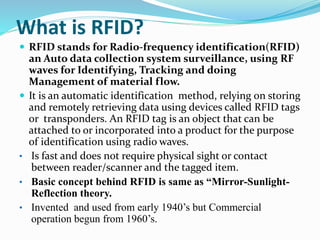
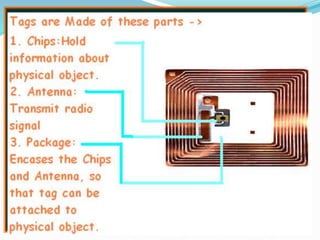
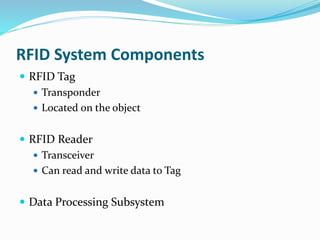
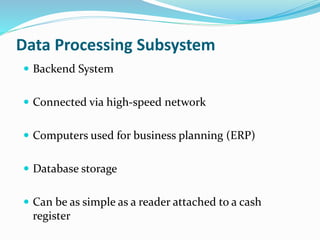
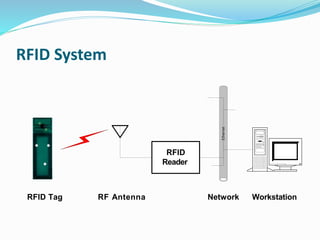
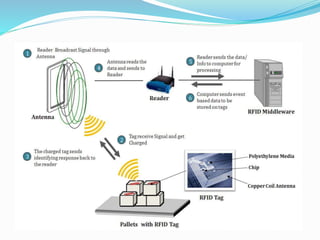
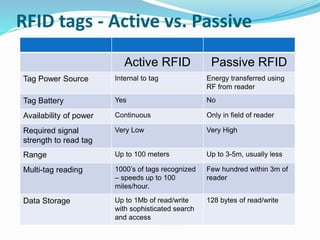
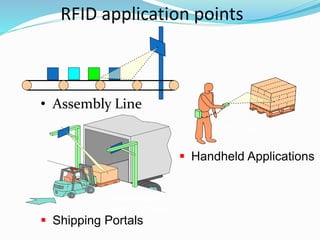
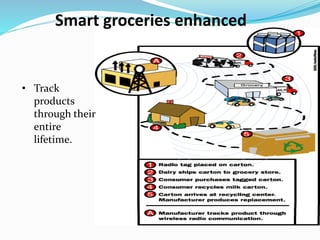
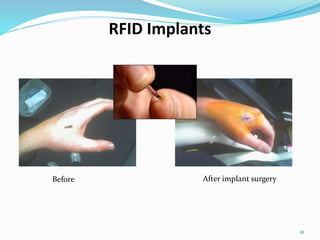
RFID is a technology that uses radio waves to automatically identify objects. It consists of RFID tags attached to objects and RFID readers that can read the tags. RFID tags contain antennas to receive and transmit radio signals to readers, which can then pass the identification information from the tag to backend computer systems. Common applications of RFID include inventory tracking, access control, payment systems, and monitoring of assets or animals. Advantages include contactless and fast identification of multiple tags, while disadvantages include potential impacts from environmental factors and cost of implementation. The future of RFID may include more uses in healthcare, retail, and smart home applications.