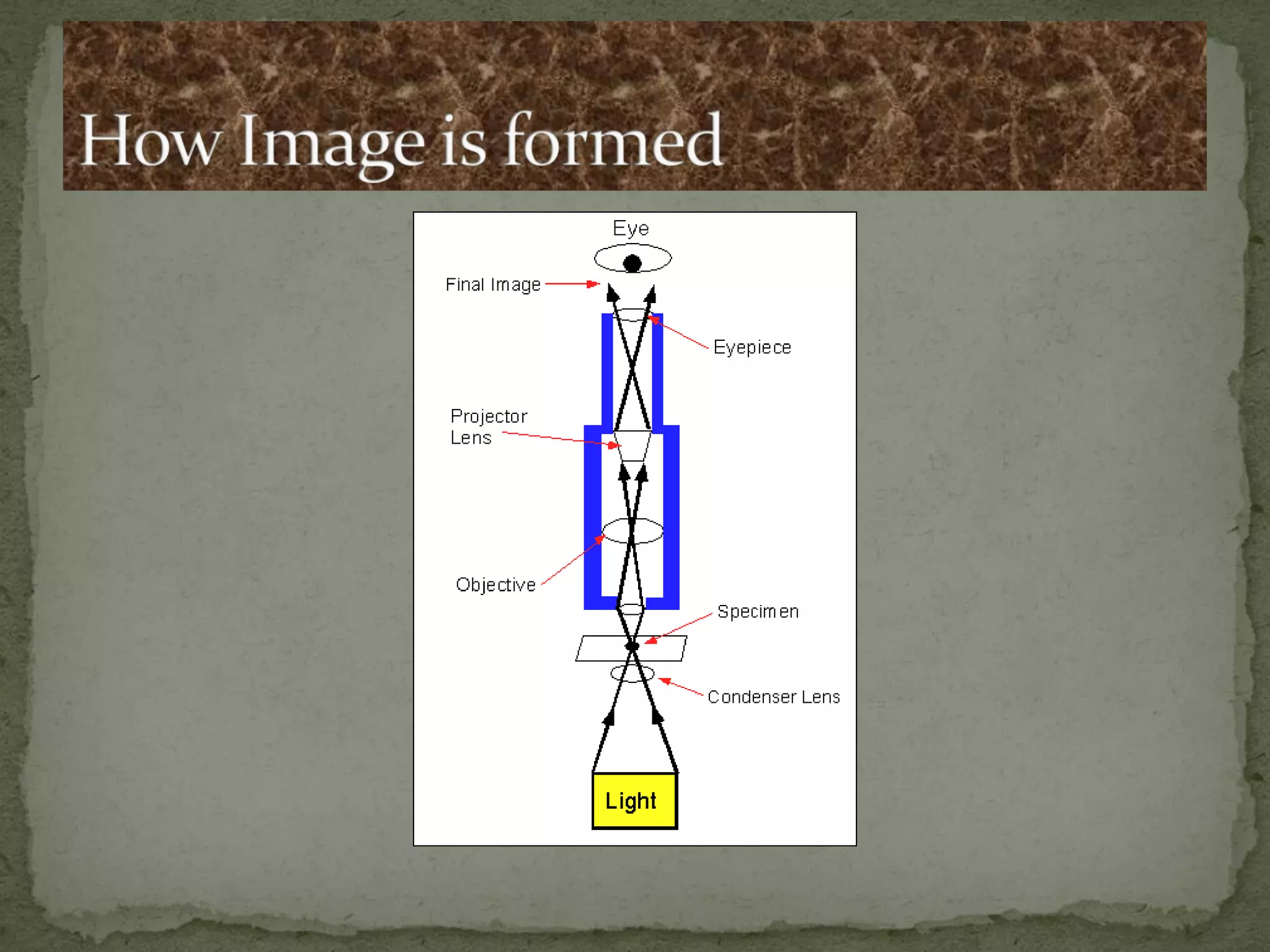
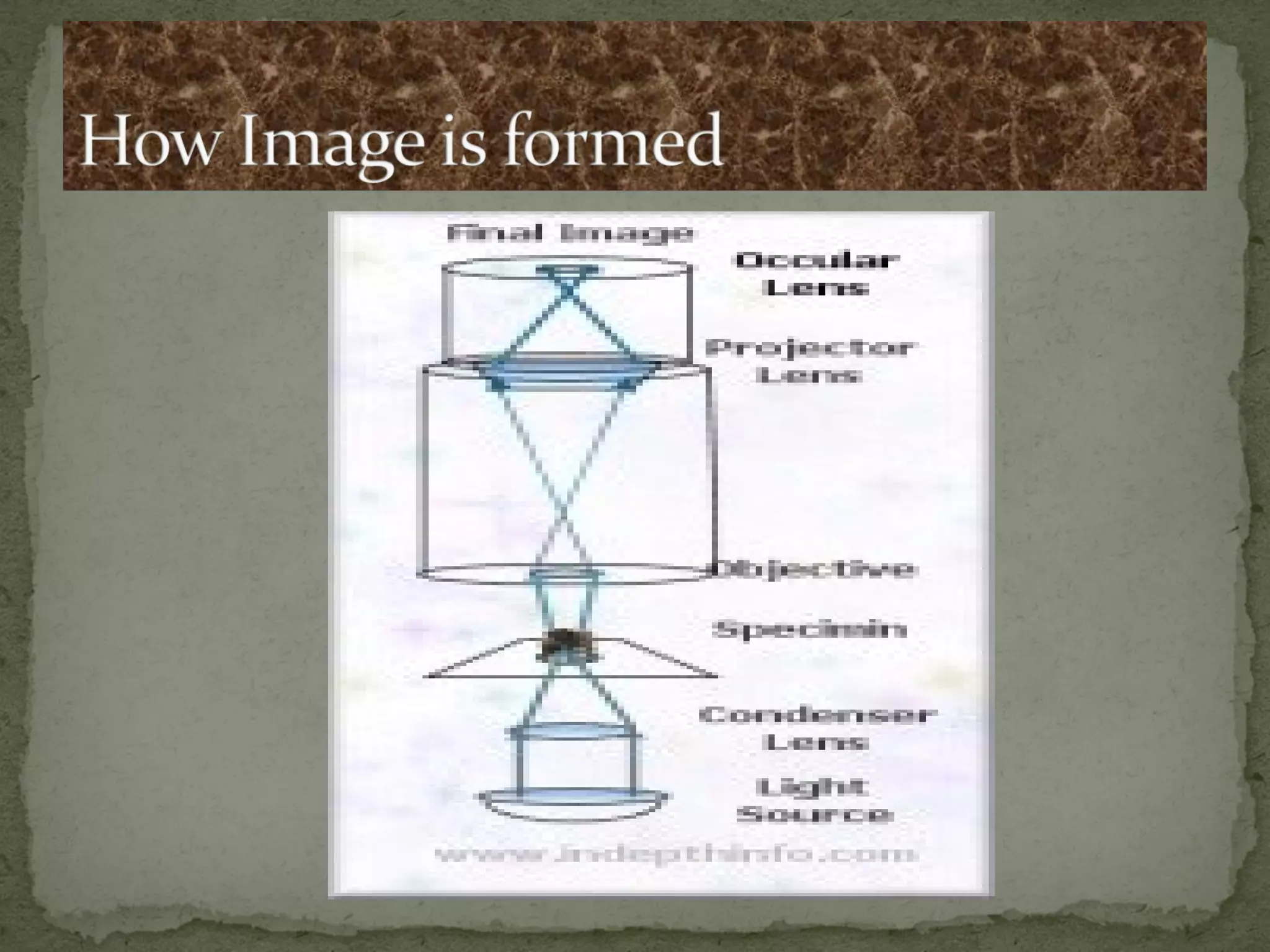
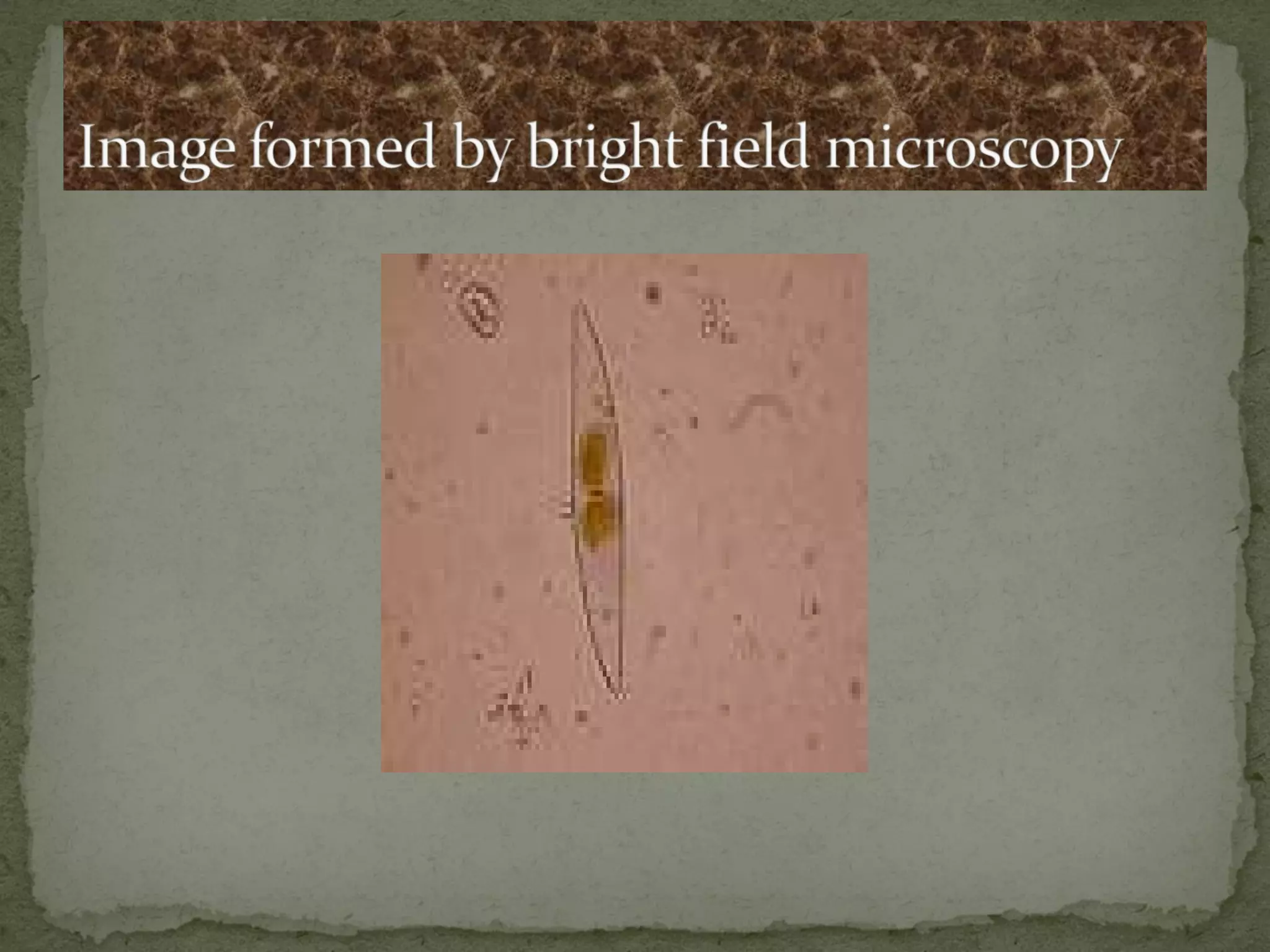
