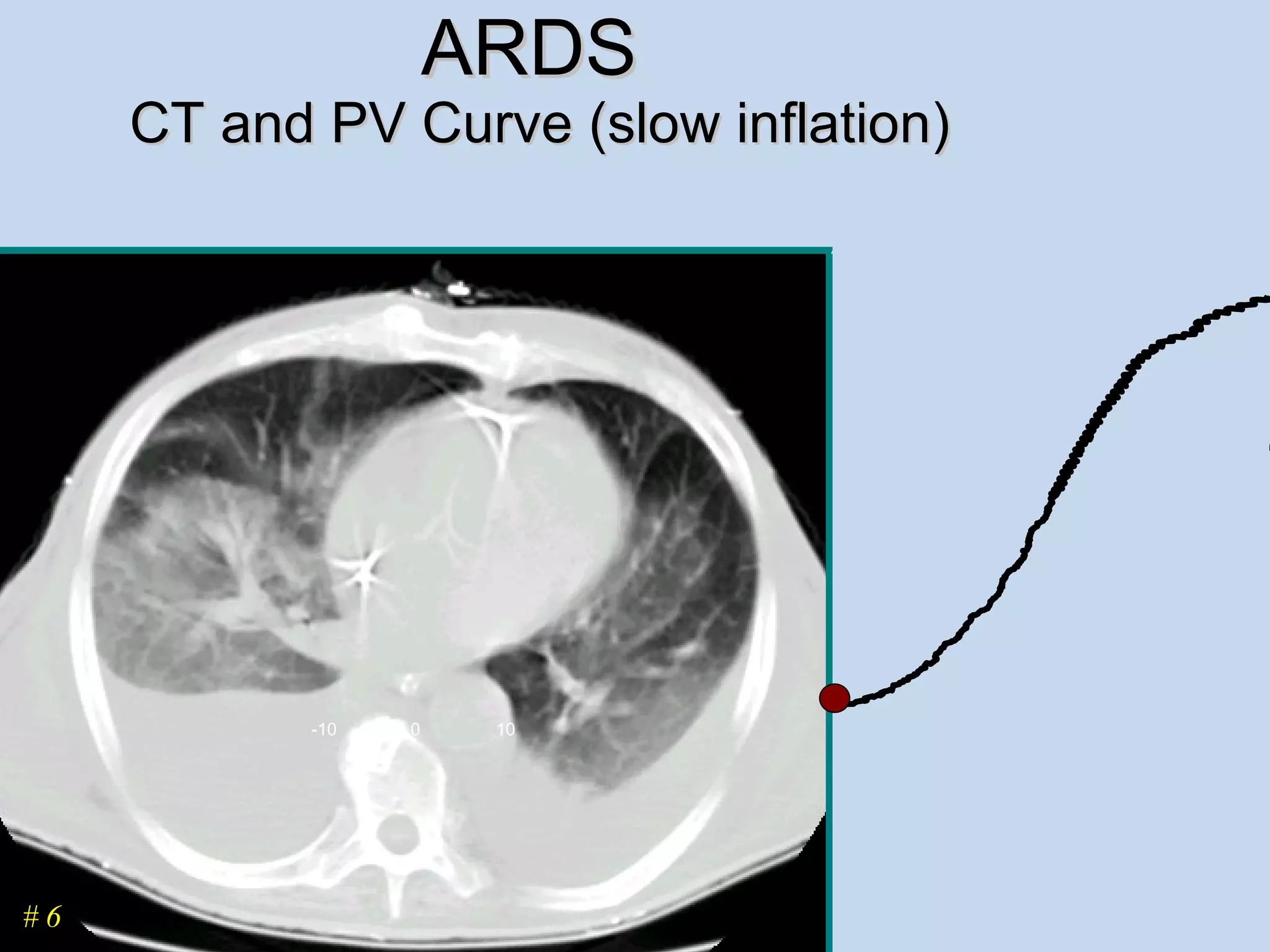
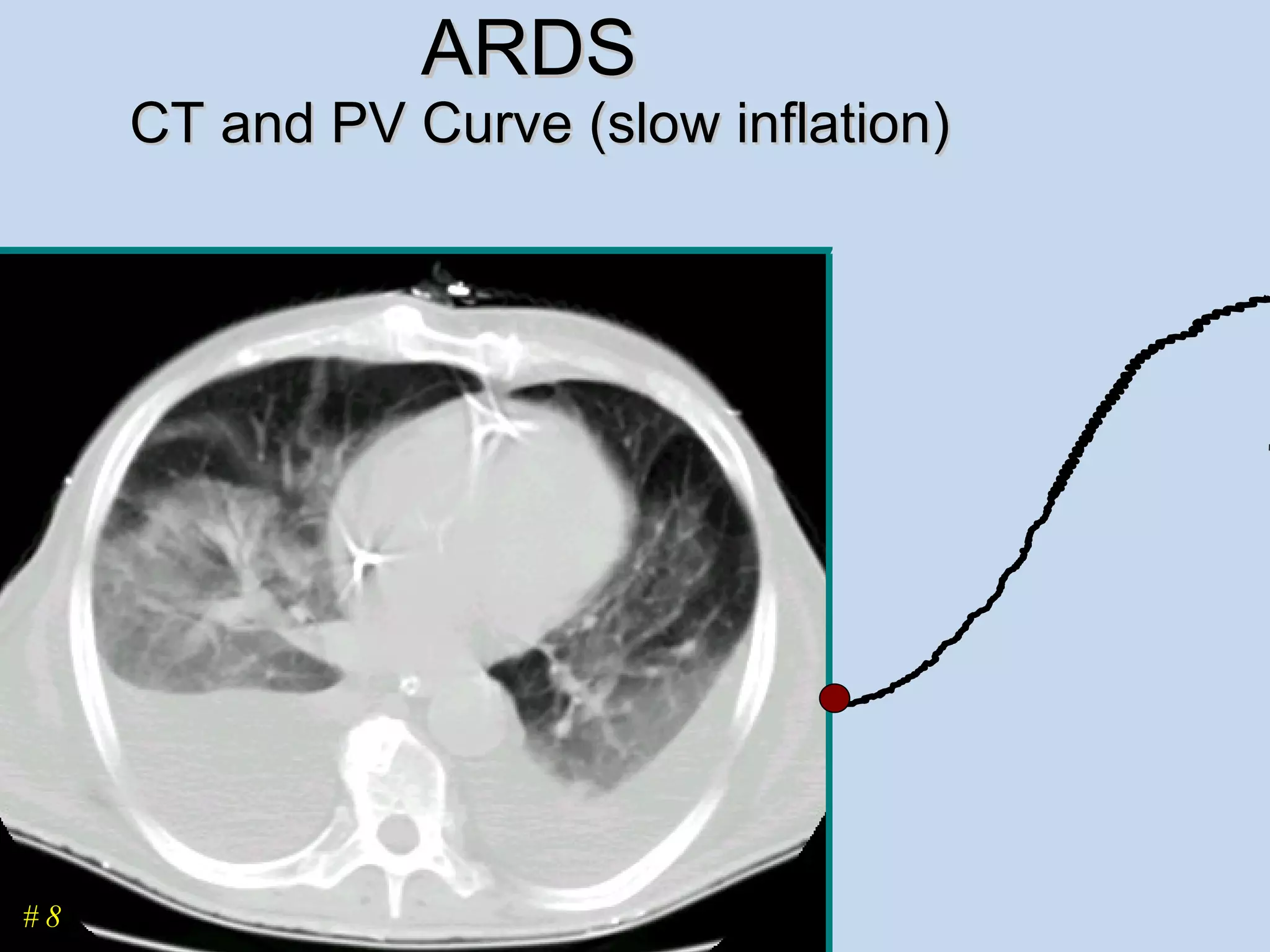
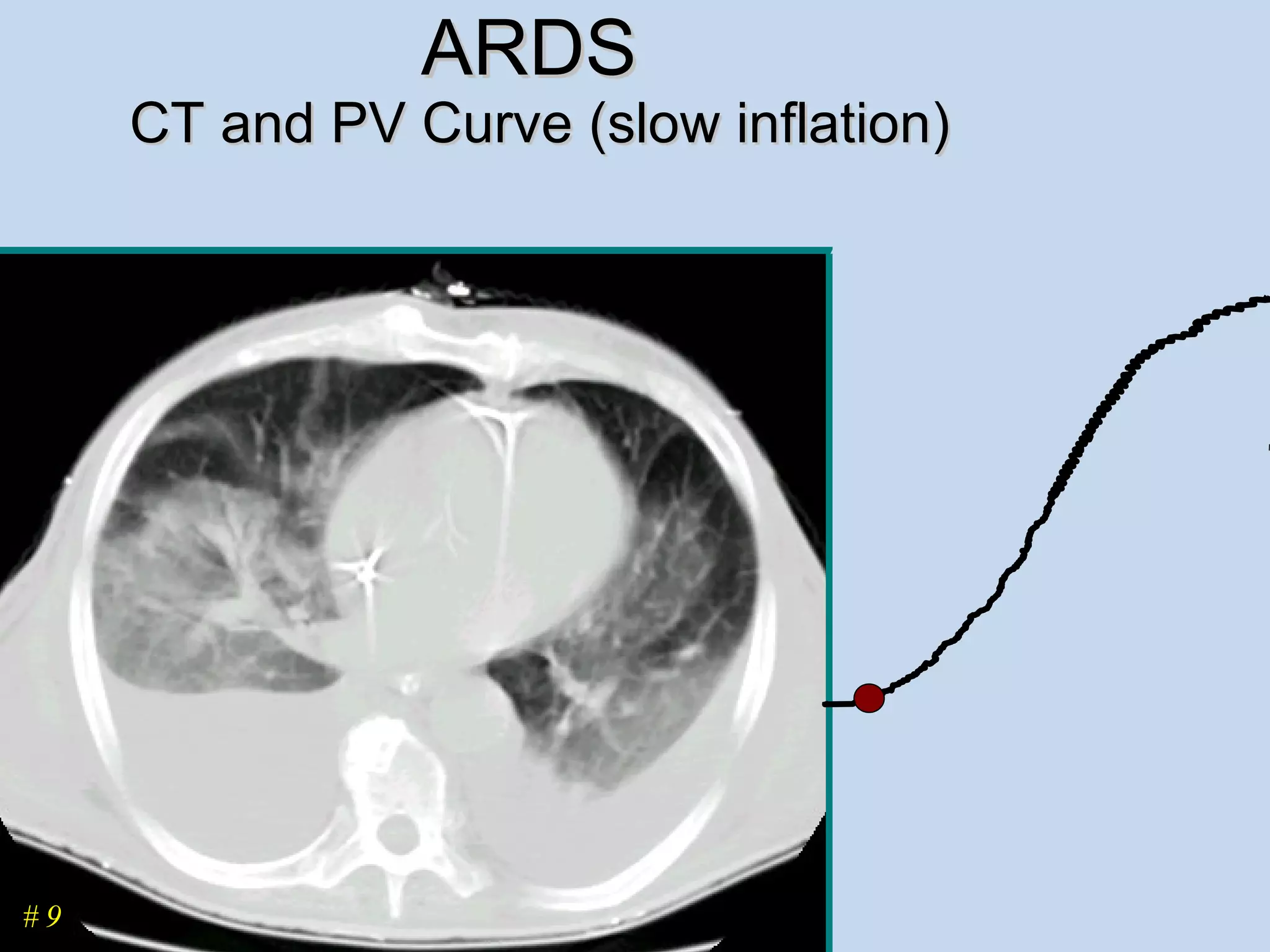
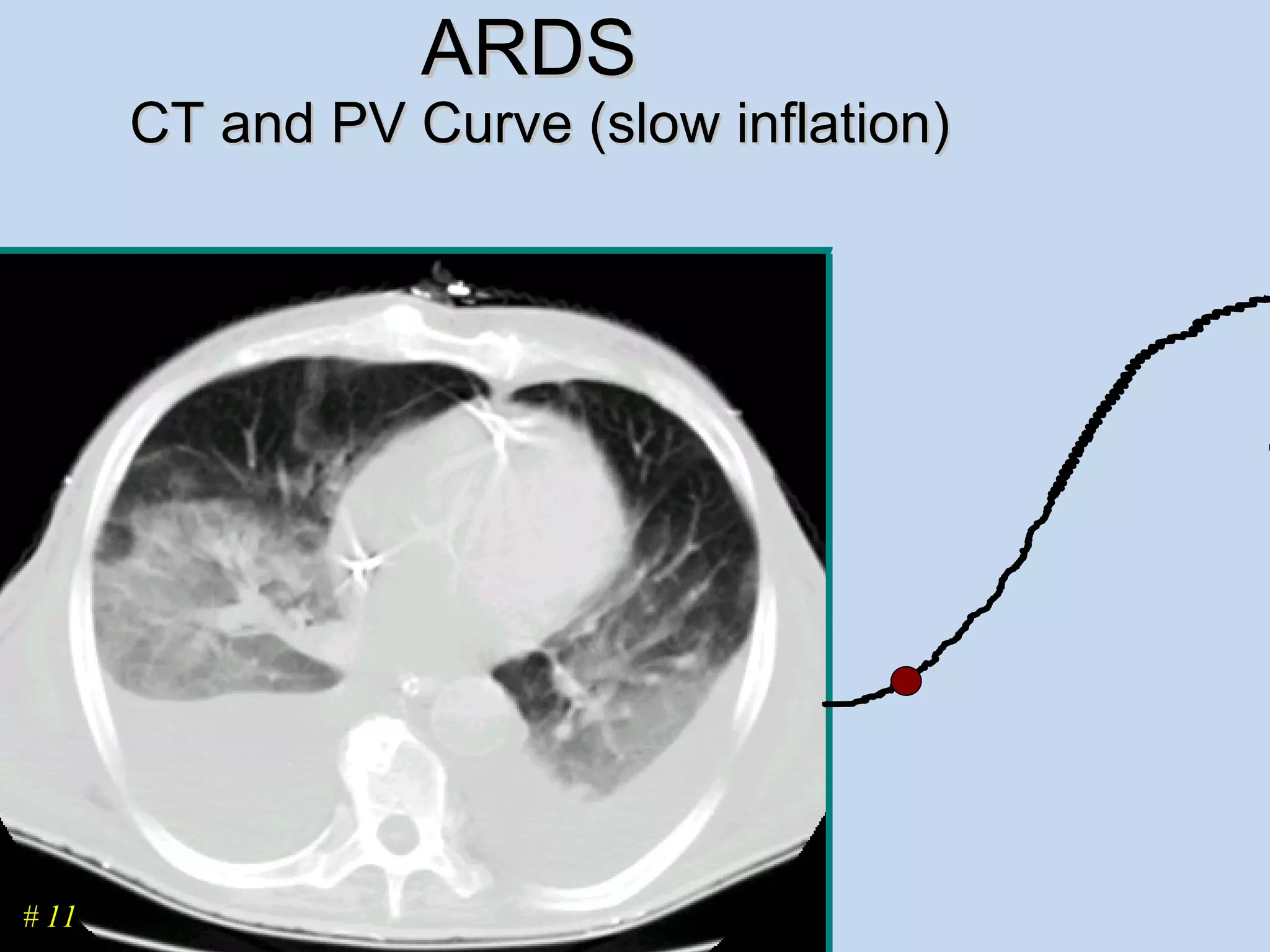
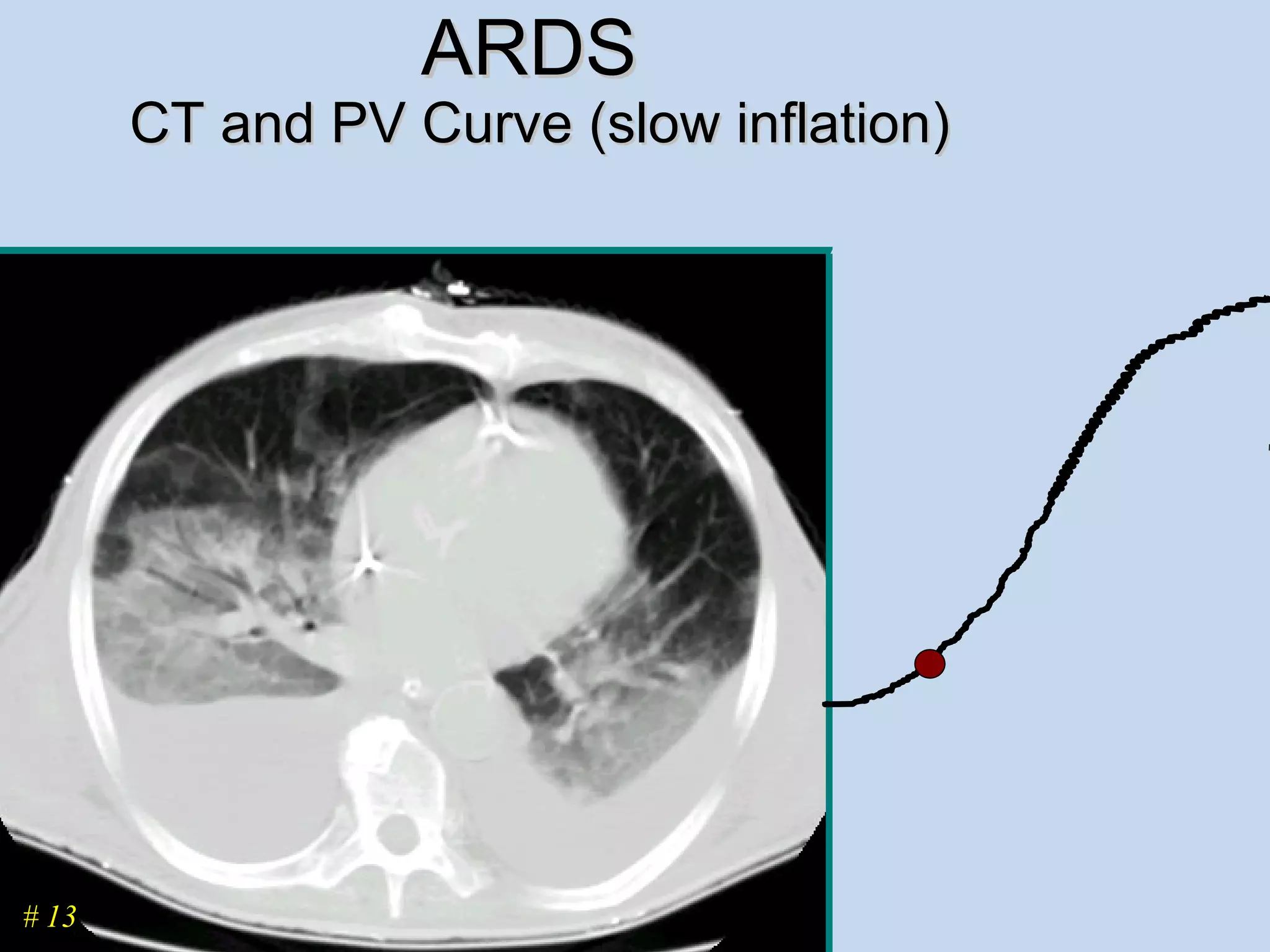
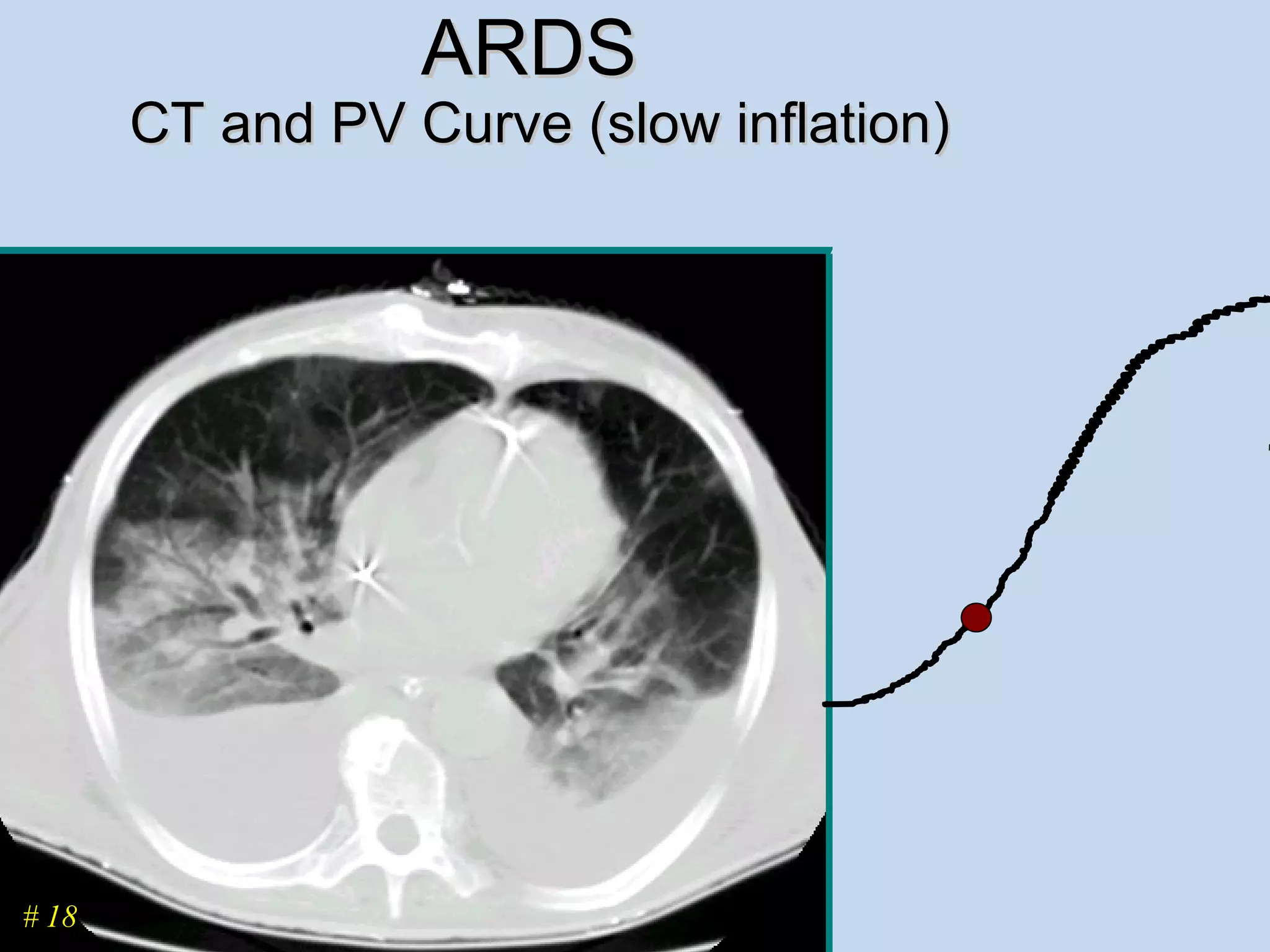
