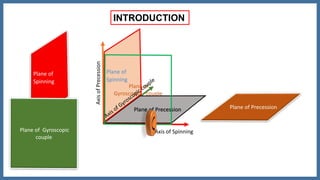
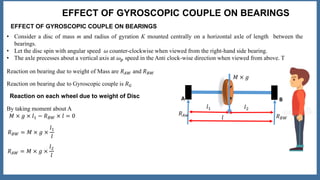
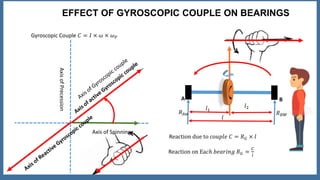
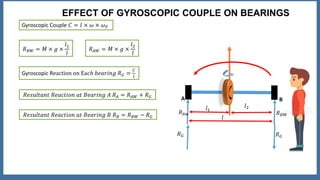
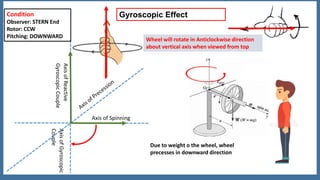
This document discusses the gyroscopic effect on bearings that support a spinning disc or wheel. It defines key terms like gyroscope, axis of spin, gyroscopic effect, precession, and axis of precession. It then describes how a disc mounted on a horizontal axle between two bearings will experience precession when it spins, and how this causes a gyroscopic couple reaction force on each bearing. Equations are provided showing how to calculate the resultant reaction forces on each bearing when considering both the weight-induced reactions and the gyroscopic couple reaction. In summary, it analyzes how a spinning disc's precession due to its own spin introduces gyroscopic forces that affect the bearing reactions.