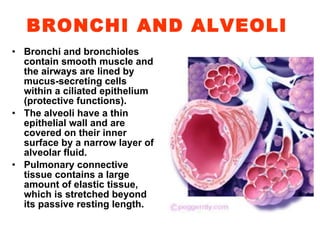
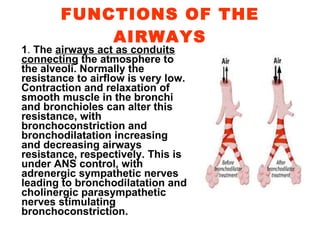
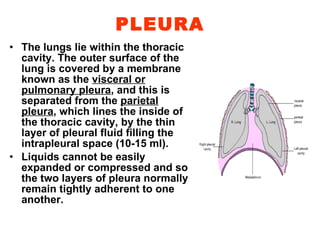
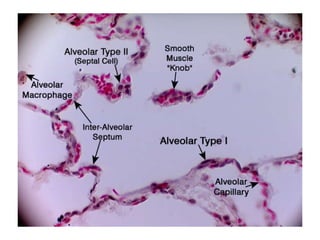
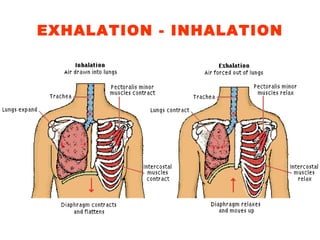
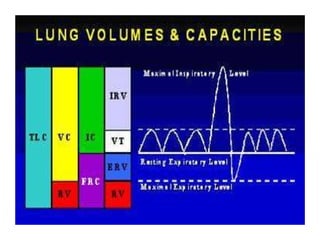
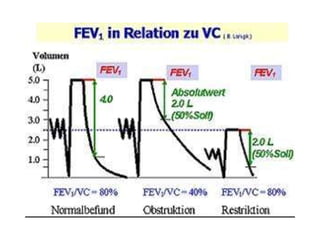
The respiratory system maintains normal levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH in the blood. Air enters the nose and travels through branching airways until reaching the alveoli in the lungs where gas exchange occurs. The lungs are kept inflated by the negative pressure between the visceral and parietal pleura, and contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles during inhalation increases the thoracic cavity volume. Exhalation is a passive process as elastic forces cause lung deflation when the muscles relax.