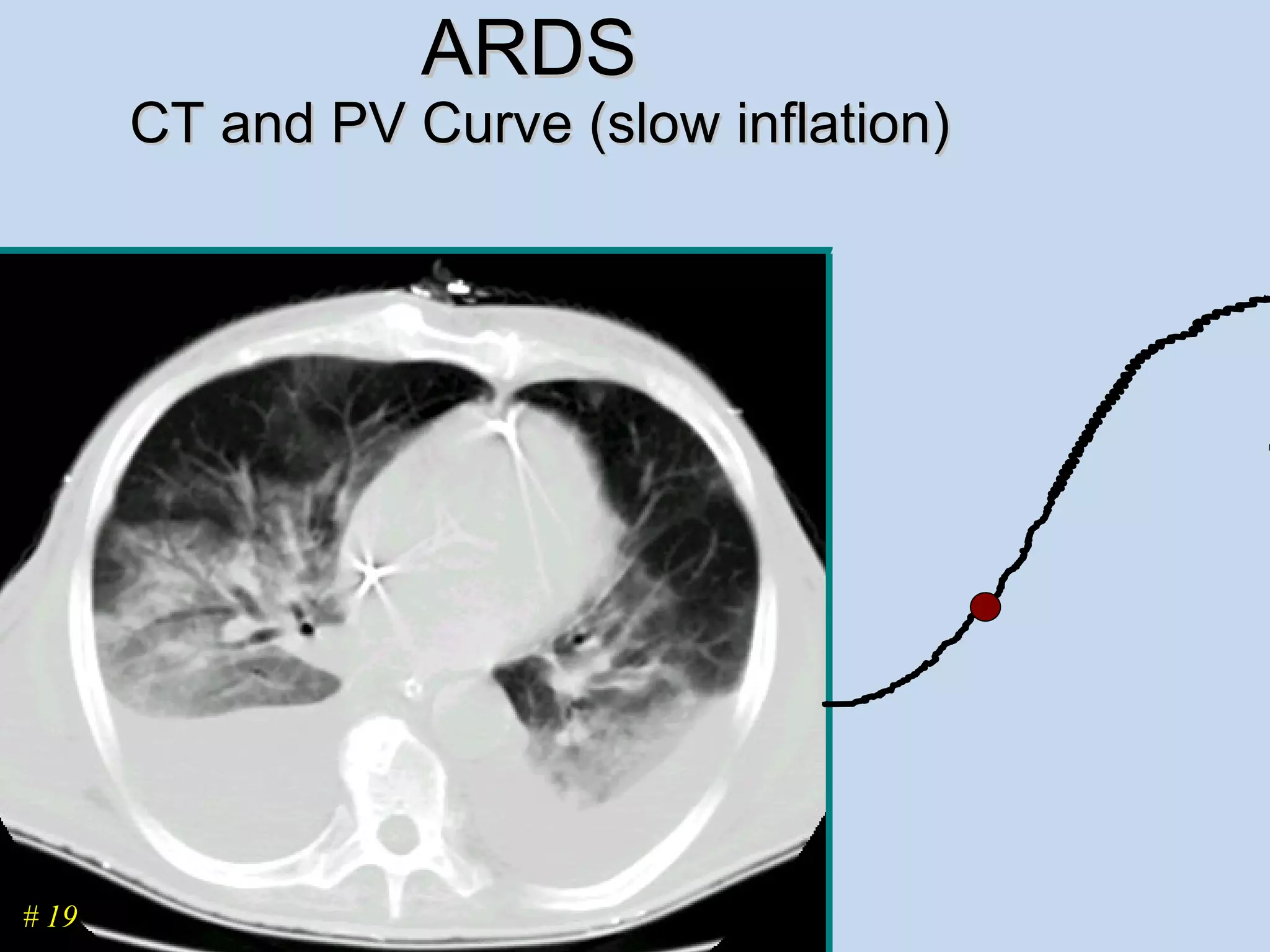
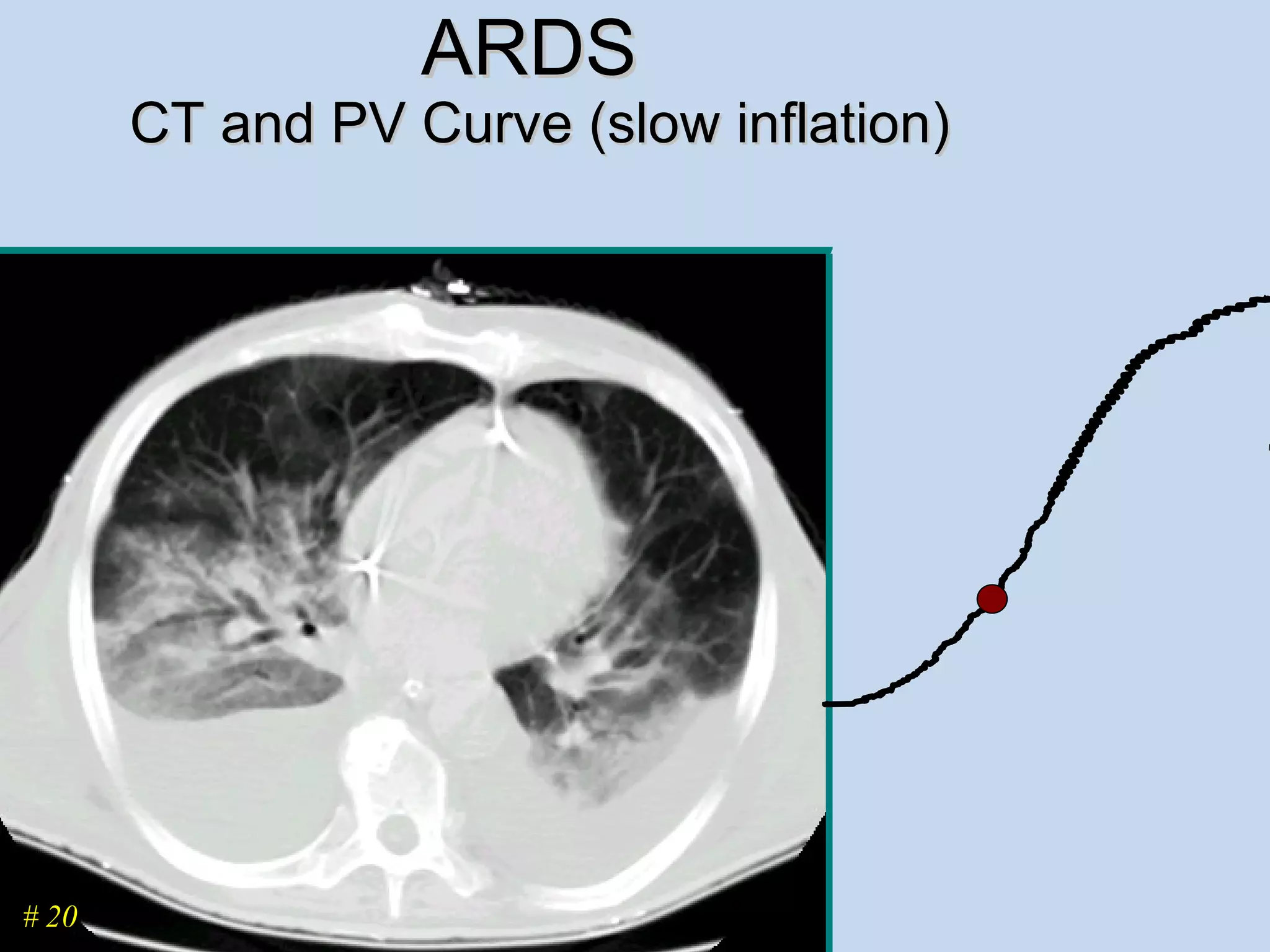
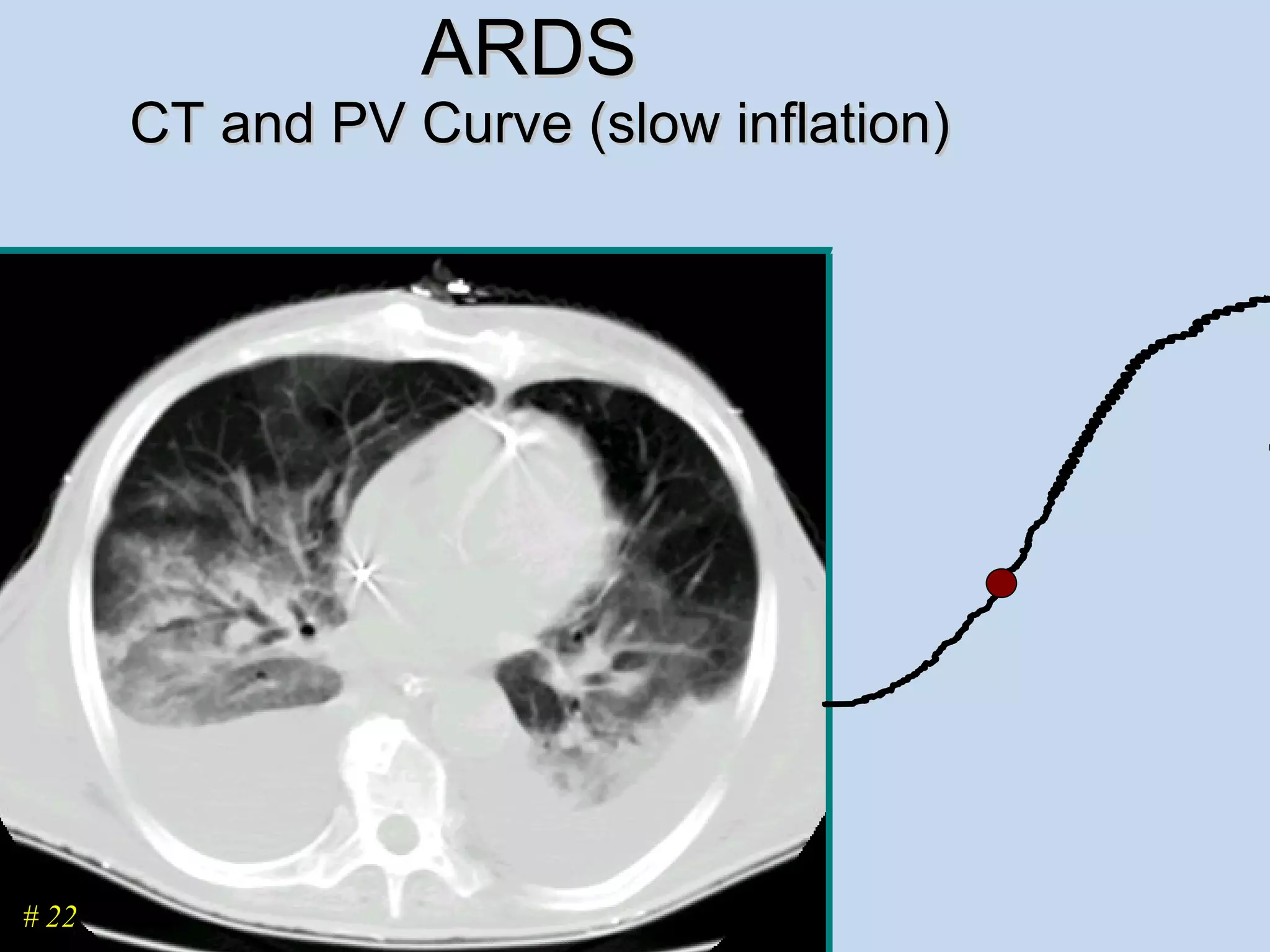
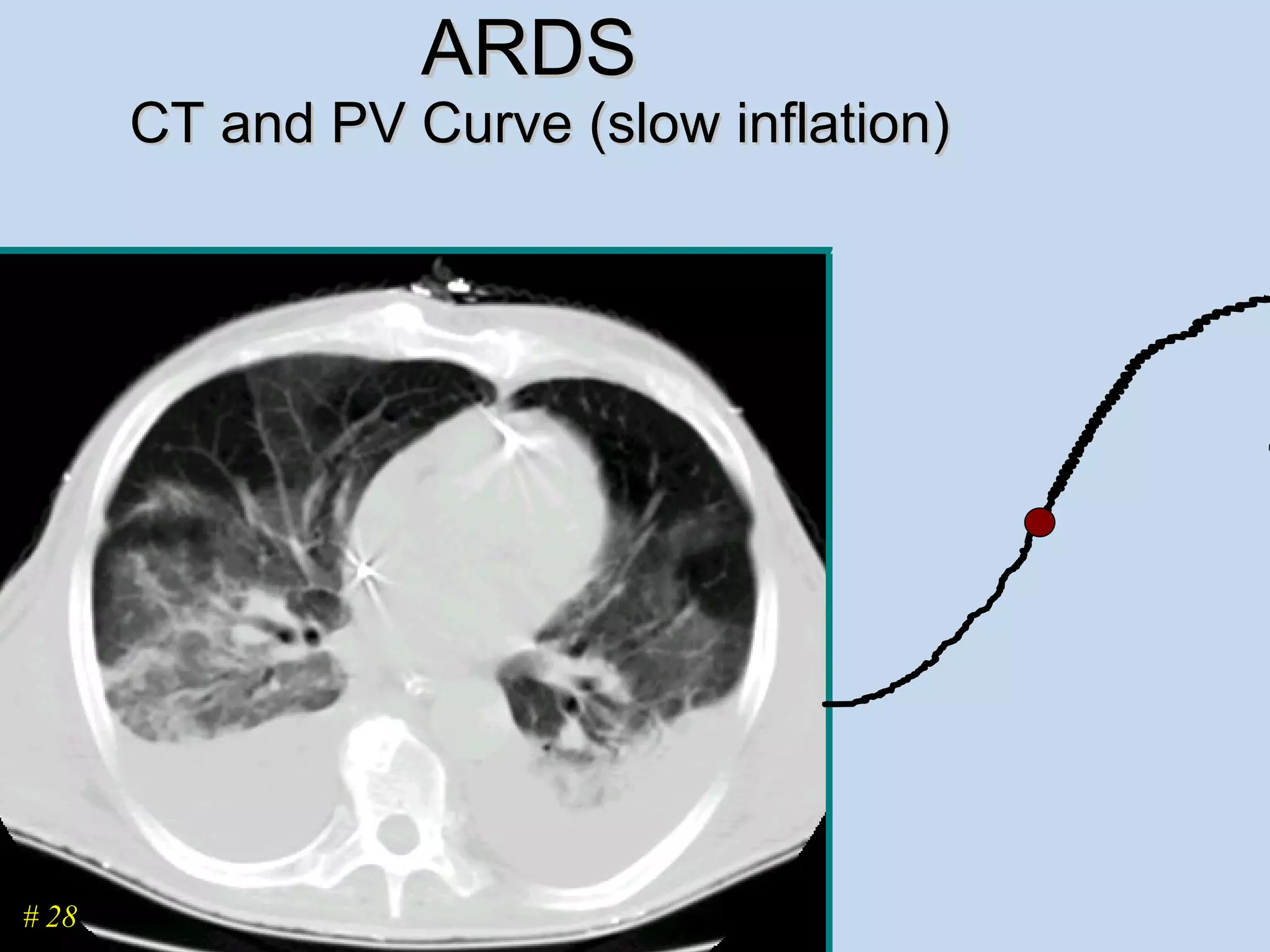
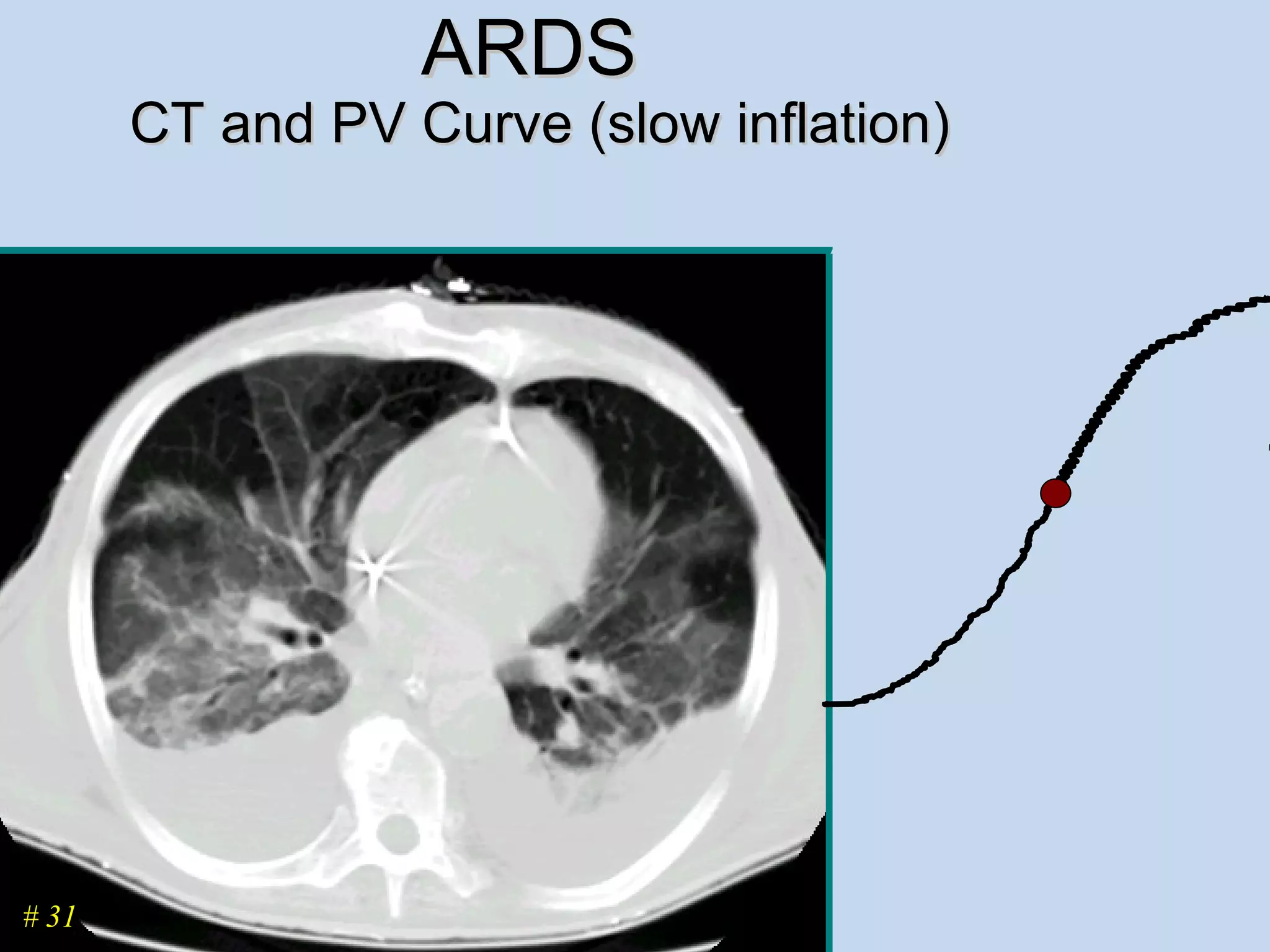
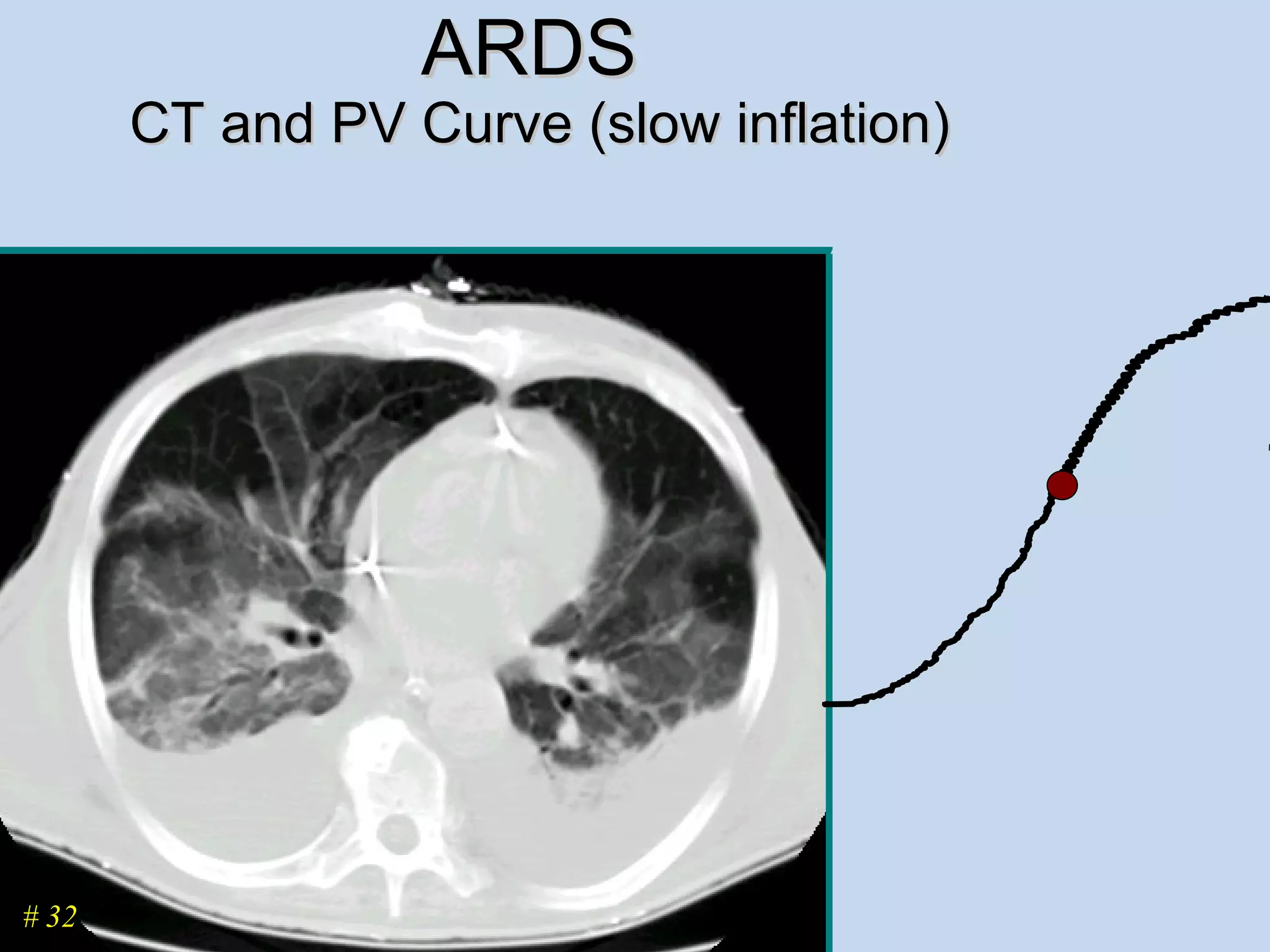
