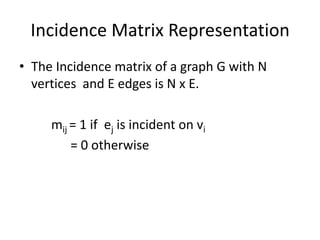
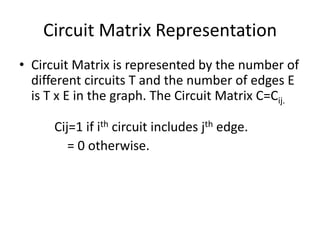
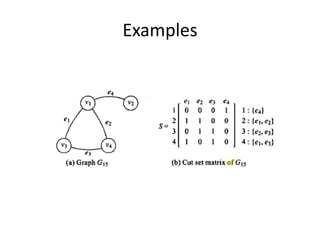
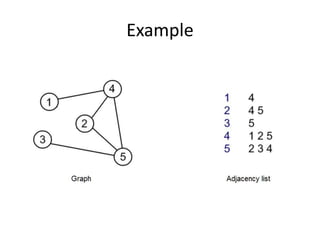
A graph consists of vertices and edges, where vertices represent entities and edges represent relationships between vertices. Graphs can be represented sequentially using matrices like adjacency and incidence matrices, or linked using data structures like adjacency lists. Adjacency matrices allow fast addition/removal of edges but use more memory, while adjacency lists use less memory but are slower to modify. The best representation depends on whether the graph is dense or sparse.





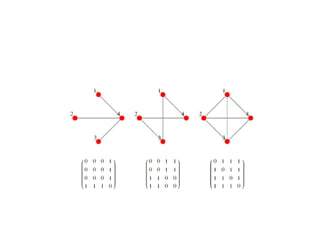
![Adjacency Matrix Representation
The Adjacency matrix of a graph G
with n vertices is N x N. It is given by A=[aij].
aij =1 if ith and jth vertices are adjacent.
=0 if ith and jth vertices are not adjacent.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphrepresentation-120903115144-phpapp01/85/Graph-representation-10-320.jpg)