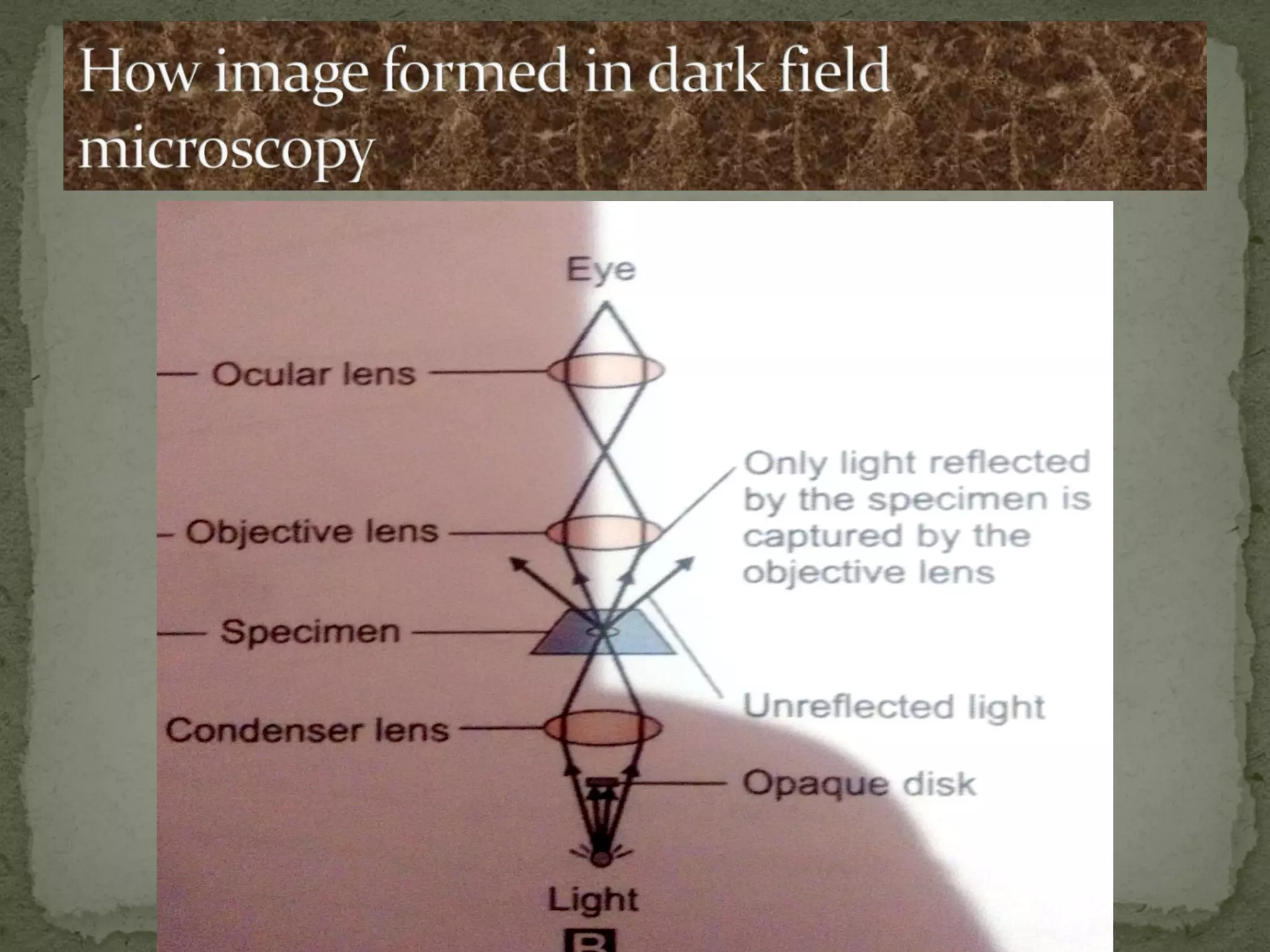
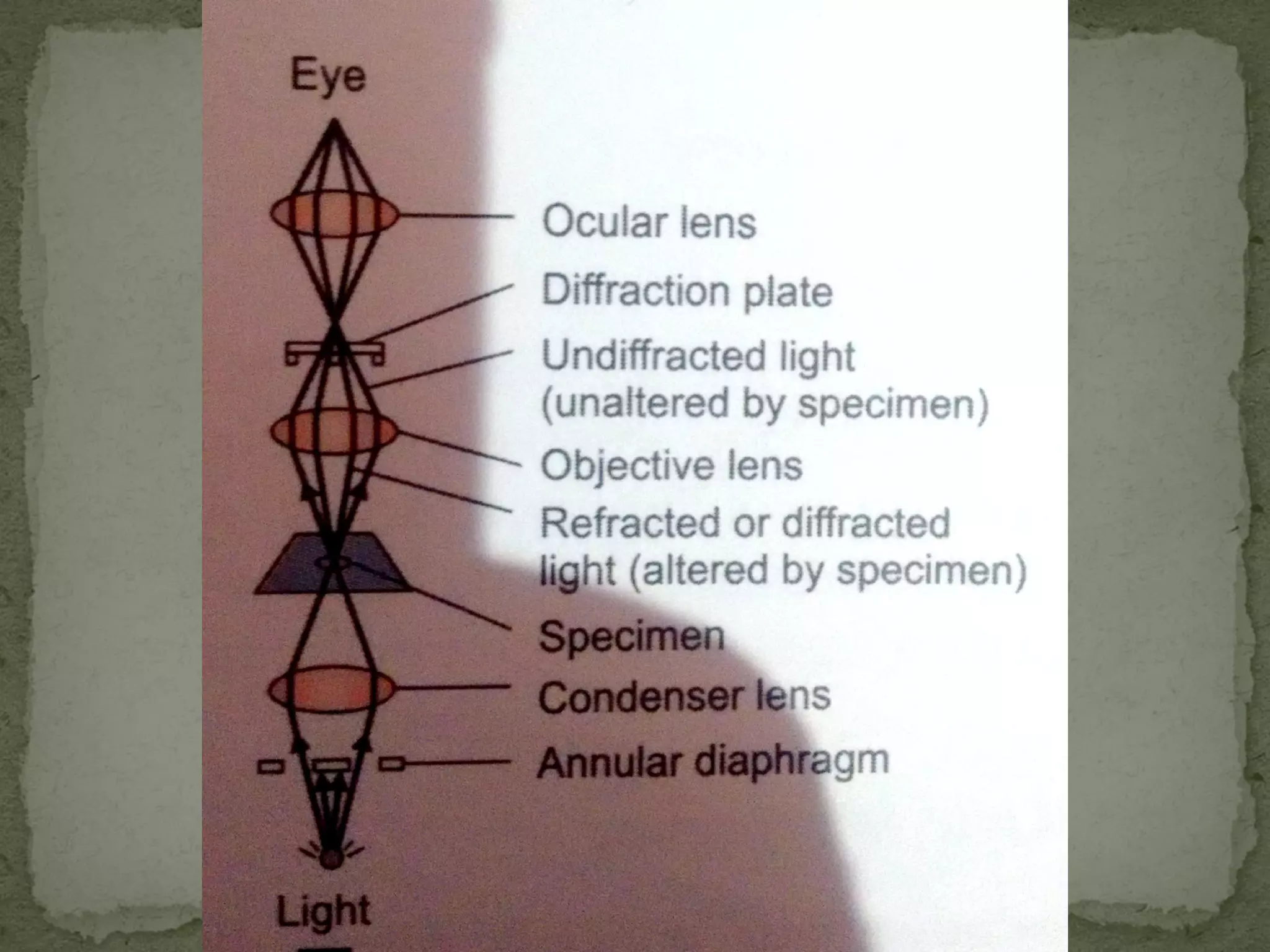
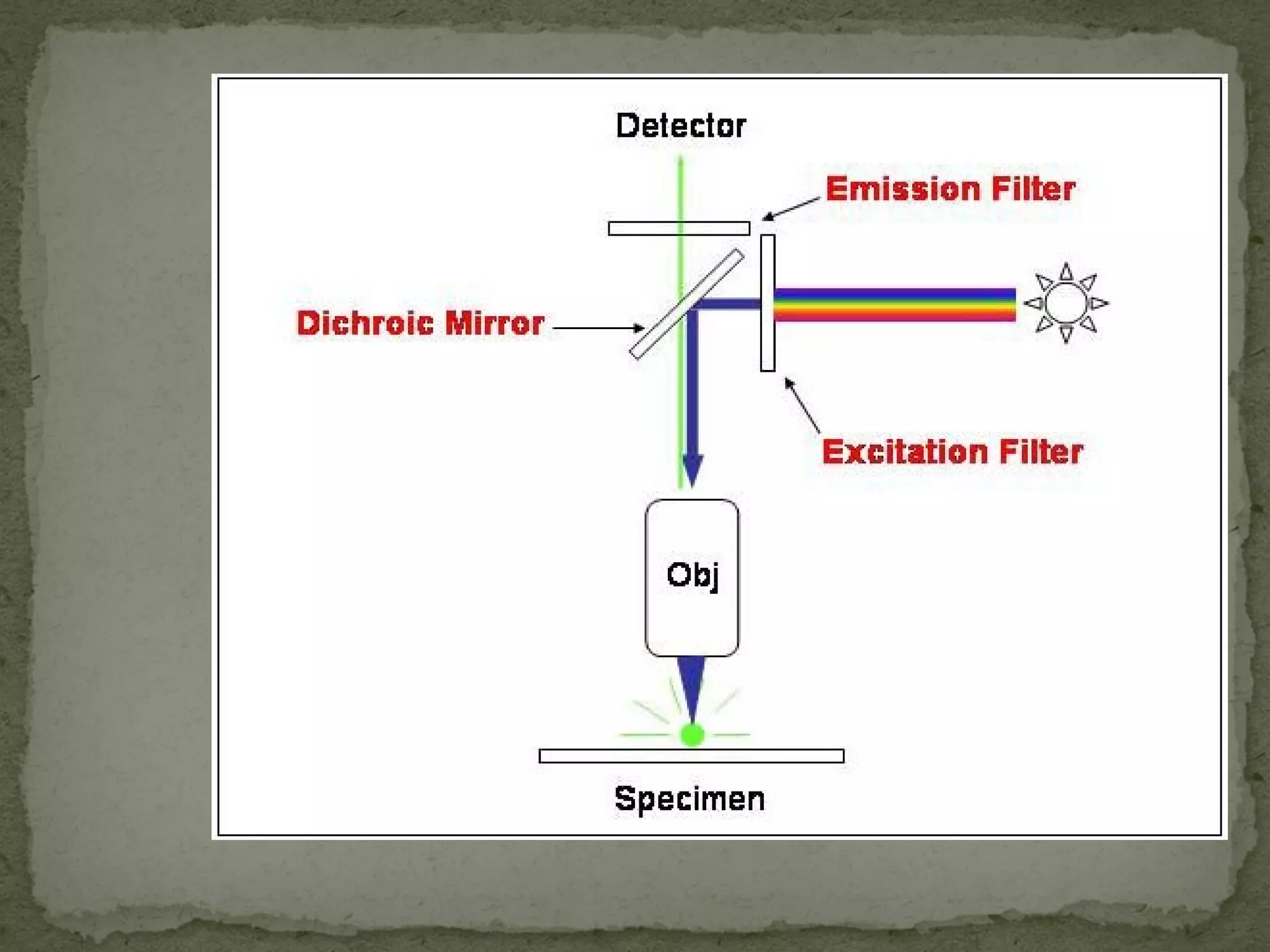
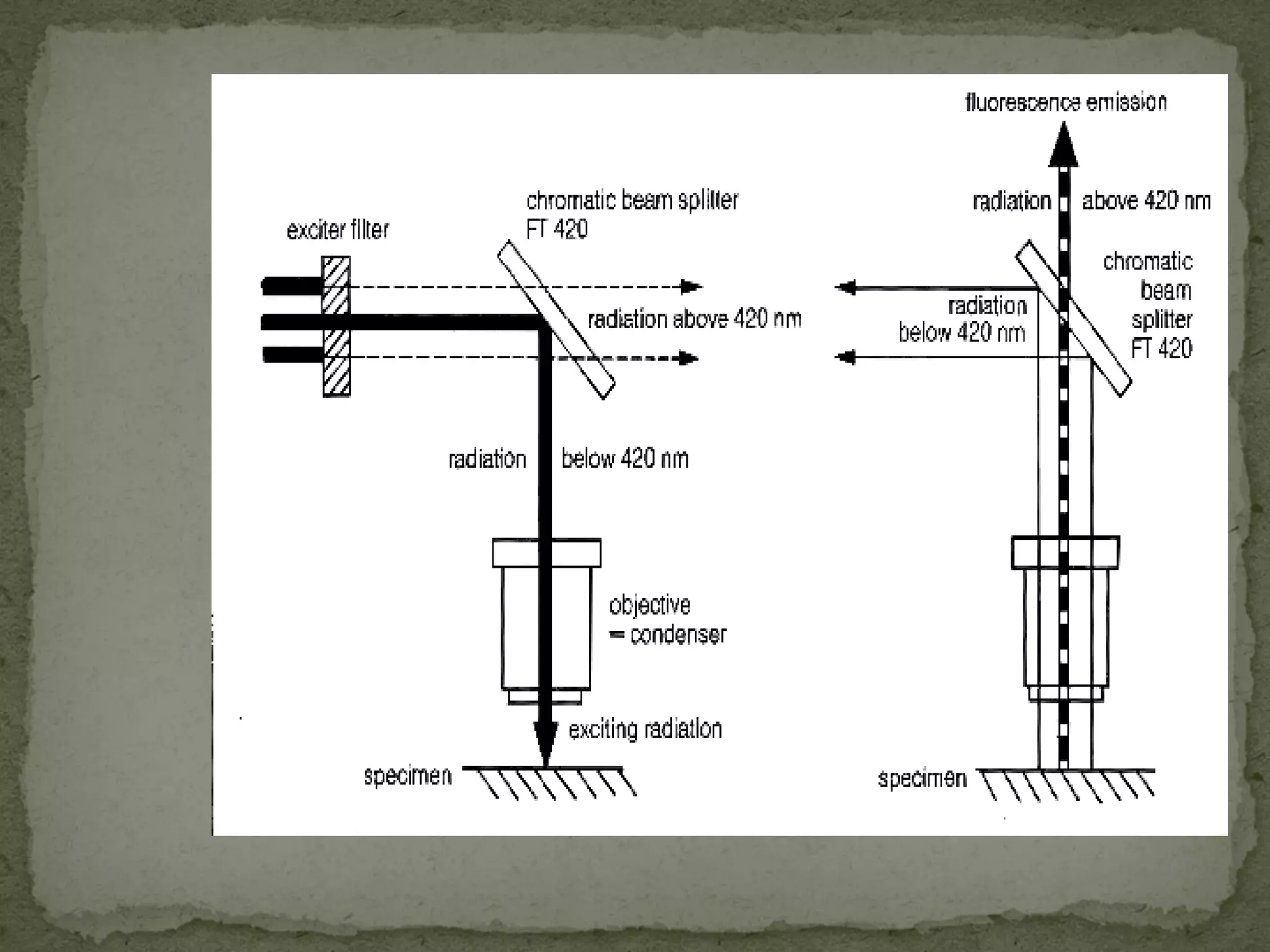