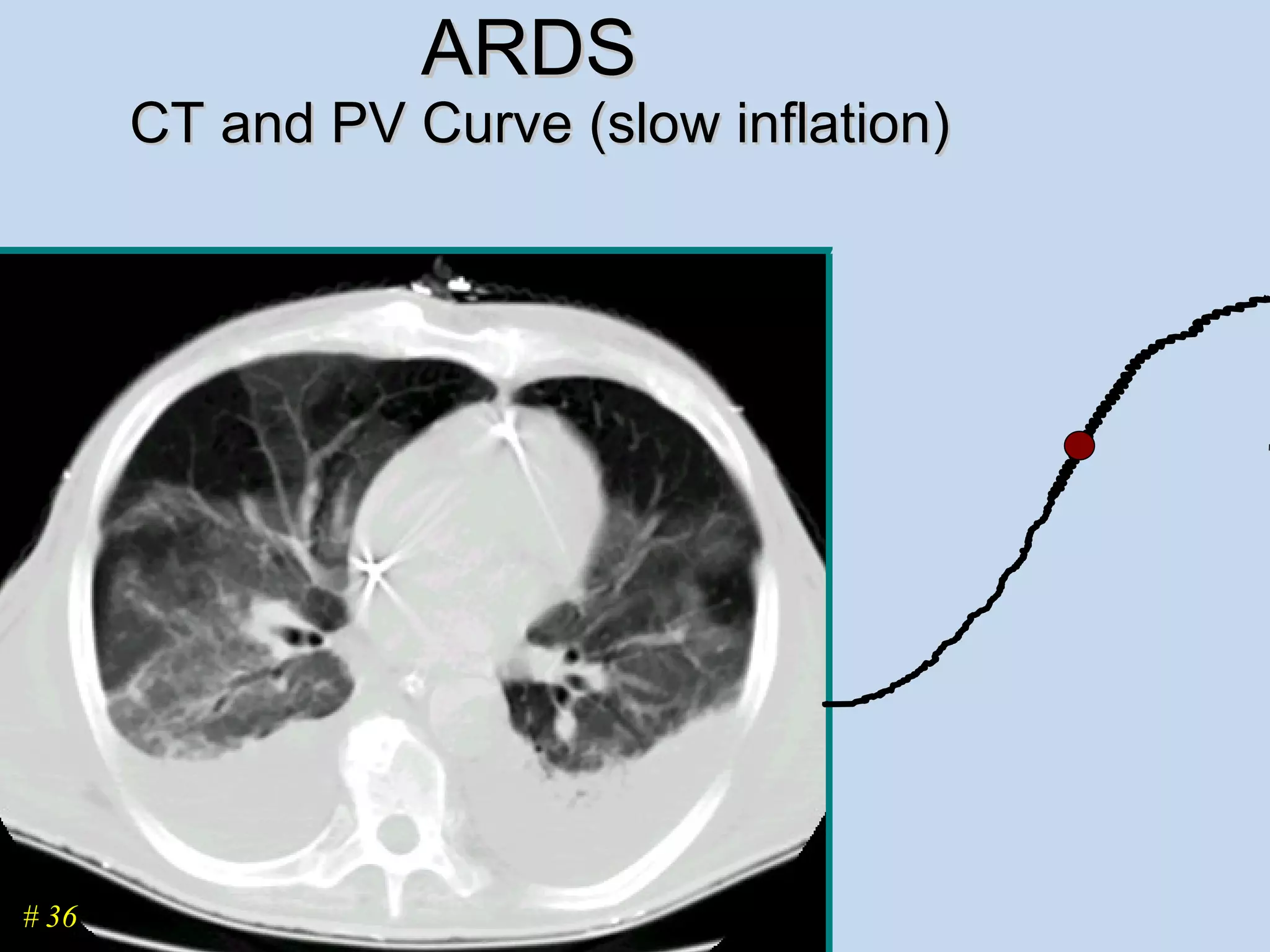
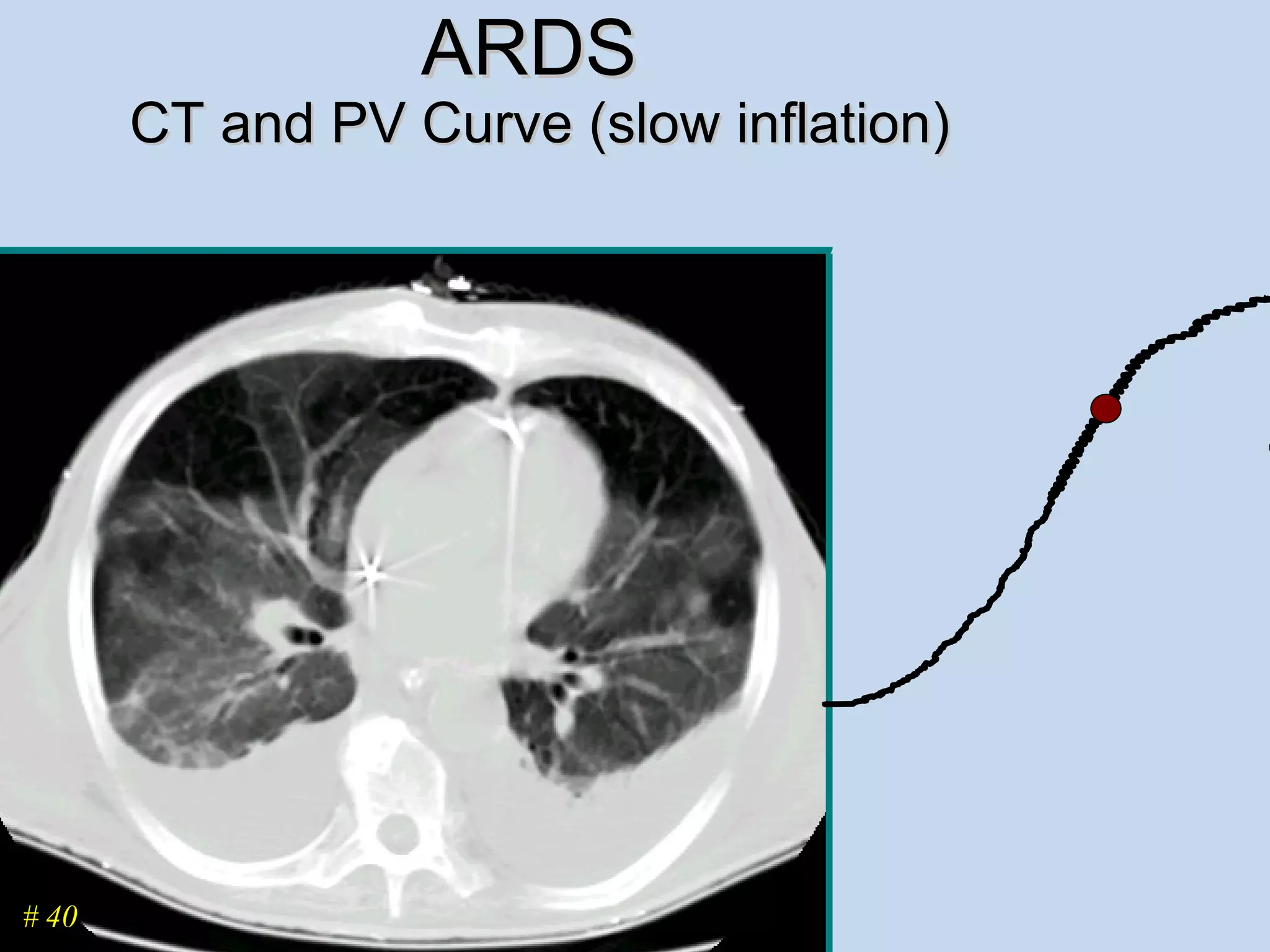
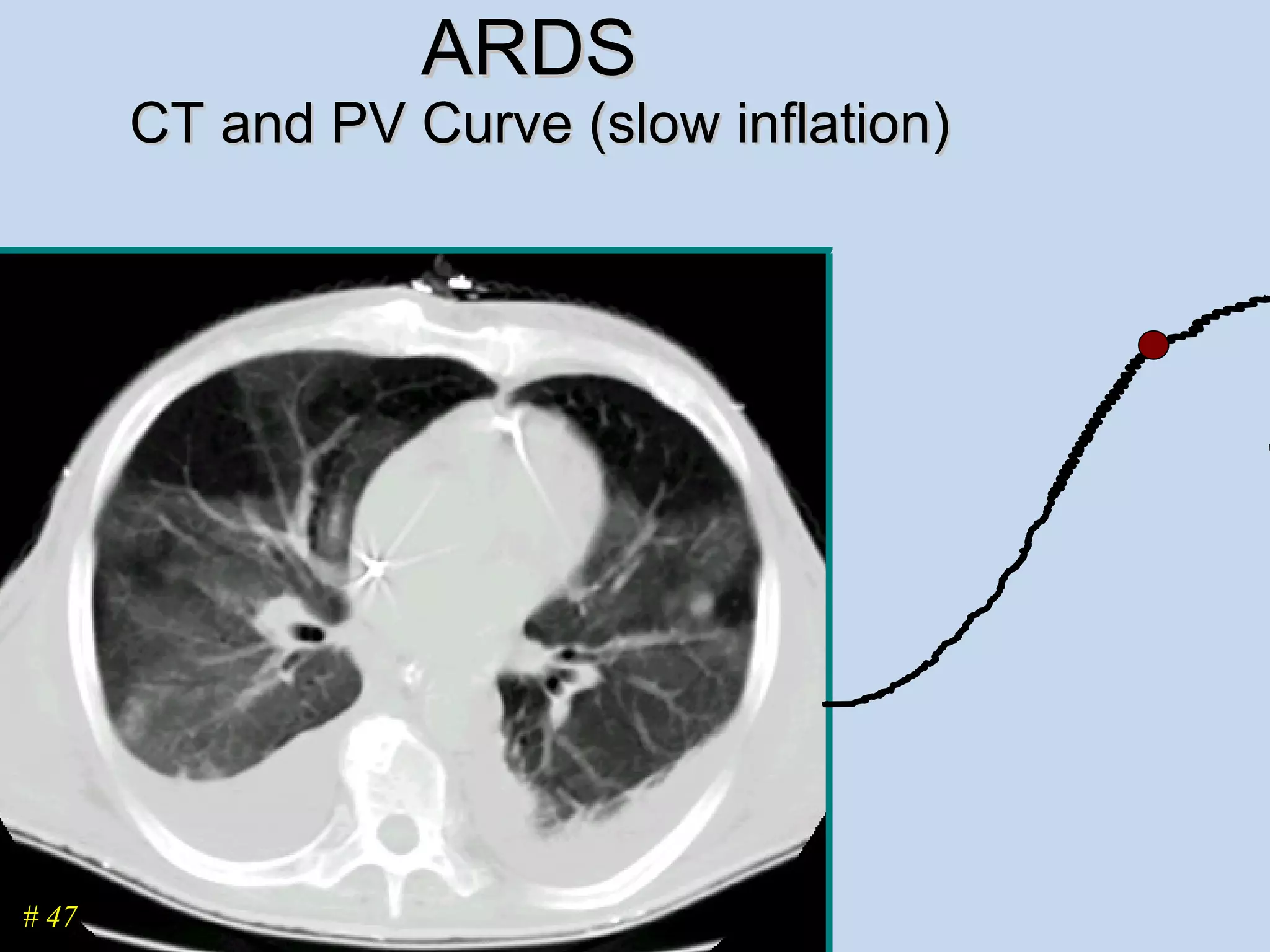
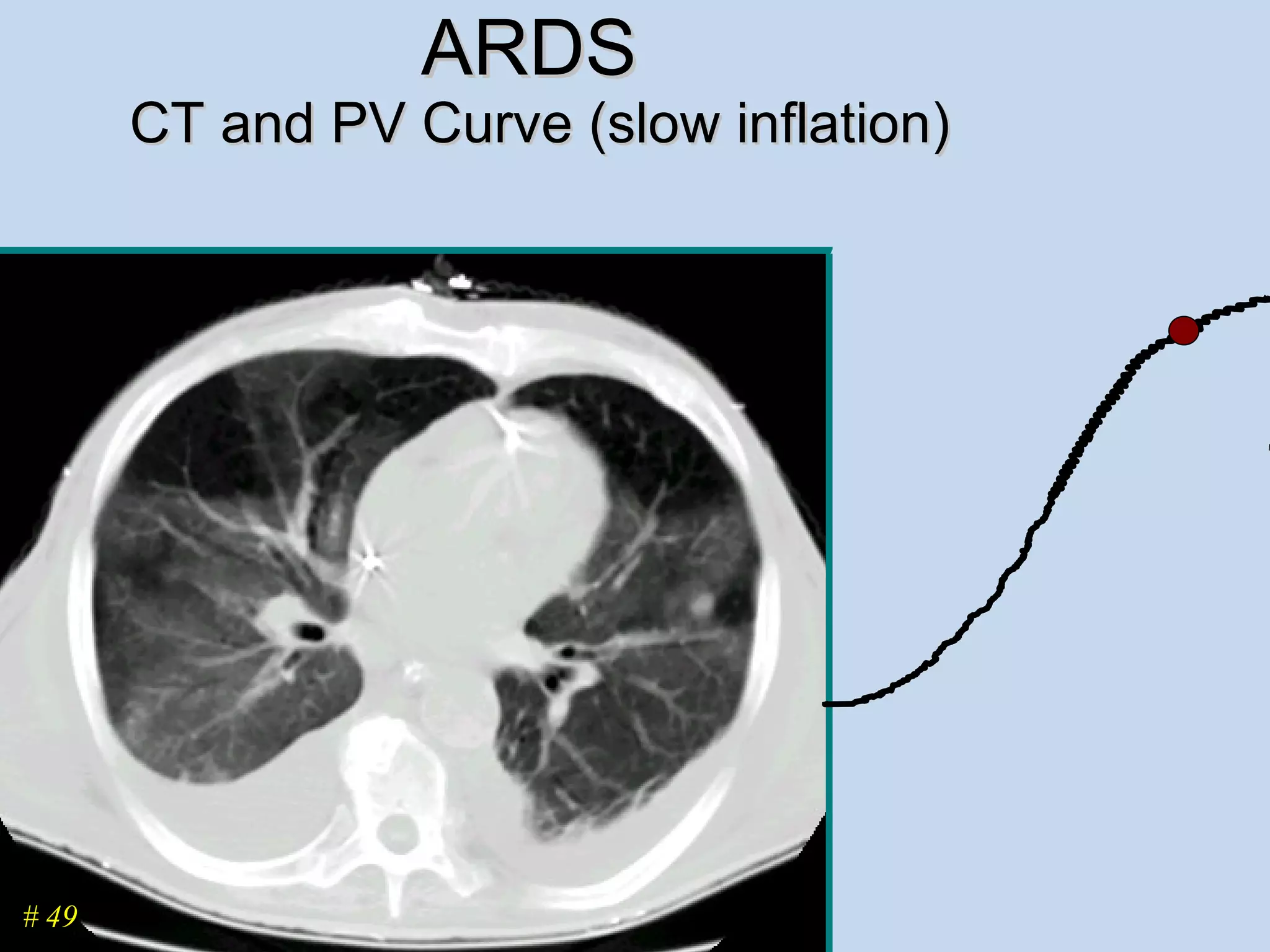
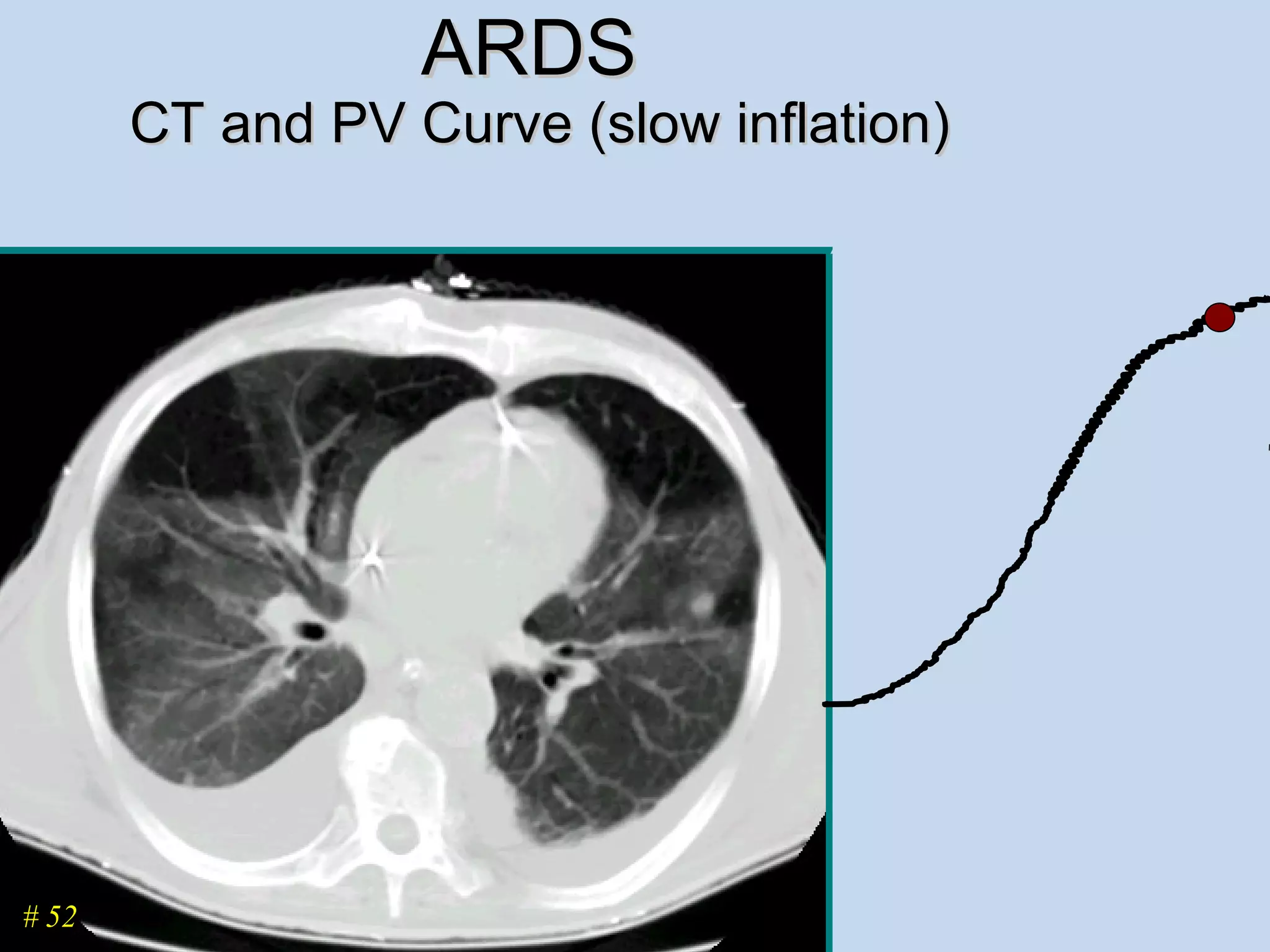
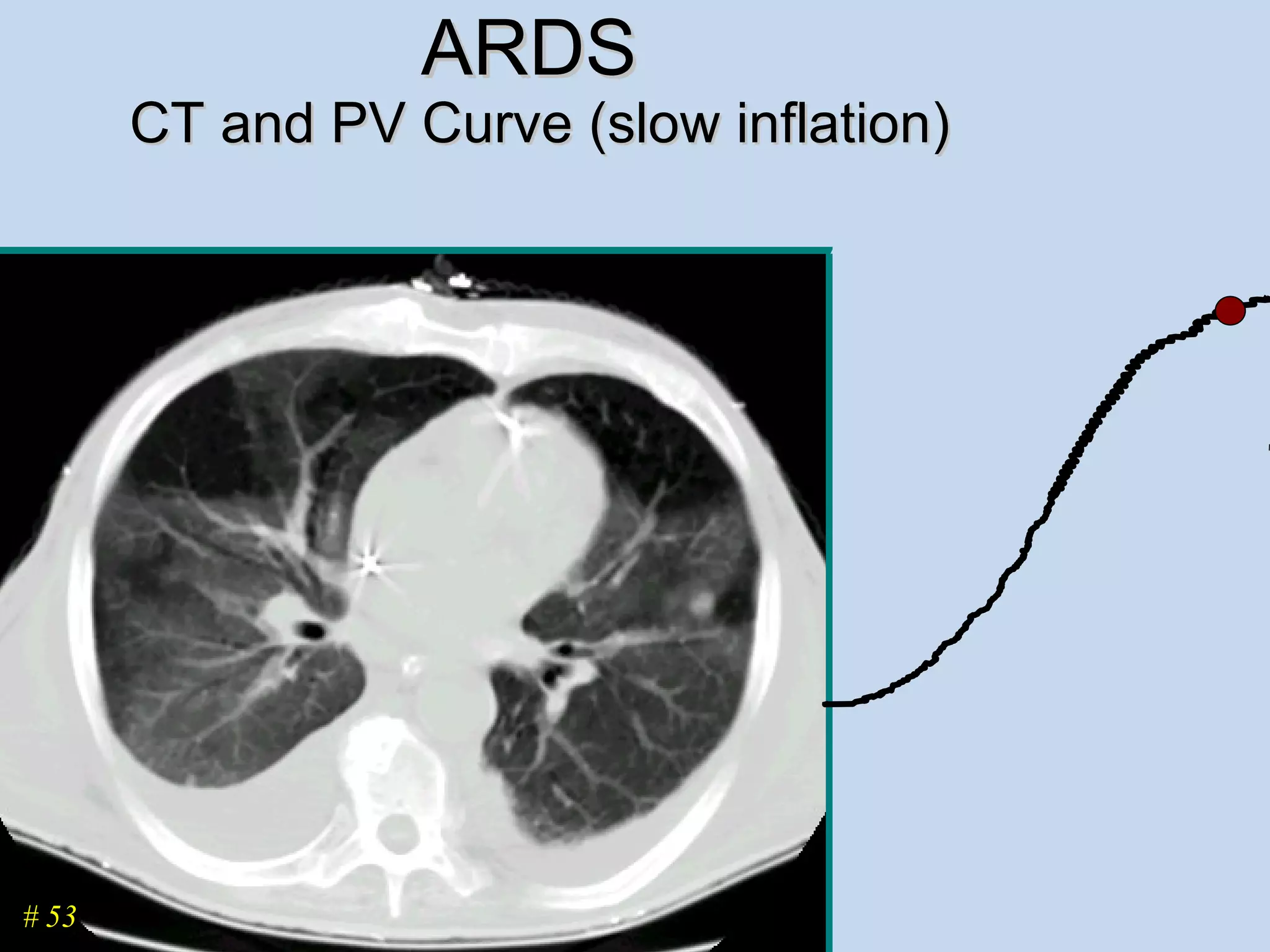
