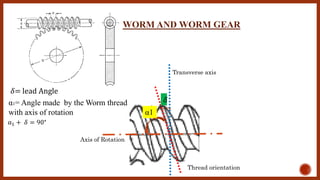
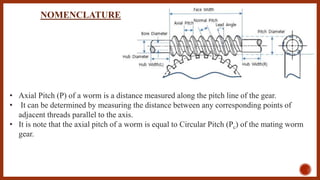
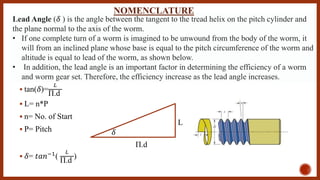
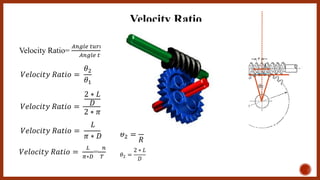
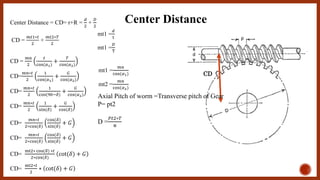
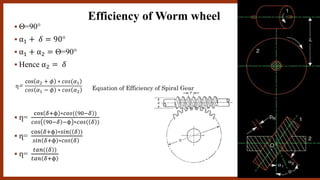
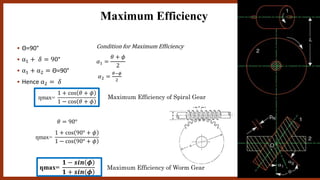
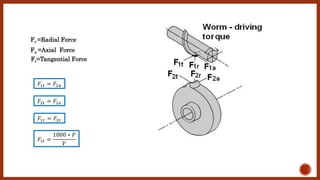
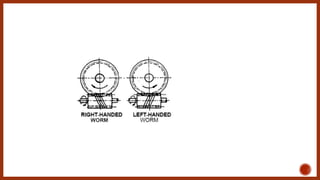
The document discusses worm gears and provides definitions and equations related to their design and operation. It defines worm gears as having large gear reductions from 20:1 up to 300:1. Worm gears are used widely in machinery because the worm can easily turn the gear but the gear cannot turn the worm. Key terms defined include lead, lead angle, velocity ratio, center distance, efficiency, and force equations. Design considerations like helix angle, module, and pitch are also addressed.