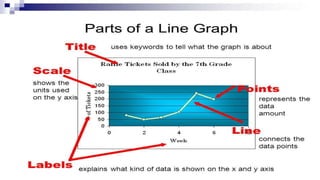
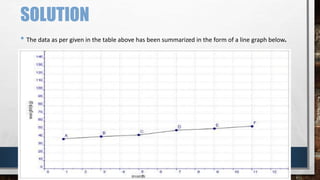
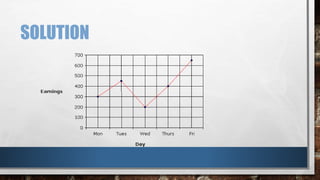
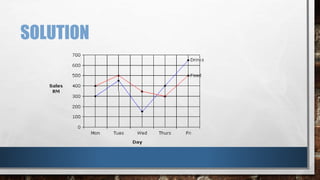
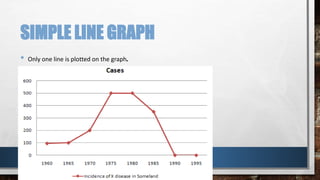
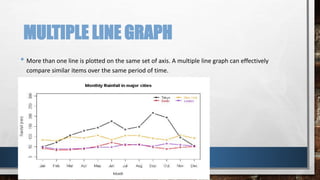
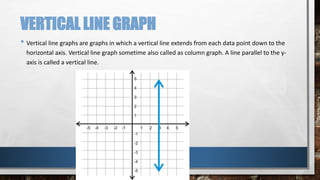
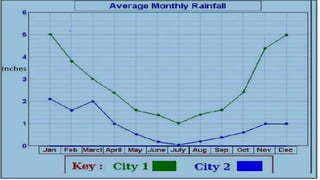
A line graph is a diagram that illustrates the relationship between two variables over time, with an independent variable typically on the x-axis and a dependent variable on the y-axis. The document outlines key components of line graphs, including titles, scales, labels, and types, as well as step-by-step instructions for creating one. Various types of line graphs such as simple, multiple, compound, vertical, and horizontal are discussed, emphasizing their usefulness in displaying data trends.