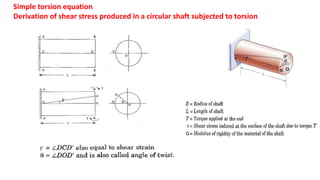
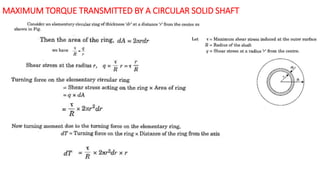
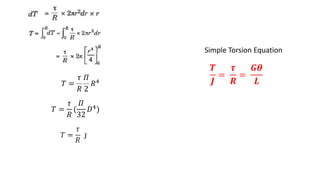
The document discusses torsion in shafts. When equal and opposite torques are applied to the ends of a shaft, it experiences twisting and shear stresses. For a circular shaft under torsion, every cross-section remains undistorted due to symmetry. Shear stress is highest at the outer surface and lowest at the axis. The maximum torque a circular solid shaft can transmit depends on the shear stress limit and material properties. Polar modulus is a measure of a shaft's resistance to twisting. Torsional rigidity describes a shaft's resistance to twisting deformation.