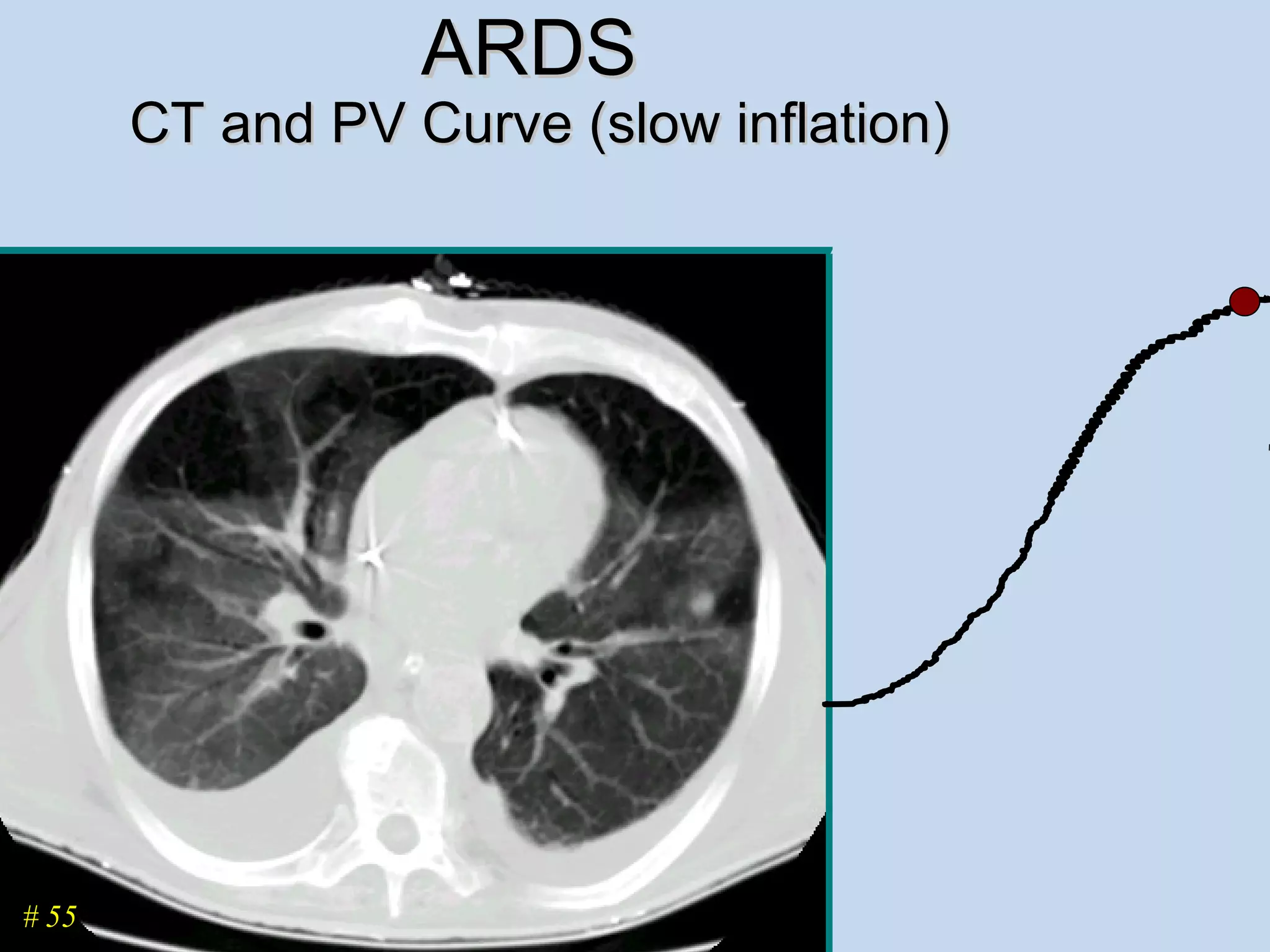
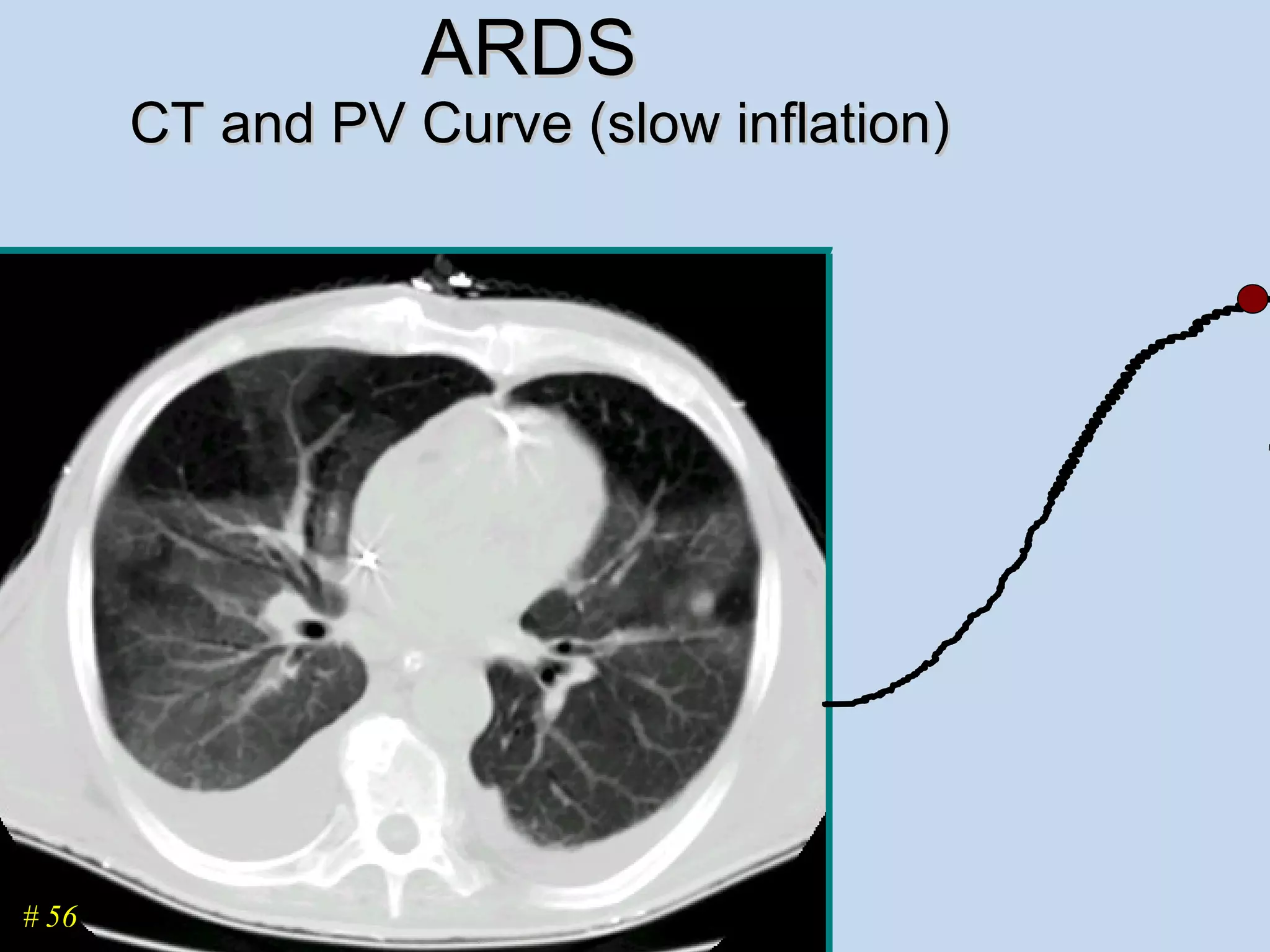
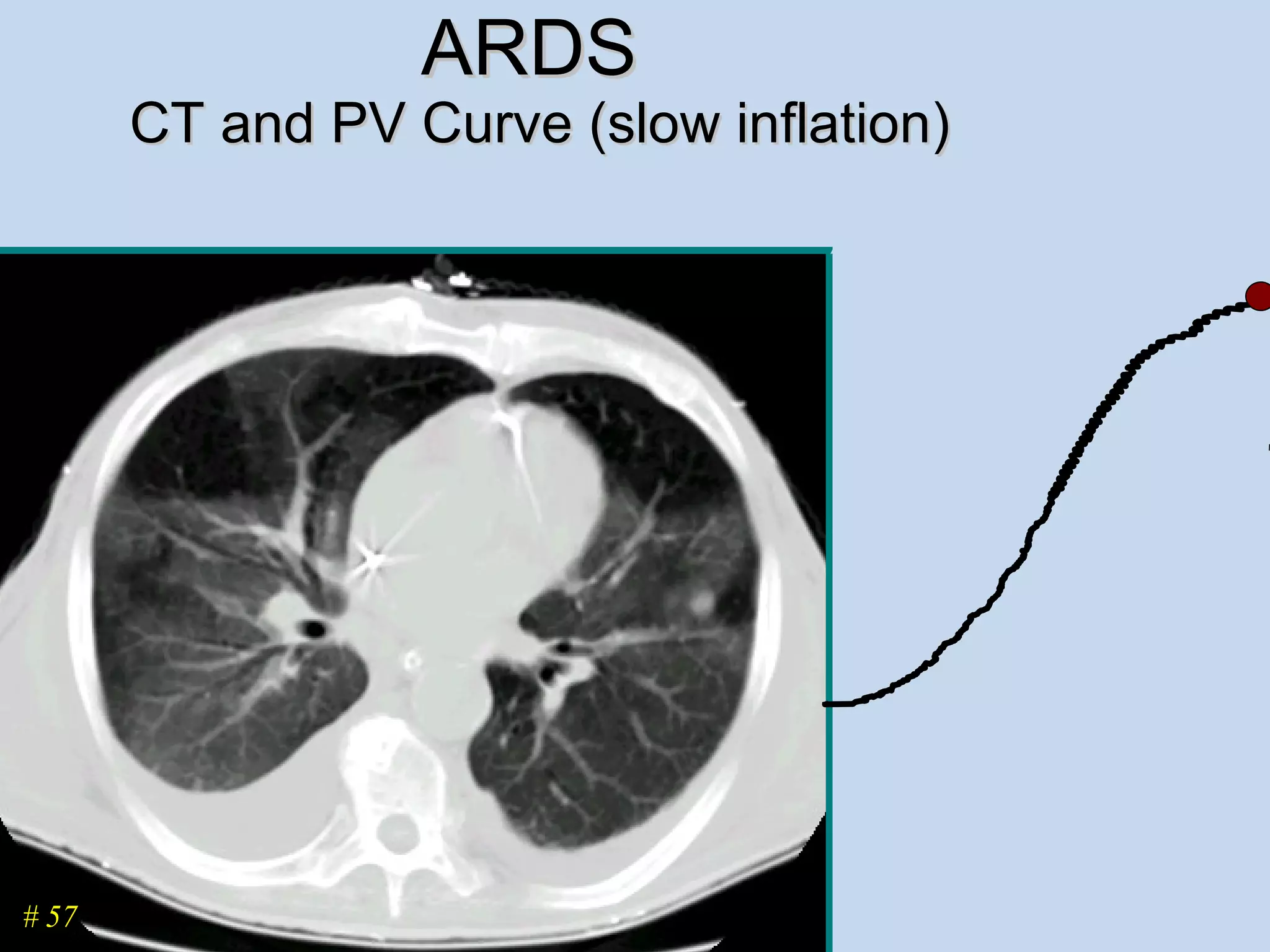
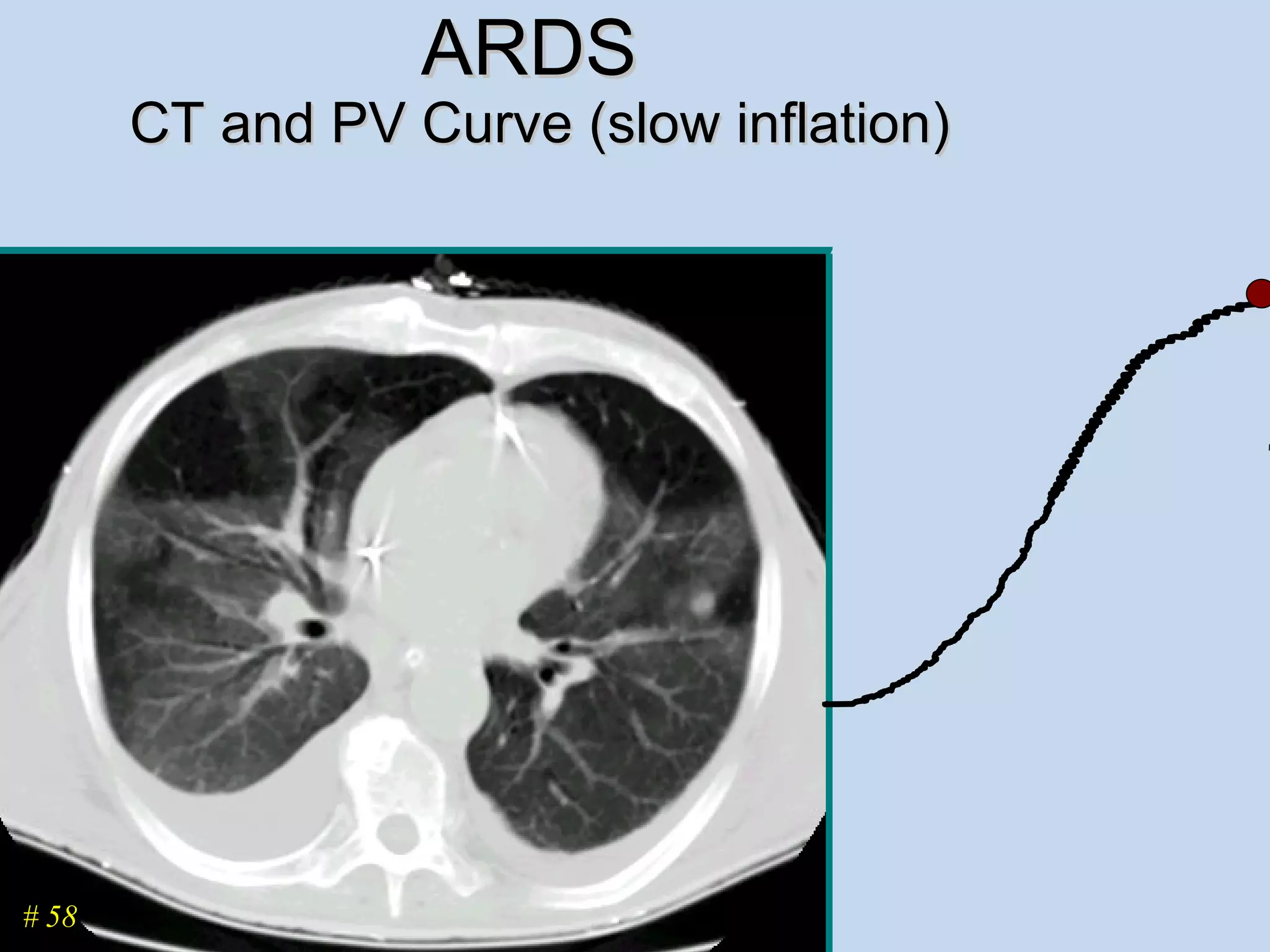
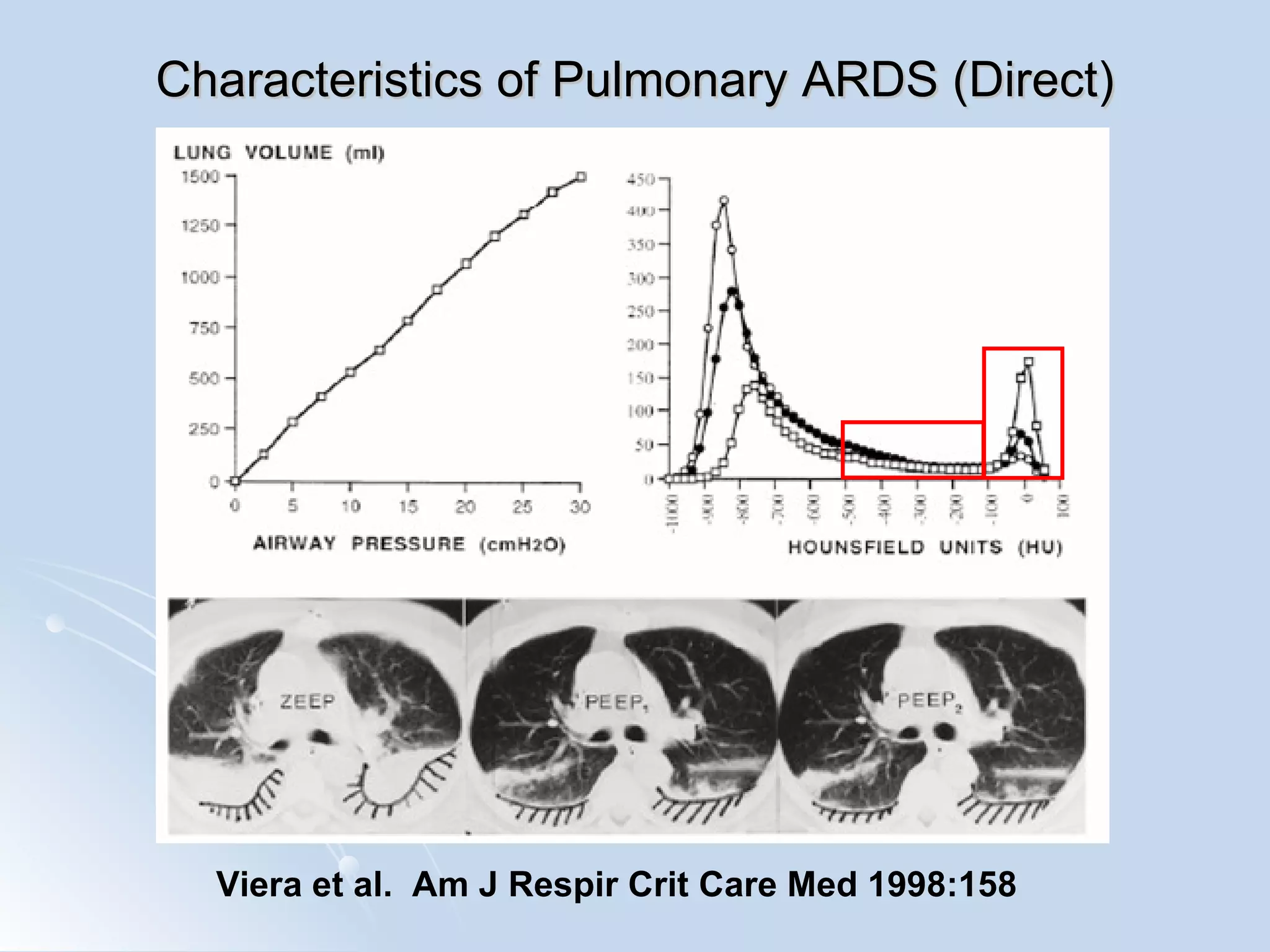
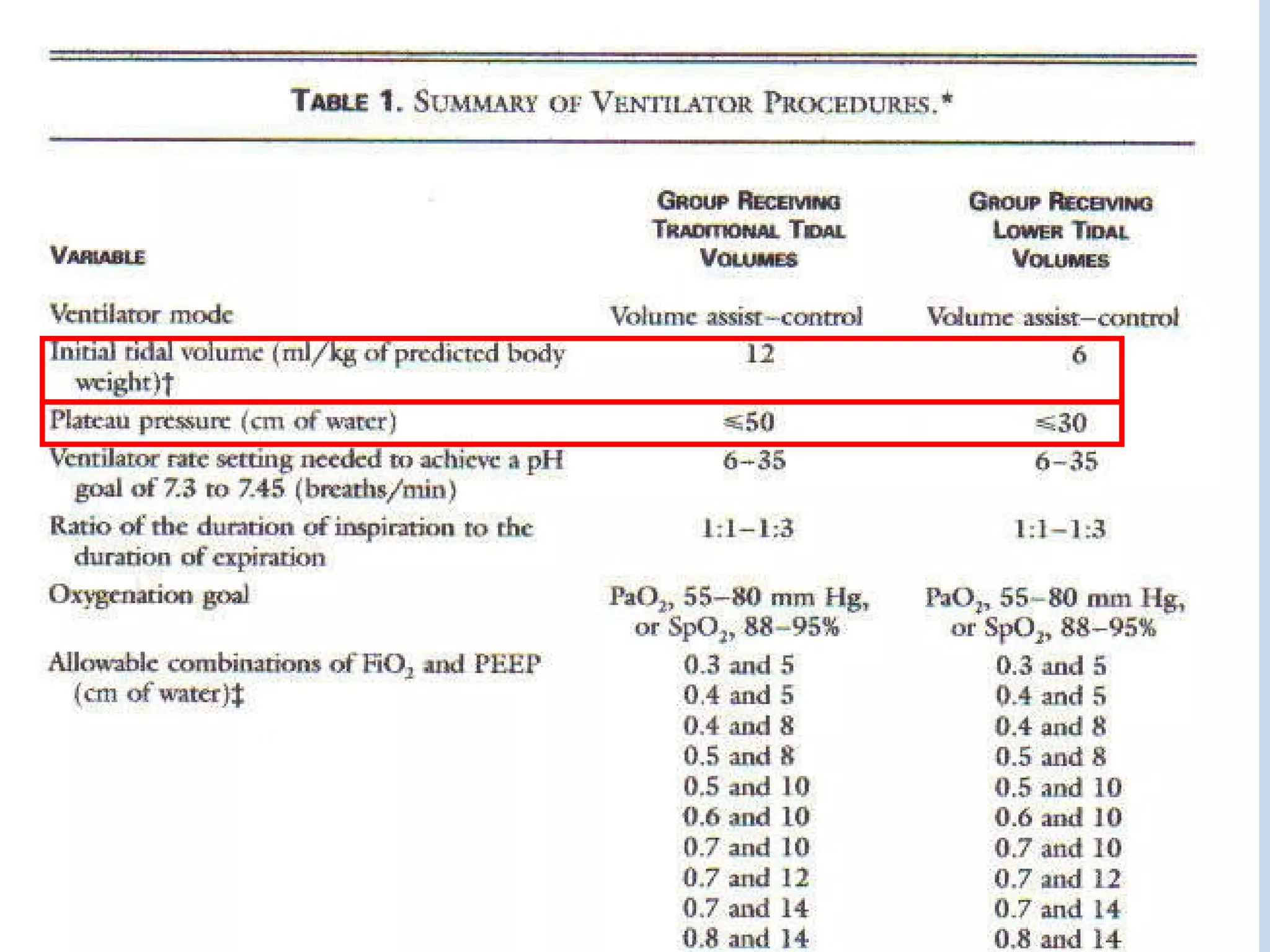
