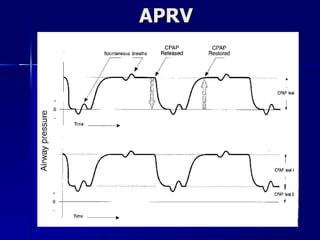
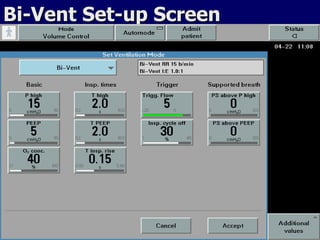
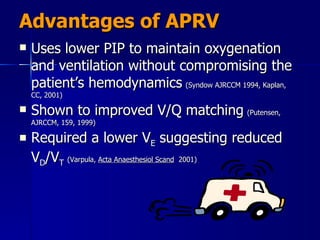
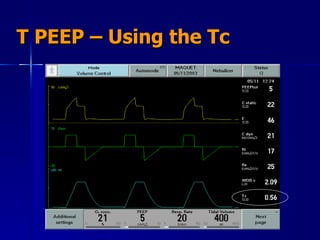
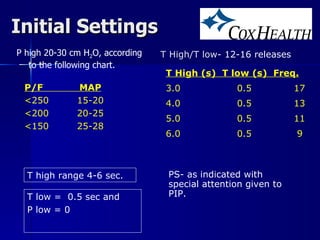
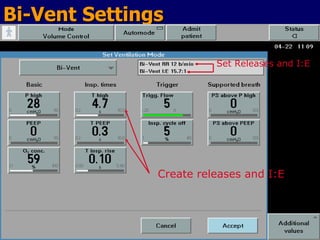
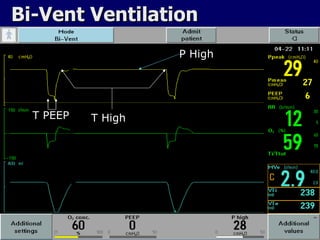
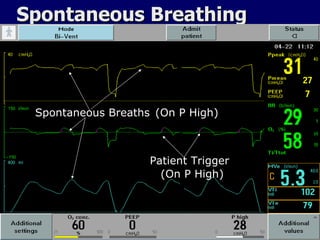
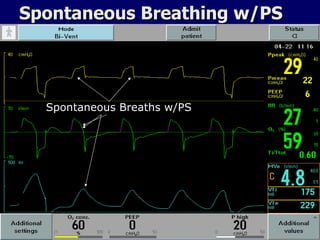
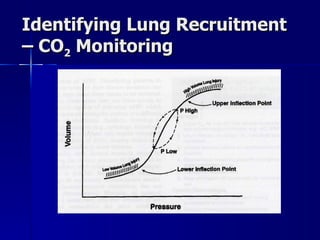
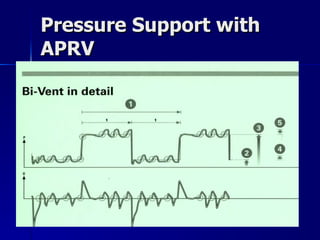
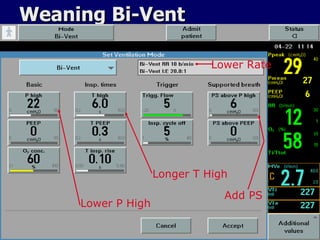
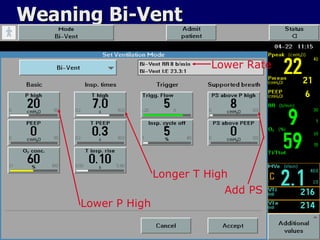
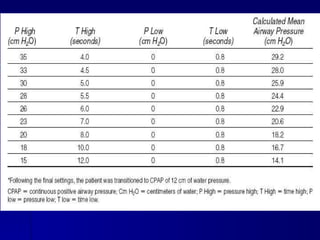
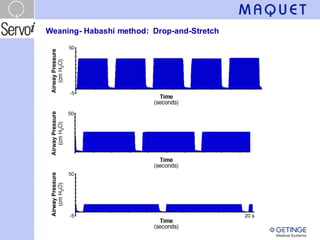
The document outlines the application and benefits of Airway Pressure Release Ventilation (APRV) for patients with Acute Lung Injury (ALI) and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), including its parameters and potential advantages over traditional ventilation methods. It emphasizes maintaining spontaneous breathing to improve ventilation and reduce complications associated with mechanical ventilation. Key settings and adjustments for APRV are discussed, along with contraindications and perceived disadvantages.