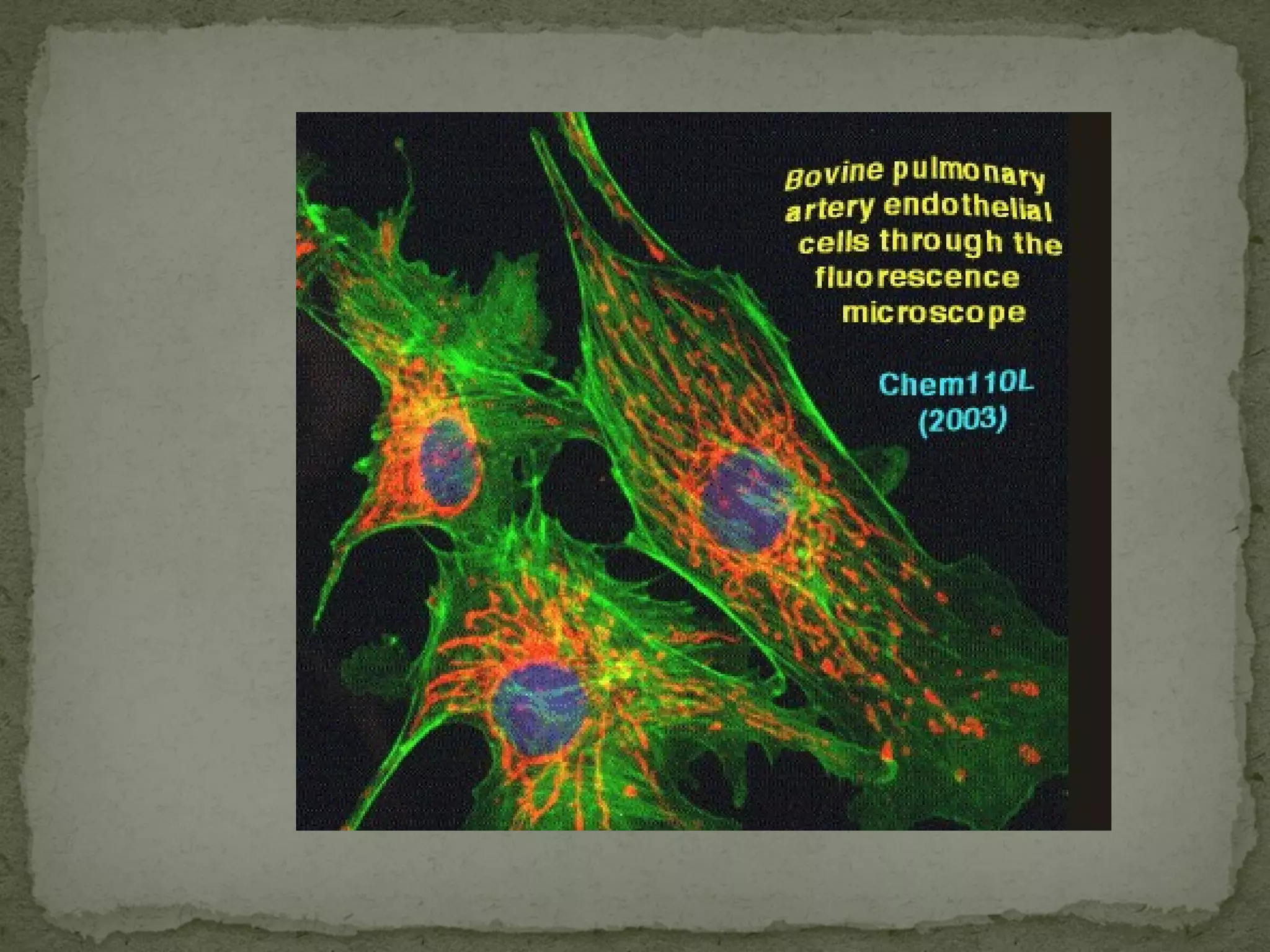
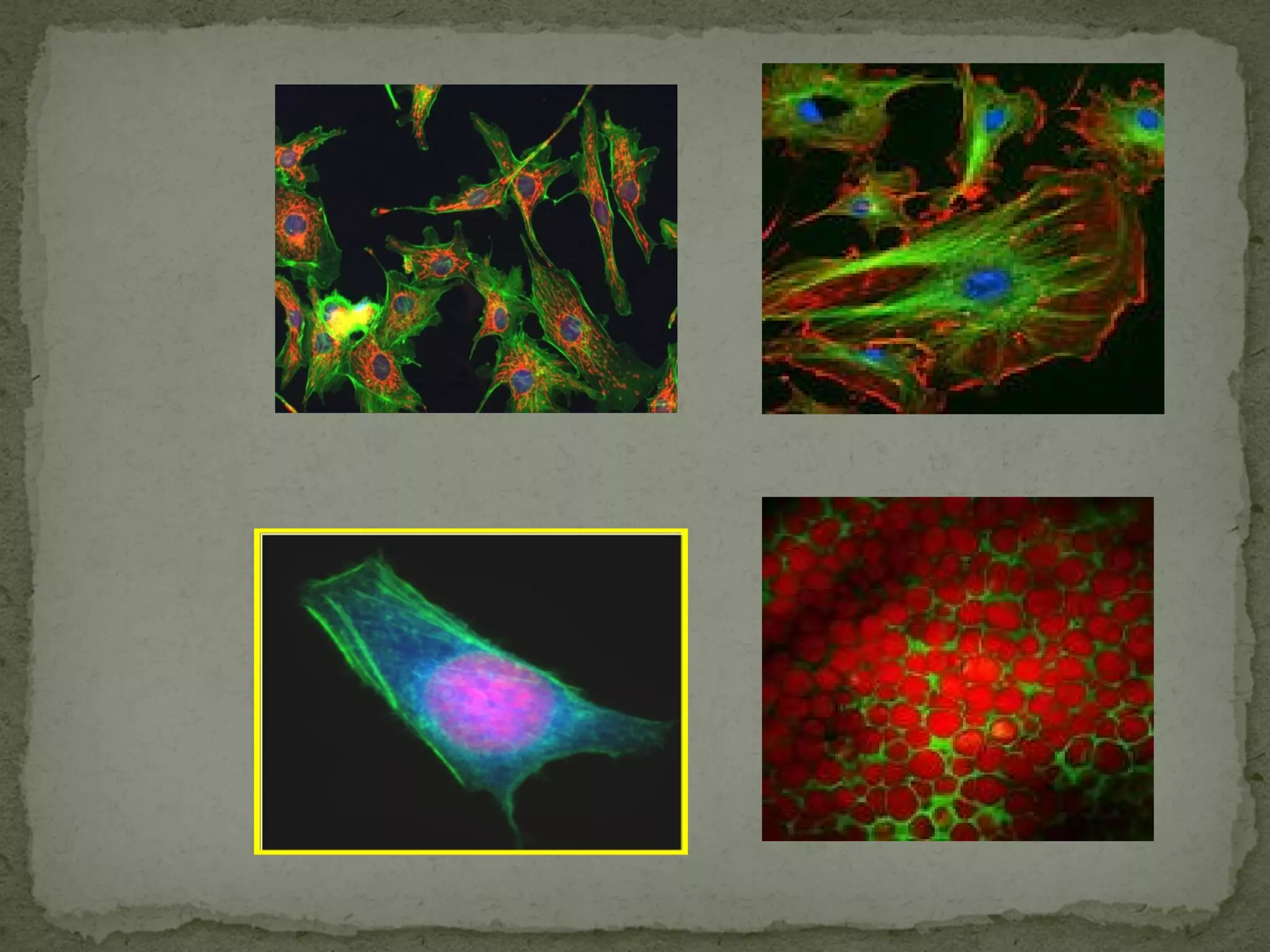
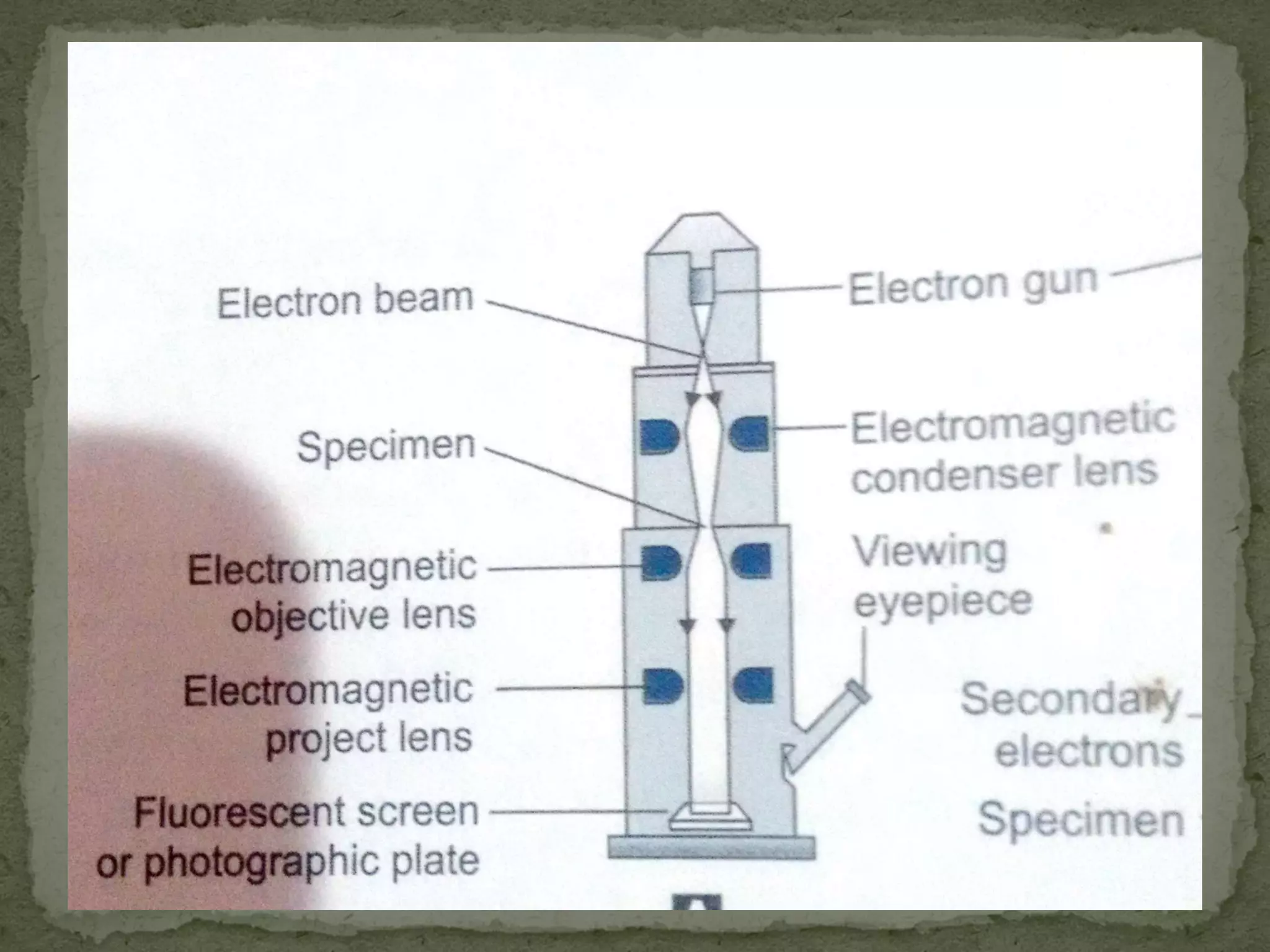