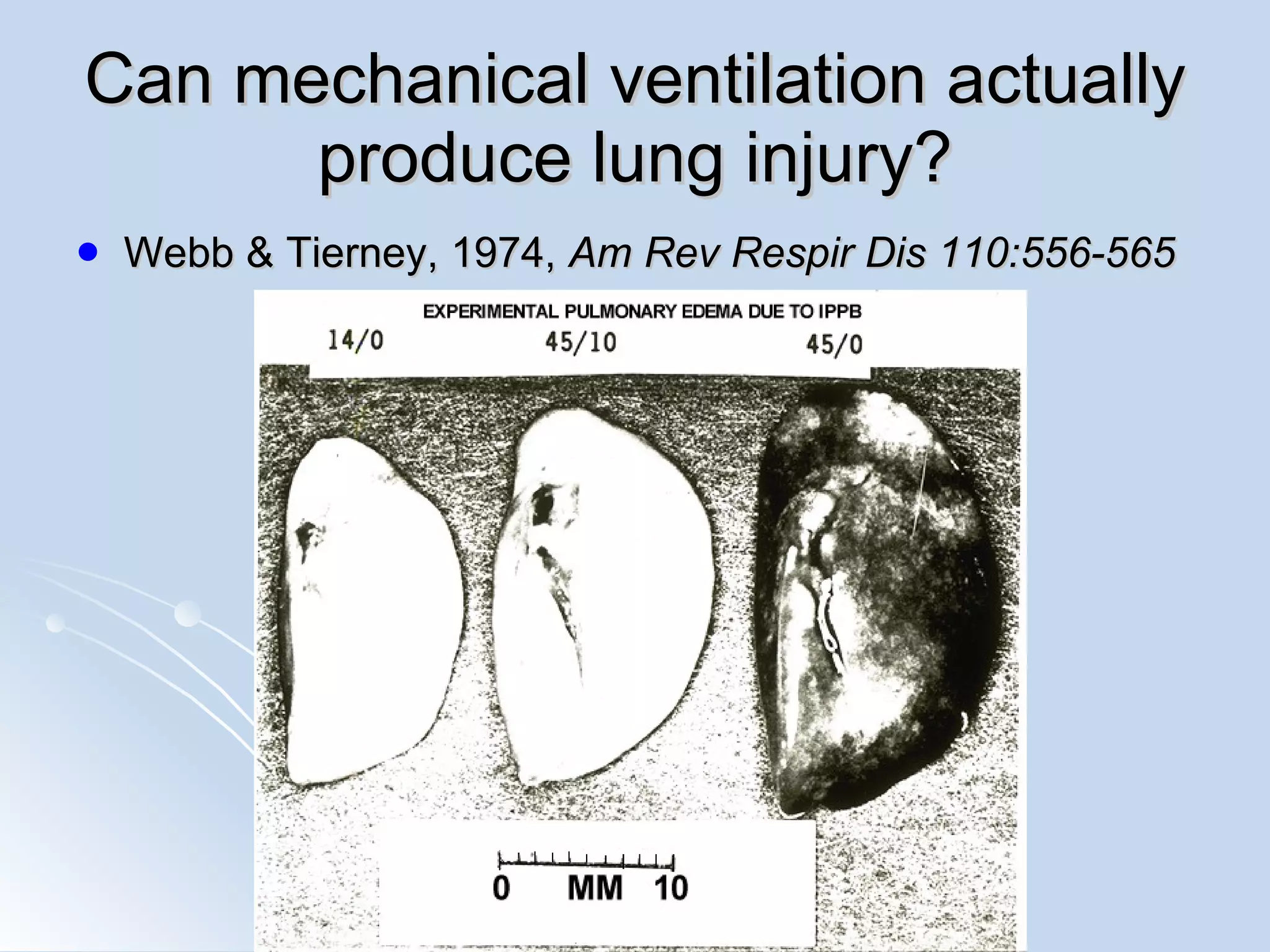
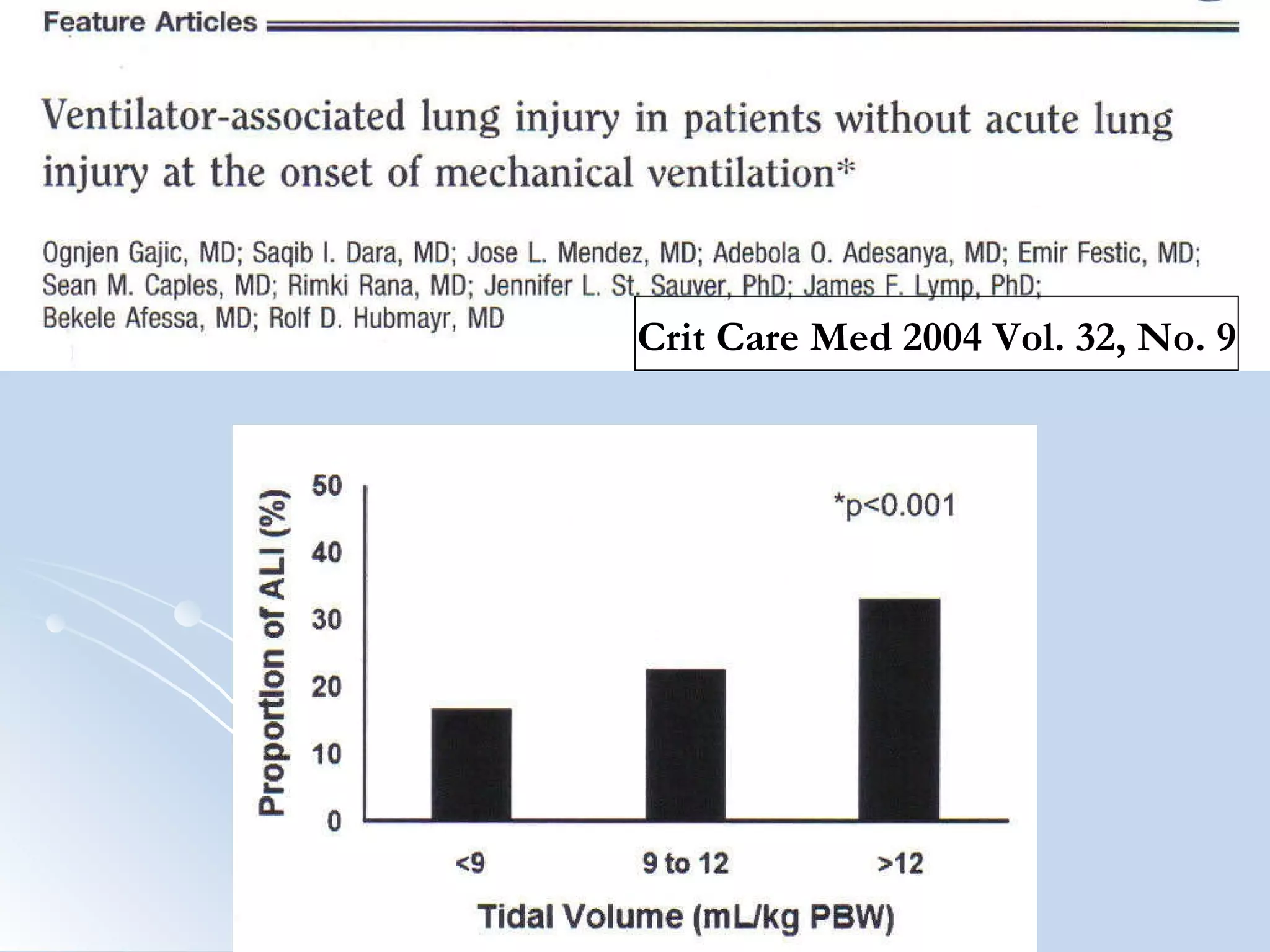
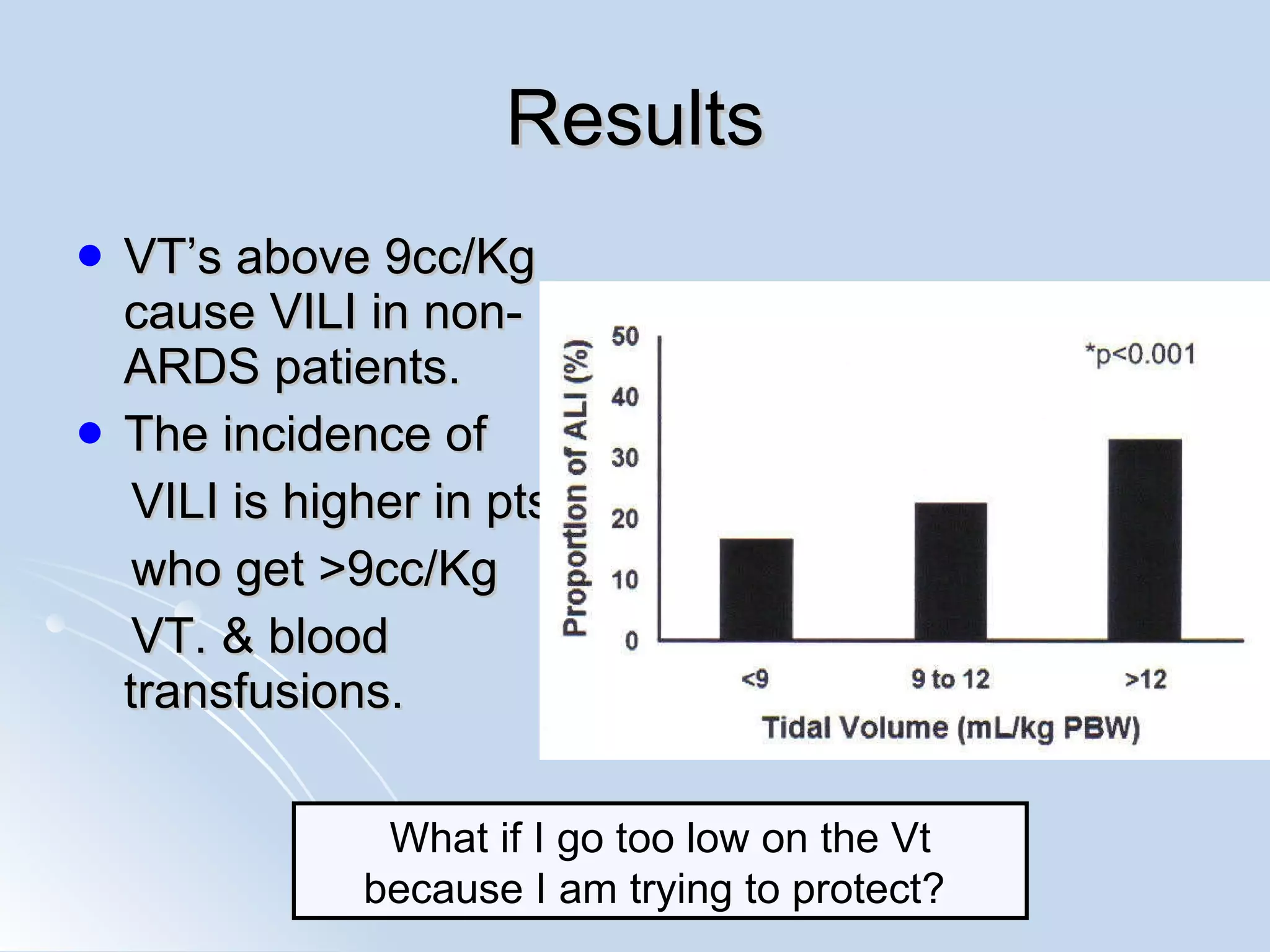
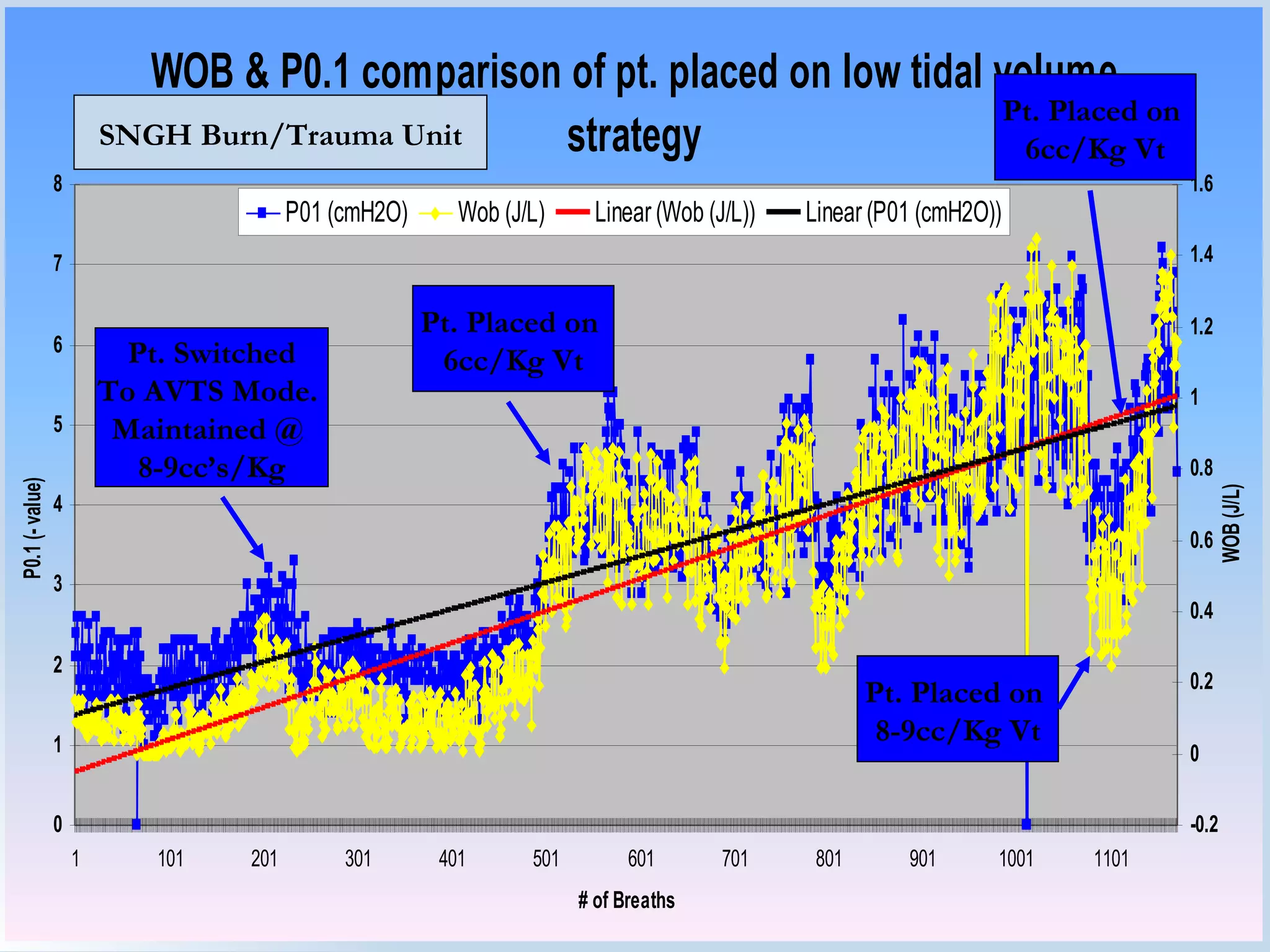
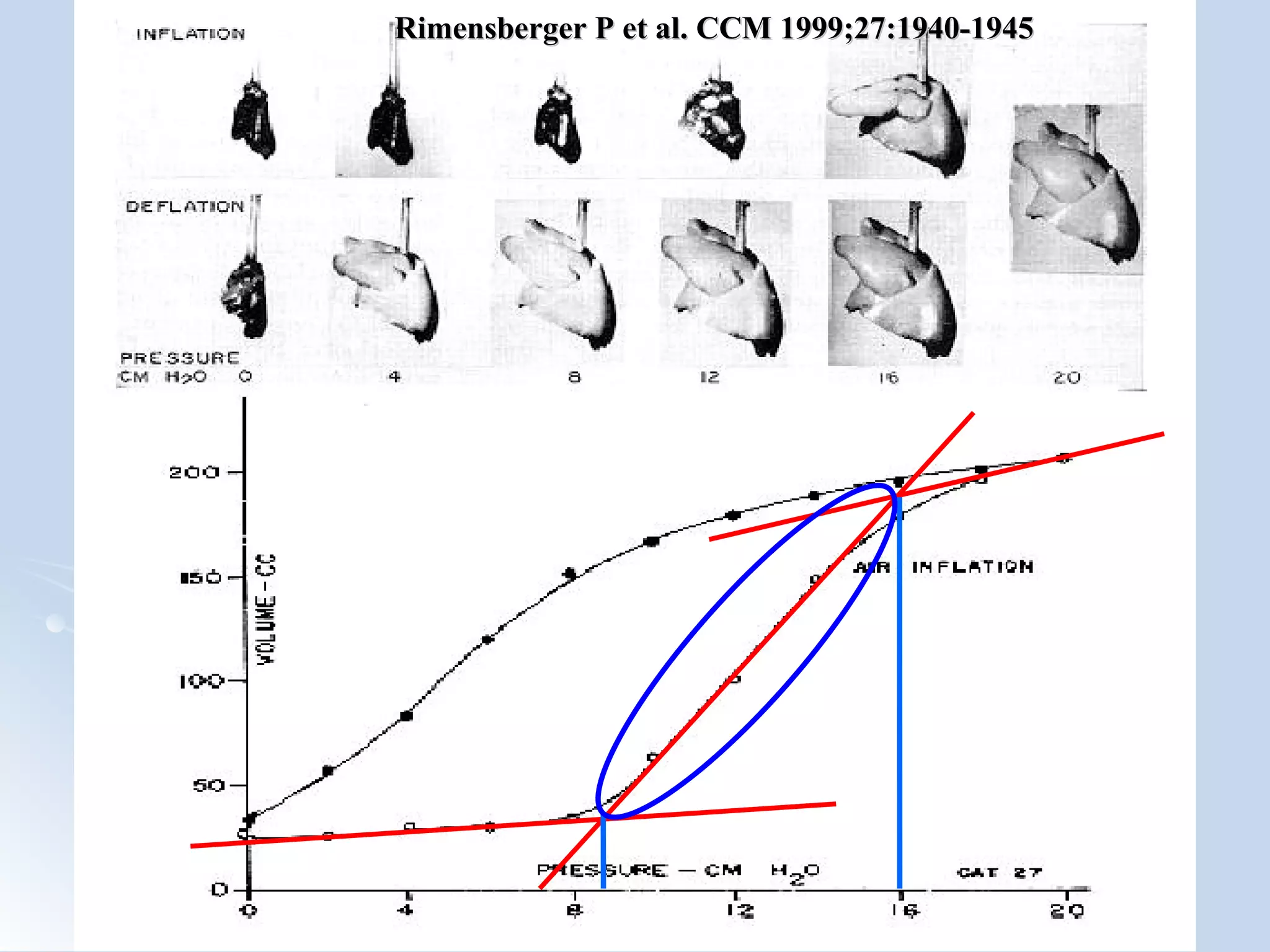
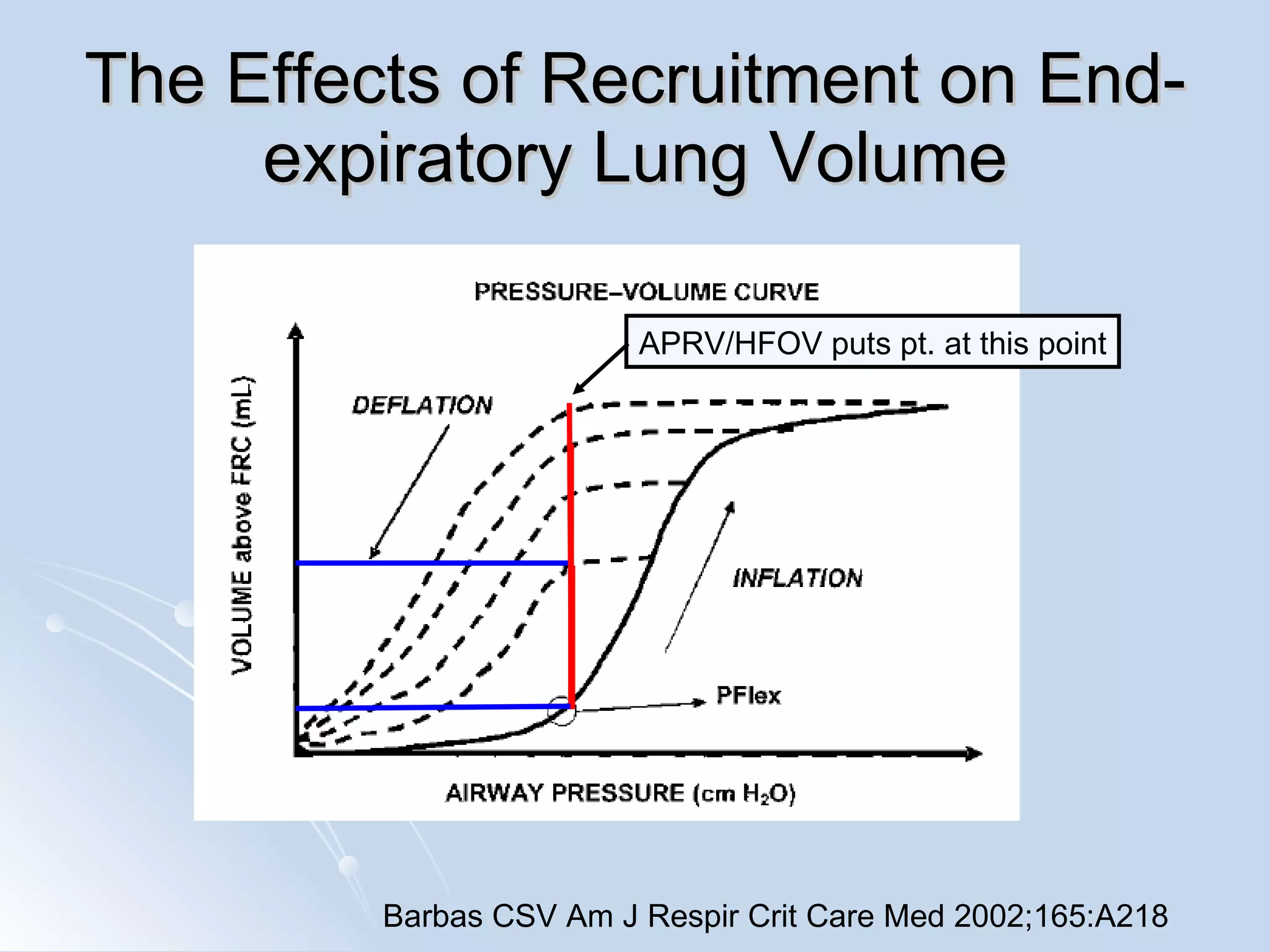
