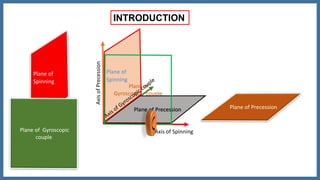
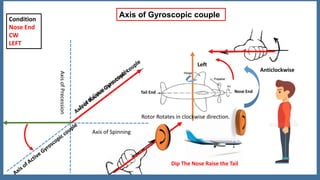
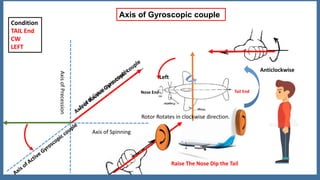
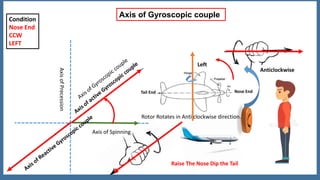
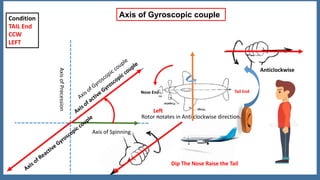
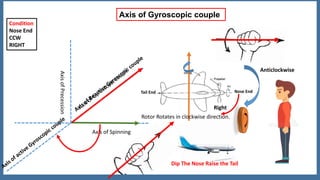
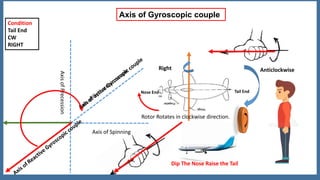
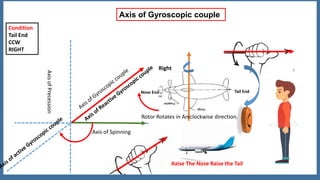
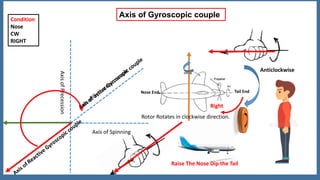
This document discusses the gyroscopic effect on airplanes. It begins by defining key terms related to gyroscopes like axis of spin, gyroscopic effect, precession, and axis of precession. It explains that when a spinning gyroscope experiences a torque perpendicular to its axis of spin, it will precess around an axis perpendicular to both. On airplanes, the spinning rotor of the vertical gyro acts to maintain equilibrium. For example, if the nose is pushed left, the rotor will cause the nose to rise and tail to dip due to the gyroscopic effect. The direction of precession depends on whether the rotor is spinning clockwise or counterclockwise. The document provides diagrams to illustrate these concepts.