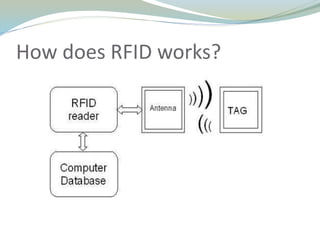
The document provides an overview of RFID technology, explaining its key components, functionality, and various applications. It compares RFID with barcodes, highlighting its advantages and disadvantages, including security benefits and challenges related to costs and effectiveness in certain environments. The applications of RFID in India are also mentioned, featuring uses in transport, manufacturing, and tracking systems.