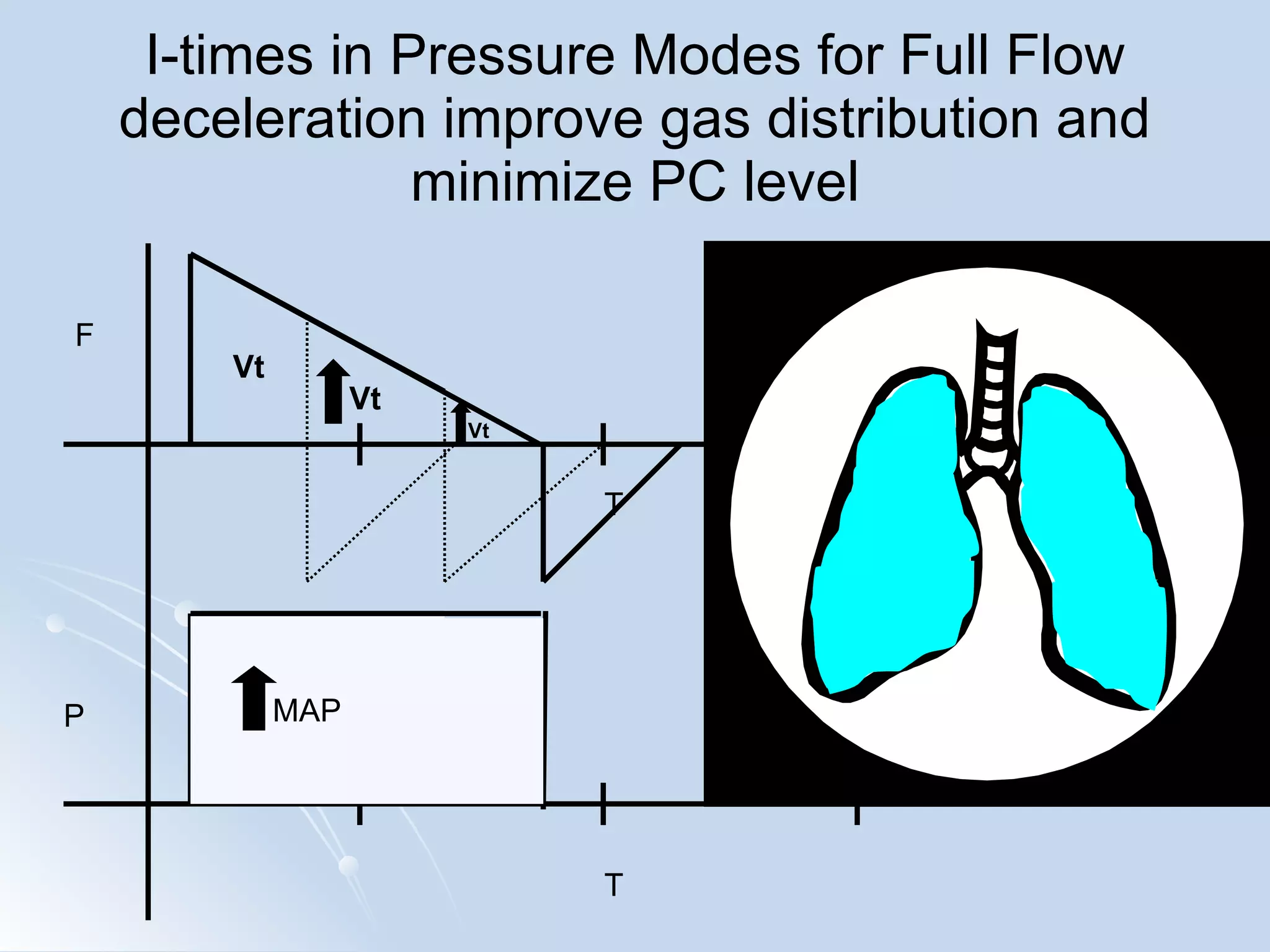
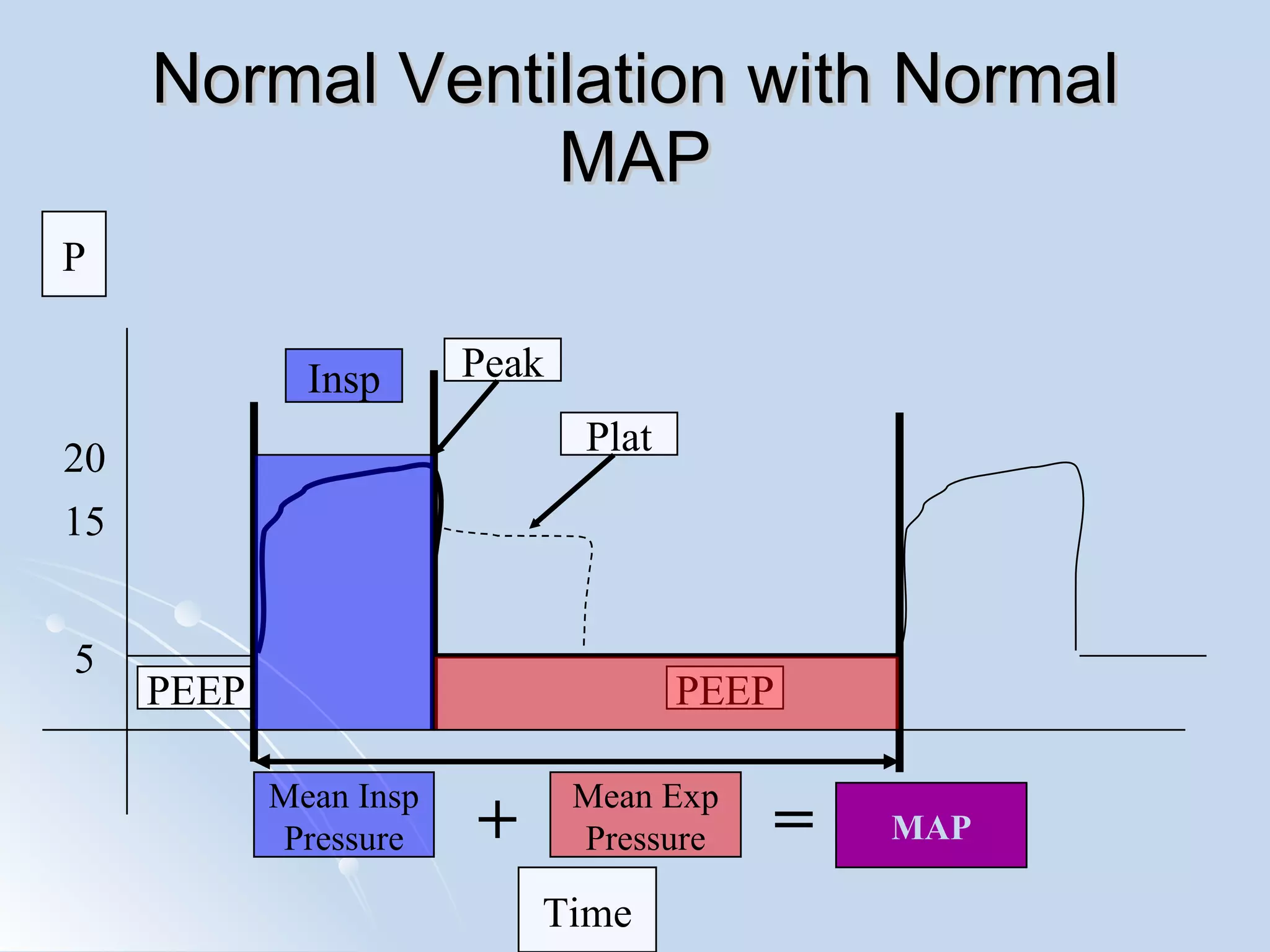
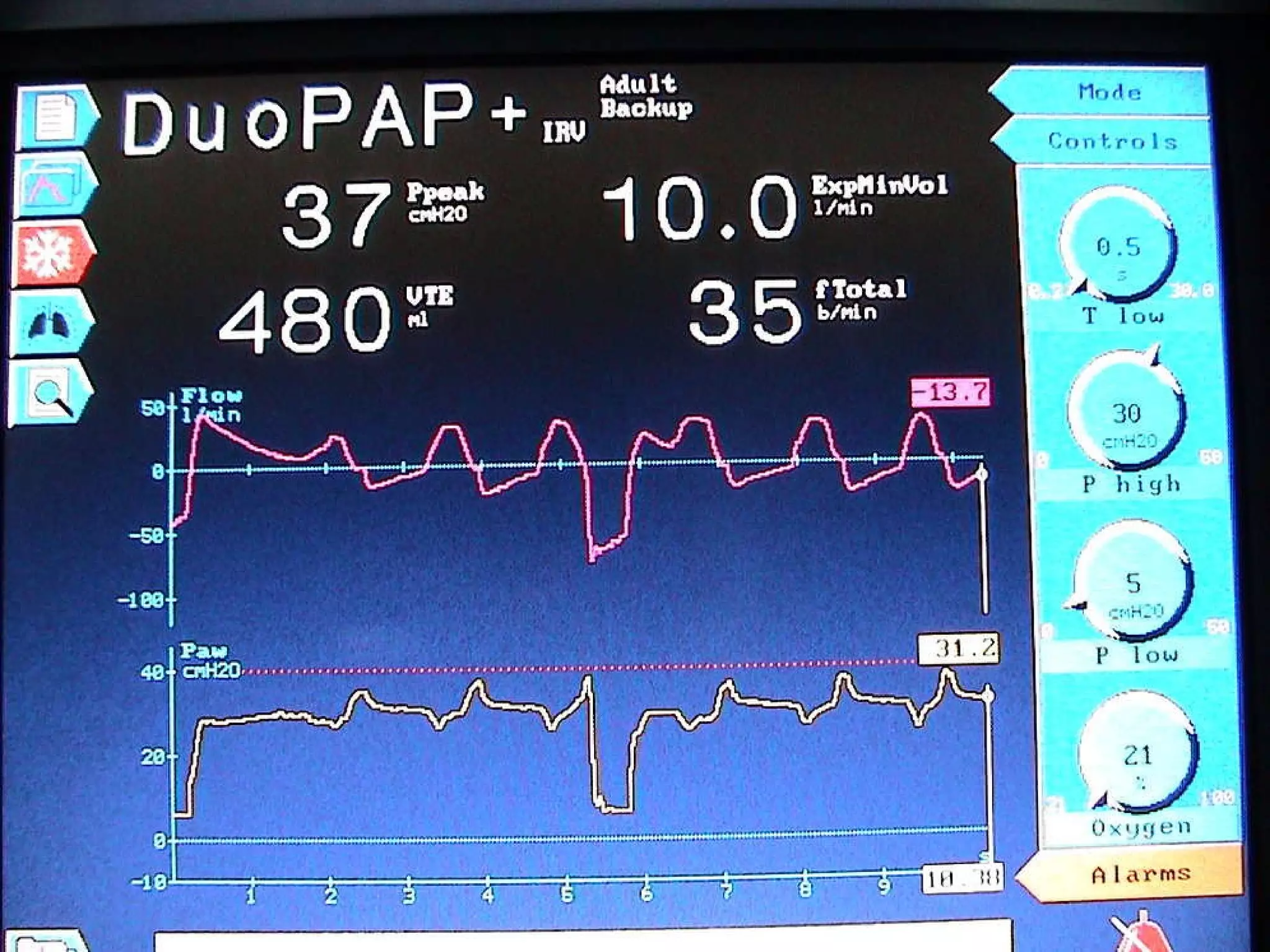
The document discusses two types of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) - pulmonary (direct) ARDS and extrapulmonary (indirect) ARDS. It notes key differences in characteristics and responses to mechanical ventilation strategies between the two types. Specifically, extrapulmonary ARDS patients tend to have better responses to higher levels of positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) compared to pulmonary ARDS patients. The document also reviews various mechanical ventilation strategies and studies regarding lung-protective ventilation in ARDS.