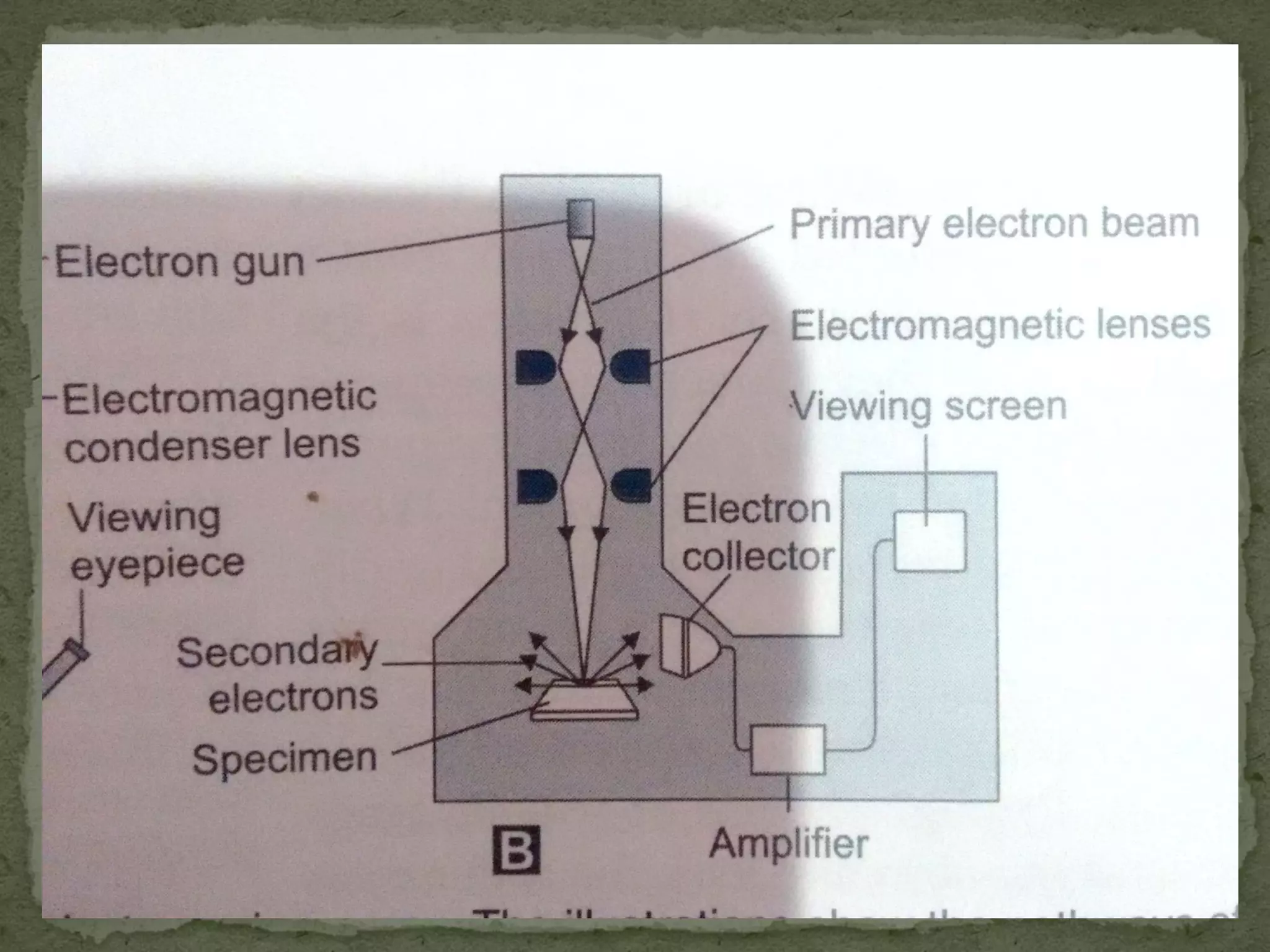
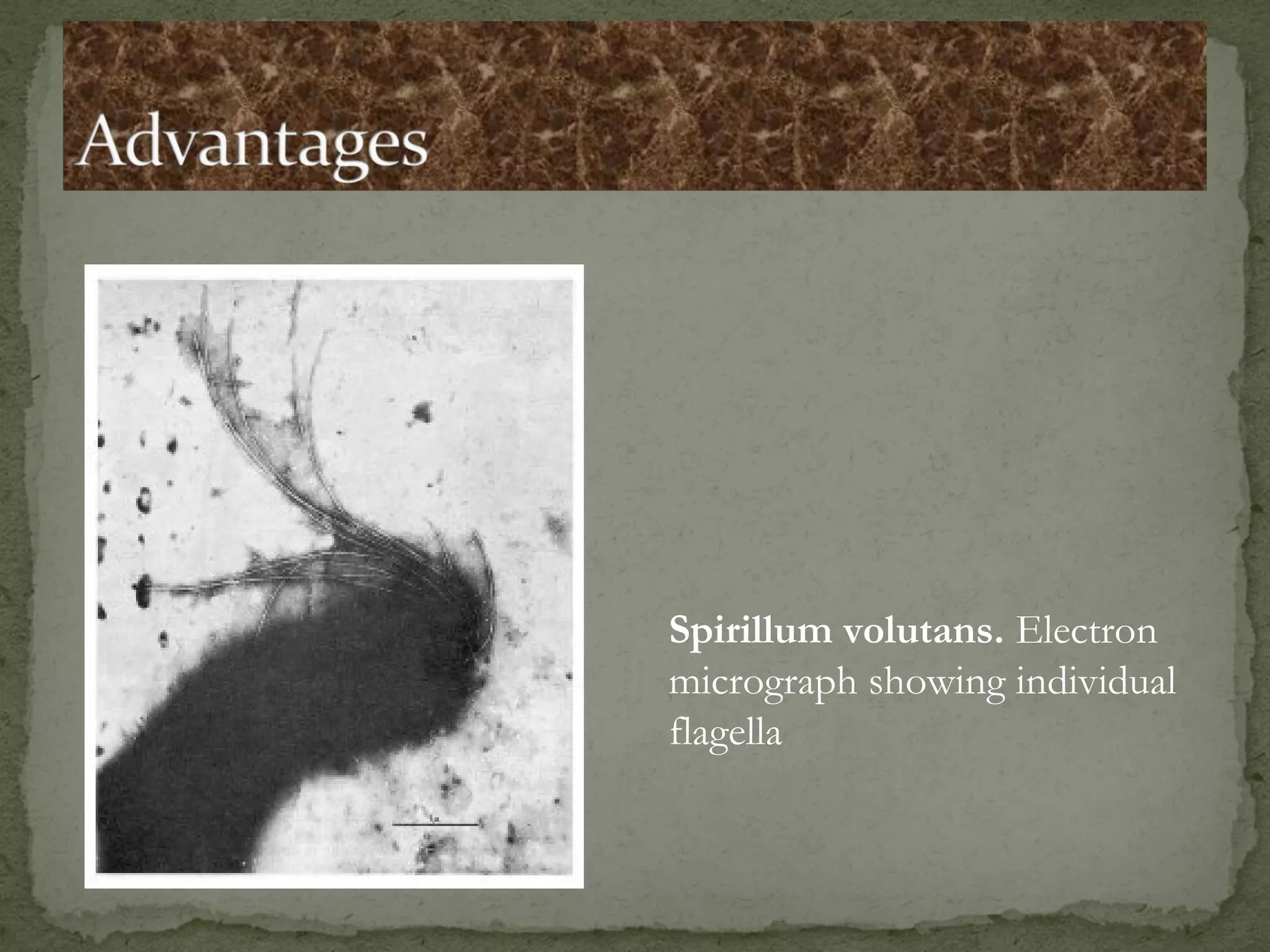
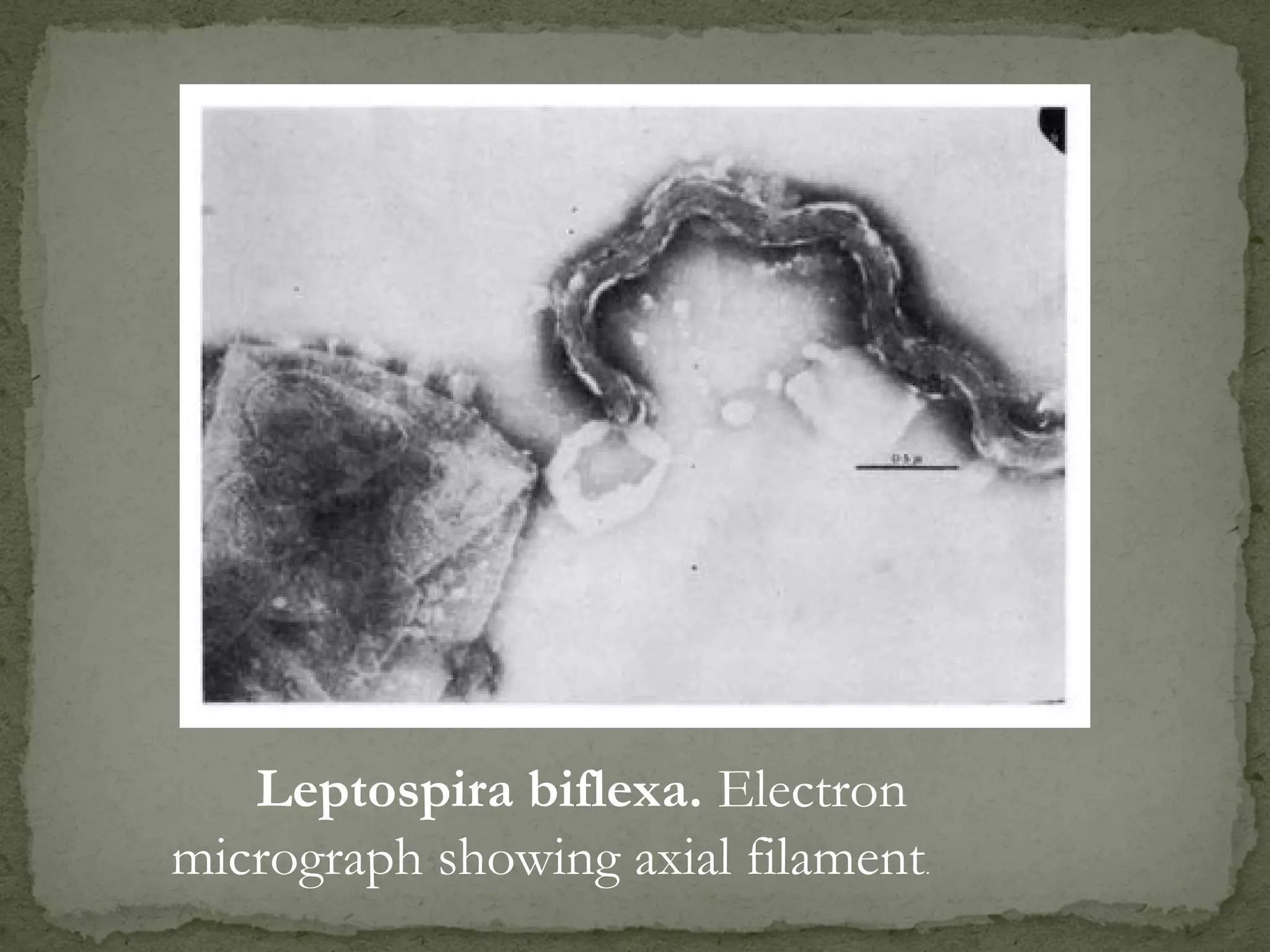
The document discusses different types of microscopes used to view microscopic specimens. It describes light microscopes, which use lenses and visible light, including brightfield, darkfield, phase contrast, and fluorescence microscopes. It also describes electron microscopes, which use electromagnetic lenses and electrons beams to view specimens, including transmission electron microscopes that pass electrons through thin specimens, and scanning electron microscopes that scan surfaces to produce 3D images. Key aspects and uses of each microscope type are outlined.