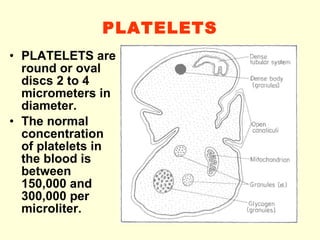
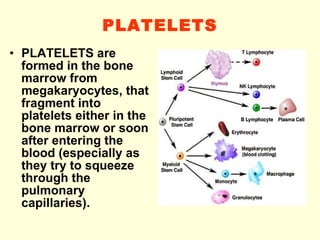
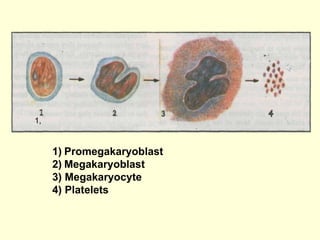
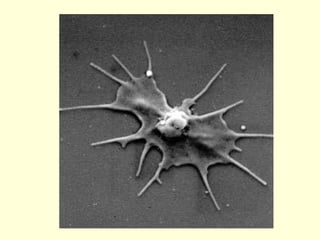
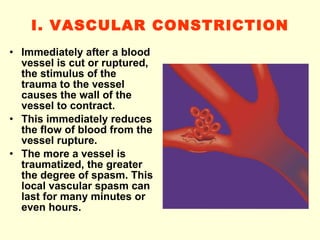
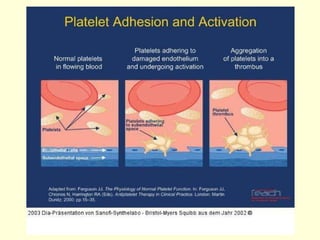
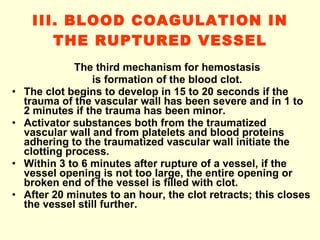
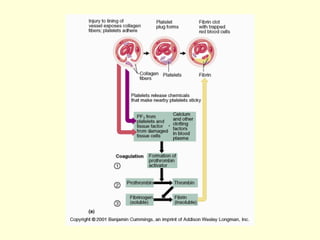
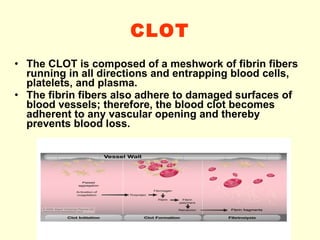
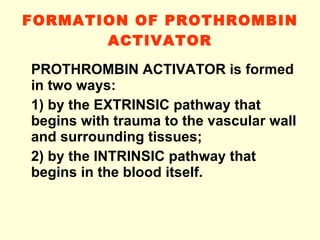
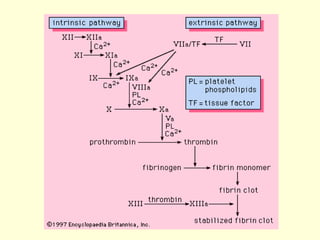
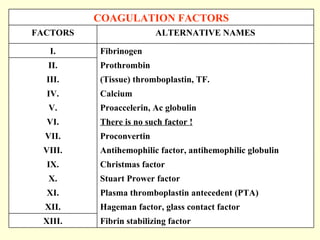
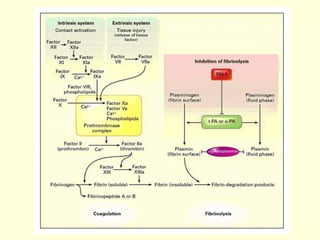
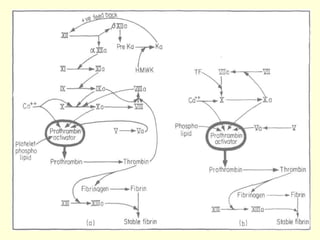
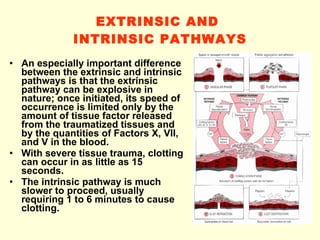
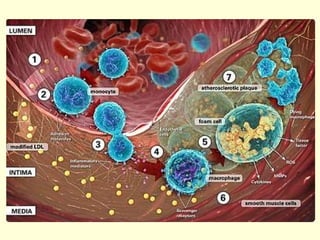
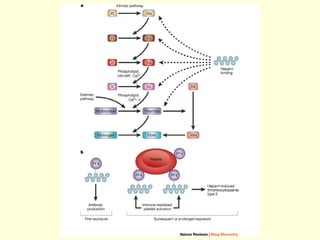
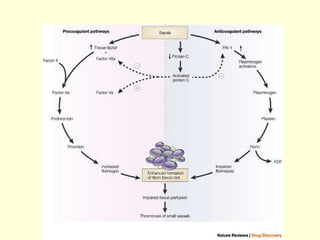
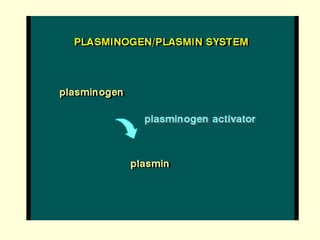
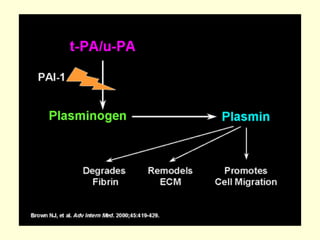
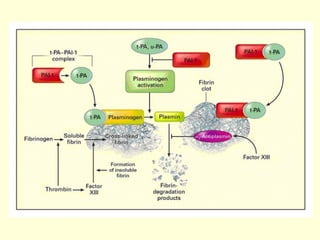
Hemostasis is achieved through three mechanisms: 1) vascular constriction to reduce blood flow, 2) formation of a platelet plug to block small ruptures, and 3) blood coagulation and clot formation within 3-6 minutes. The clot contracts and closes the vessel opening, then either dissolves or is organized into fibrous tissue over 1-2 weeks. Blood coagulation is initiated through intrinsic and extrinsic pathways activating thrombin, which converts fibrinogen to fibrin fibers that form the clot mesh. The endothelium and natural anticoagulants normally prevent clotting within vessels.