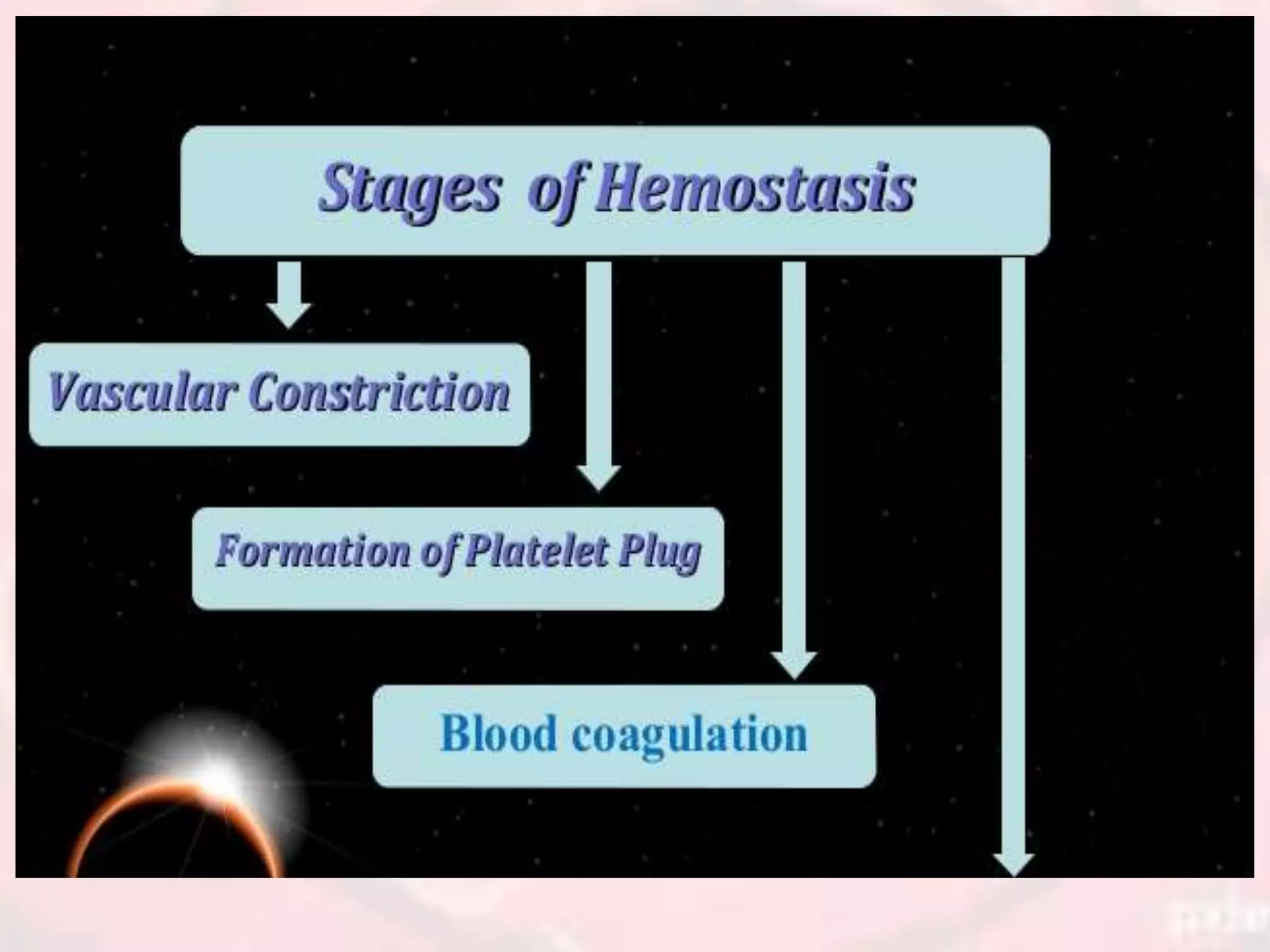
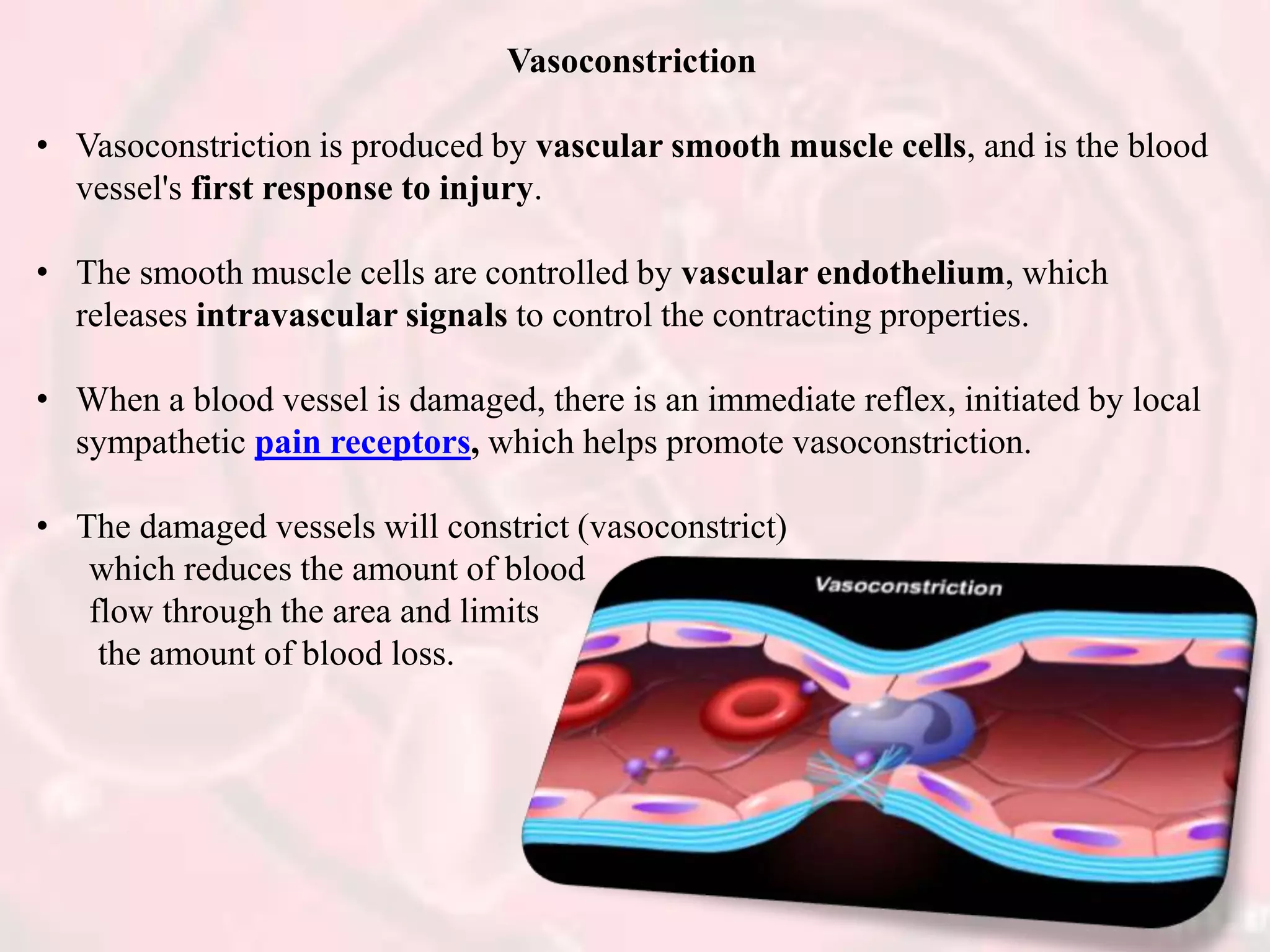
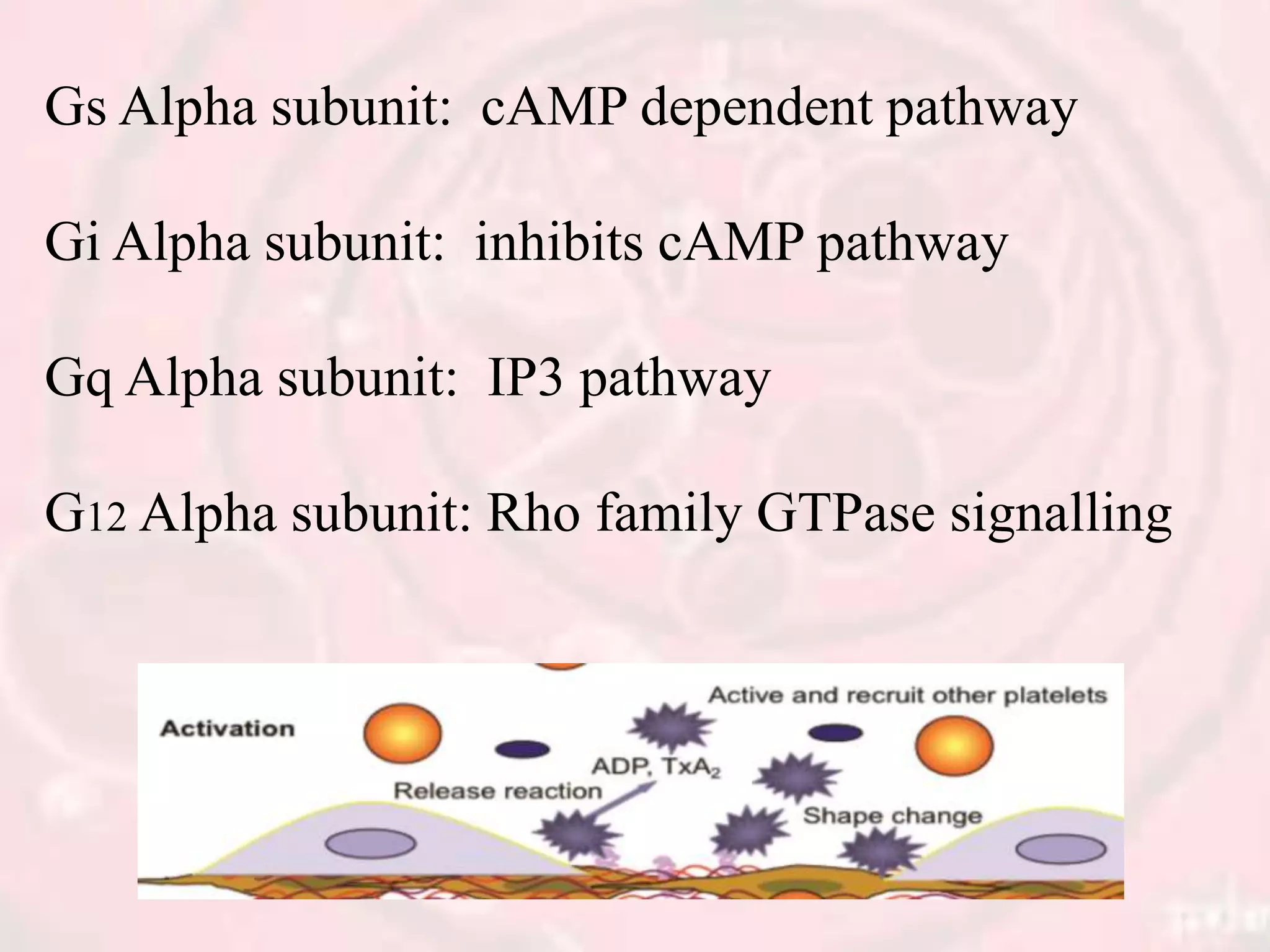
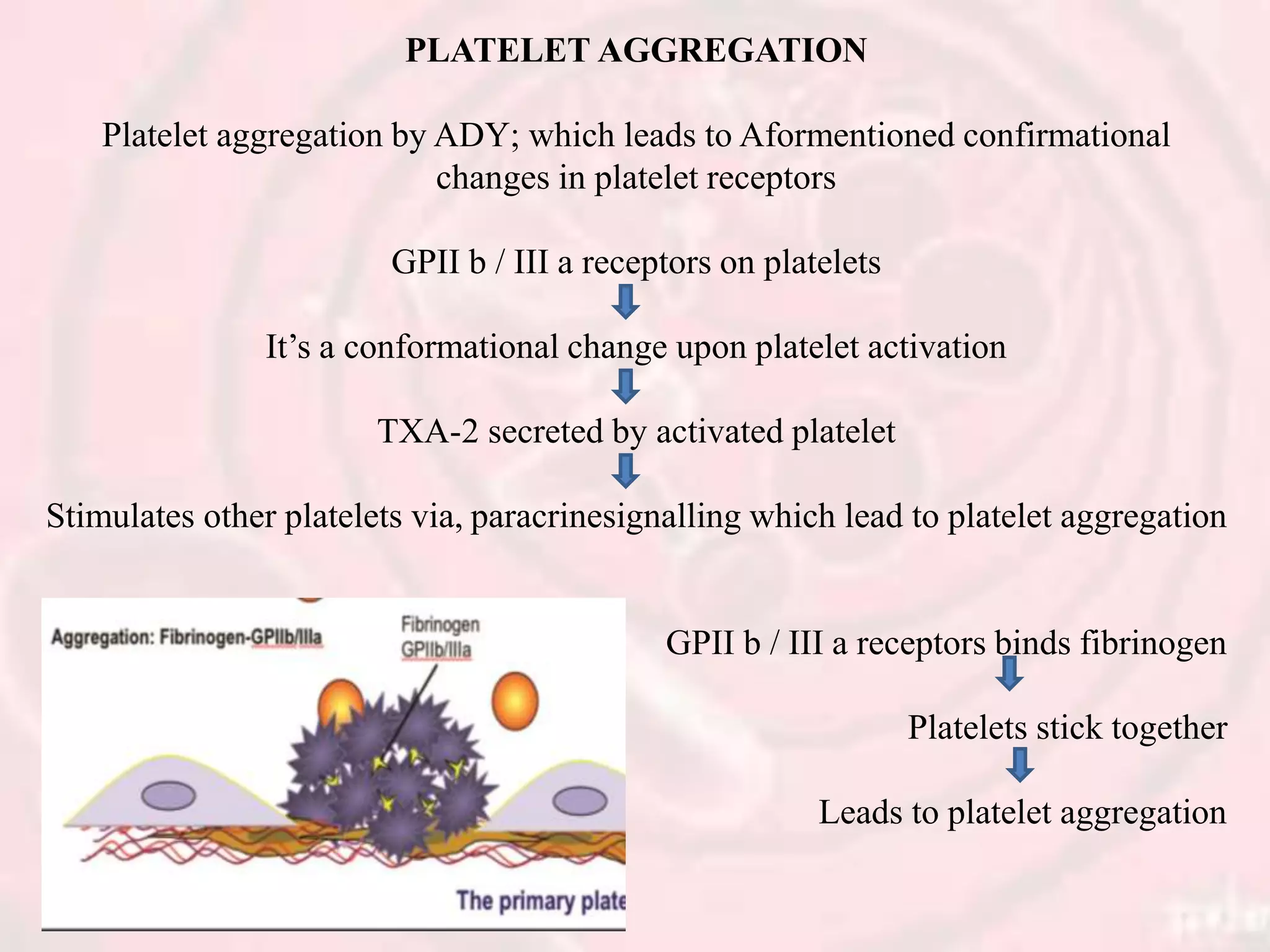
The document presents an overview of hemostasis, detailing its definition as the stoppage of bleeding and explaining the processes involved, including vasoconstriction, platelet plug formation, and blood coagulation. It discusses the mechanisms of platelet function, activation, and aggregation, as well as the cascade of chemical reactions leading to clot formation. Additionally, the document covers various methods of hemostasis, including mechanical, chemical, and thermal techniques used in medical practices.